Functional Description
DD+DIS150.06E
DOCUMENT CONTROL NOTE:
The controlled version of this document resides on MedNet. Any printed copy of this document is uncontrolled.
6 Stall Detection
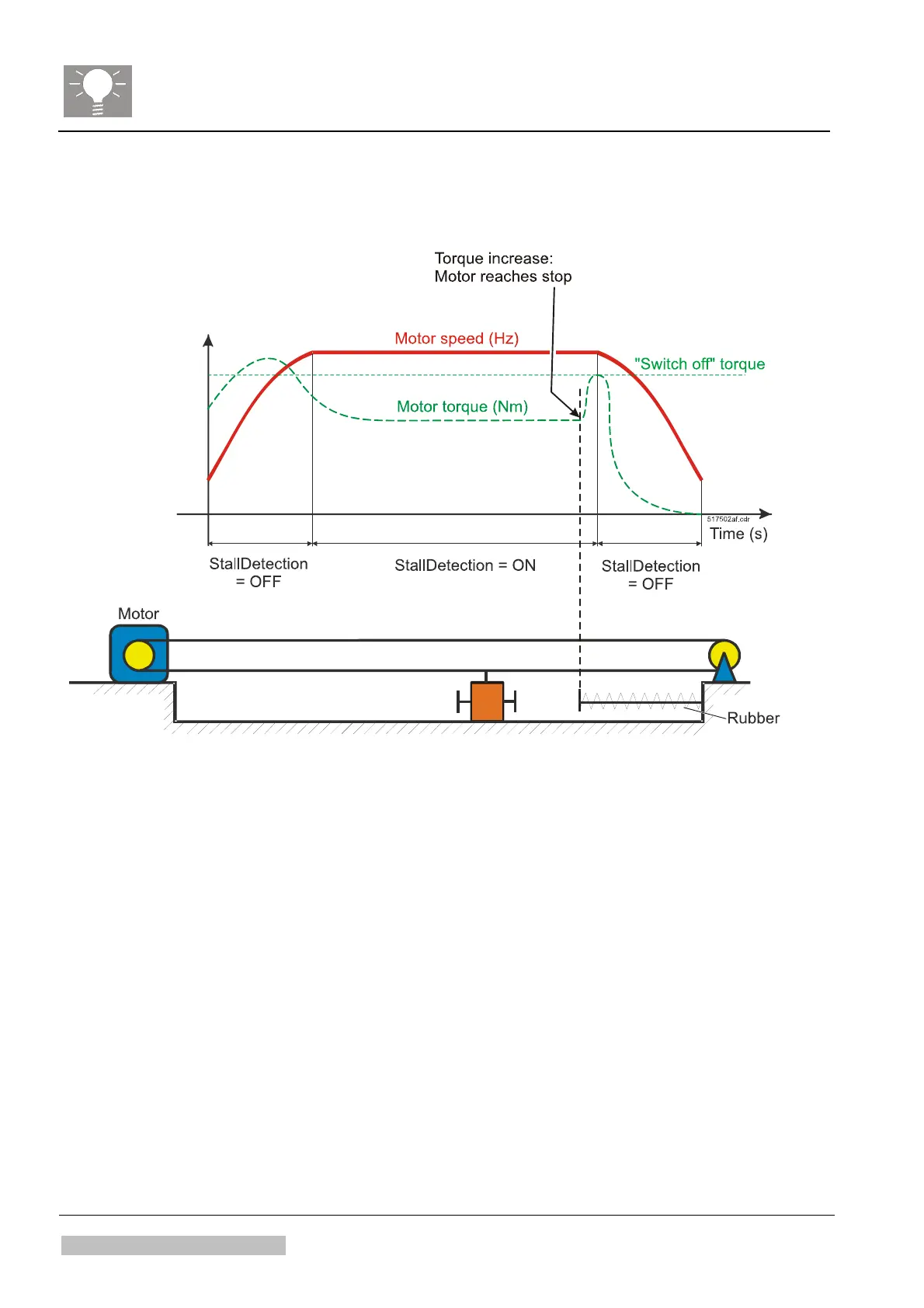
Figure 10
Stall detection =
• Motor stall (home/end position) detection without the use of additional
sensors
• Made by evaluation of stepper motor control curve on the motor controller
chip
Advantage compared to home/end position detection via light sensors:
• Monitoring of motor run not only in home and end position, but also
between home and end position (except acceleration / deceleration time)
• Less sensors (costs, reliability) and cabling (costs).
How does it work in general:
• When the stepper motor is accelerating the stall detection is switched off,
as torque differs to much during acceleration.
• When the motor reaches a stable speed, e.g. after 200 steps, the stall
detection is active for a number of steps, e.g. 5000 steps: The motor
control curve is evaluated by the motor controller chip.
Chapter 2 / 12 CR30-X Edition 1, Revision 0
Agfa Company Confidential Type 5175/100
 Loading...
Loading...