AX-4030
1-7
AUTION MAX AX-4030 OPERATING MANUAL
F
These reflectivities “R” are compared against calibration curves stored in the instrument and
output as measurement results. Also, temperature is corrected to eliminate changes caused by
environmental temperature.
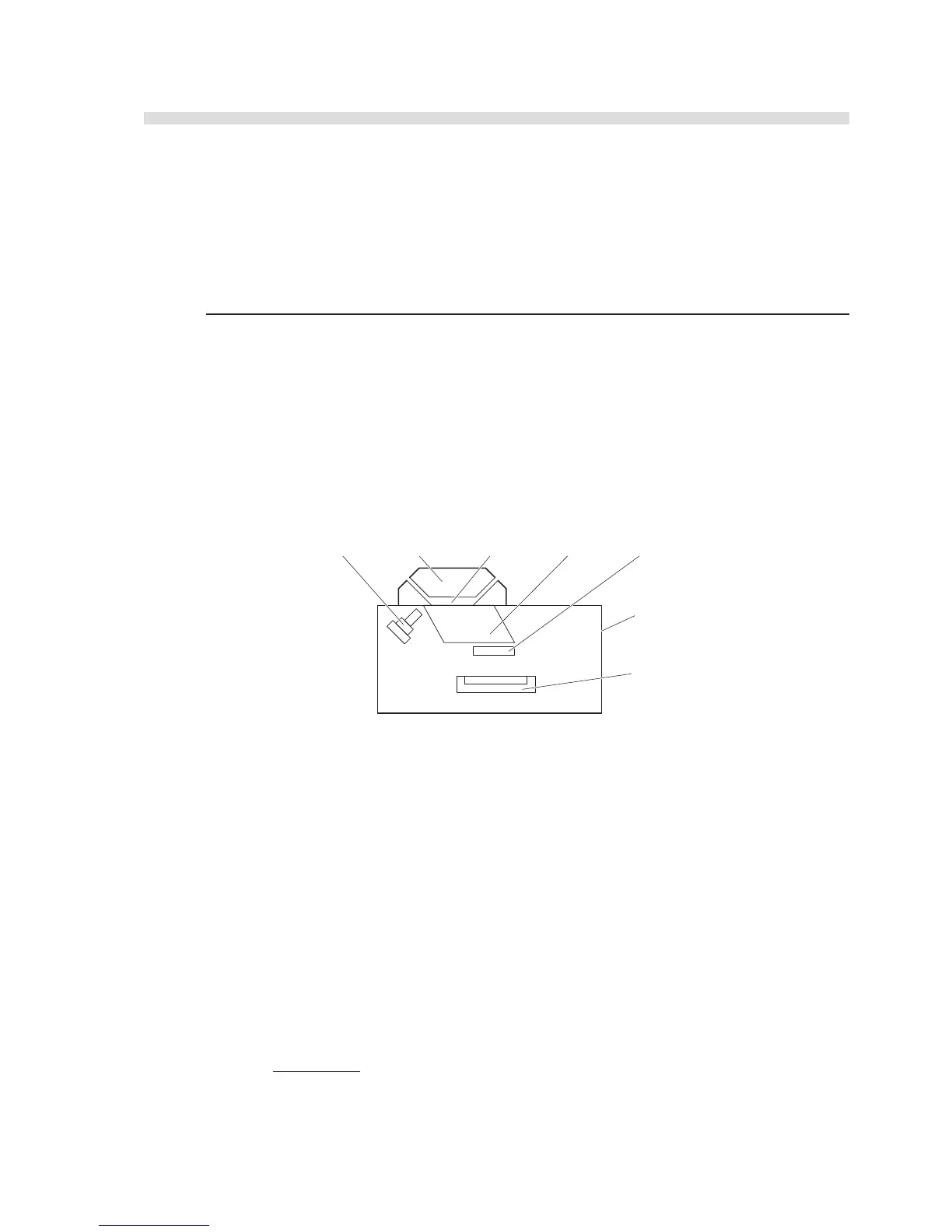
Specific Gravity (S.G.) Measurement
Specific gravity of a urine sample is obtained by measuring the refraction of the sample using a
prism and subjecting results to a calculation formula (reflection refractometry). The light from an
LED passes through the prism and is reflected on the prism face contacting the sample. The light
reflected off the prism is collimated into a thin beam by passing through a slit and directed to a
detector (CCD image sensor). At this point, the refractive index at the interface between the prism
face and sample will change according to the specific gravity, therefore the position of the incident
light from the slit will change. The refractive index is obtained by detecting the position of the
incident light and, after correcting it for temperature effects, it is converted into a Brix value. The
specific gravity of the sample is then obtained using this Brix value and a conversion formula.
The Brix value is the sugar content of an aqueous solution measured at 20°C and represents the
strength of the solution as percentage by weight.
For example, the Brix value is 30% for a 30% sucrose solution (30 g of sucrose sugar and 70 g of
water in a 100 g solution).
Specific gravity is calculated as follows:
1. The specific gravity of the sample is calculated.
SGx´ = 1 + (4/900)
*
Brix value
(However, specific gravity is equal to 1,000 if the Brix value is below 0.)
2. Correction coefficients
a and b are calculated from the low and high specific gravity values
obtained from S.G. calibration.
a =
SGL – SGH
KL – KH
b = SGL – (a × KL)
 Loading...
Loading...