Version 6.8 383 Mediant 2600 E-SBC
User's Manual 21. SBC Configuration
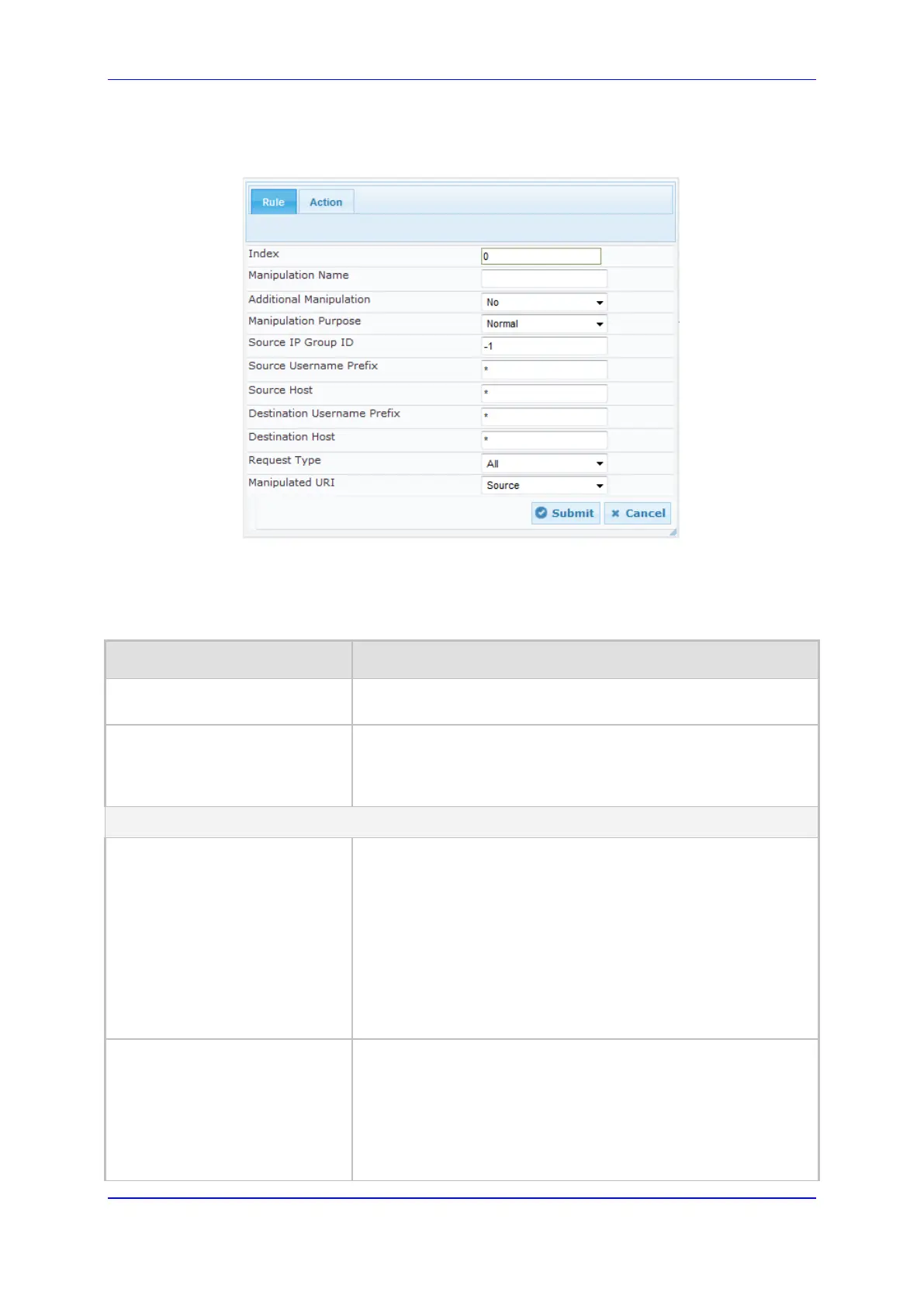
2. Click Add; the following dialog box appears:
Figure 21-13: IP to IP Inbound Manipulation Page - Add Dialog Box
3. Configure the IP-to-IP inbound manipulation rule according to the parameters
described in the table below.
4. Click Submit, and then save ("burn") your settings to flash memory.
Table 21-8: IP to IP Inbound Manipulation Parameter Descriptions
Parameter Description
Index
[IPInboundManipulation_Index]
Defines an index number for the new table record.
Manipulation Name
CLI: manipulation-name
[IPInboundManipulation_Manip
ulationName]
Defines an arbitrary name to easily identify the manipulation rule.
The valid value is a string of up to 20 characters. By default, no
value is defined.
Matching Characteristics - Rule
Additional Manipulation
CLI: is-additional-manipulation
[IPInboundManipulation_IsAddi
tionalManipulation]
Determines whether additional SIP URI user part manipulation is
done for the table entry rule listed directly above it.
[0] No = (Default) Regular manipulation rule (not done in
addition to the rule above it).
[1] Yes = If the above row entry rule matched the call,
consider this row entry as a match as well and perform the
manipulation specified by this rule.
Note:
Additional manipulation can only be done on a different SIP
URI, source or destination, to the rule configured in the row above
as configured by the 'Manipulated URI' parameter (see below).
Manipulation Purpose
CLI: purpose
[IPInboundManipulation_Manip
ulationPurpose]
Defines the purpose of the manipulation:
[0] Normal = (Default) Inbound manipulations affect the
routing input and source and/or destination number.
[1] Routing input only = Inbound manipulations affect the
routing input only, retaining the original source and destination
number.
[2] Shared Line = Used for the Shared-Line Appearance

 Loading...
Loading...