Chapter 2 Flight Safety 13
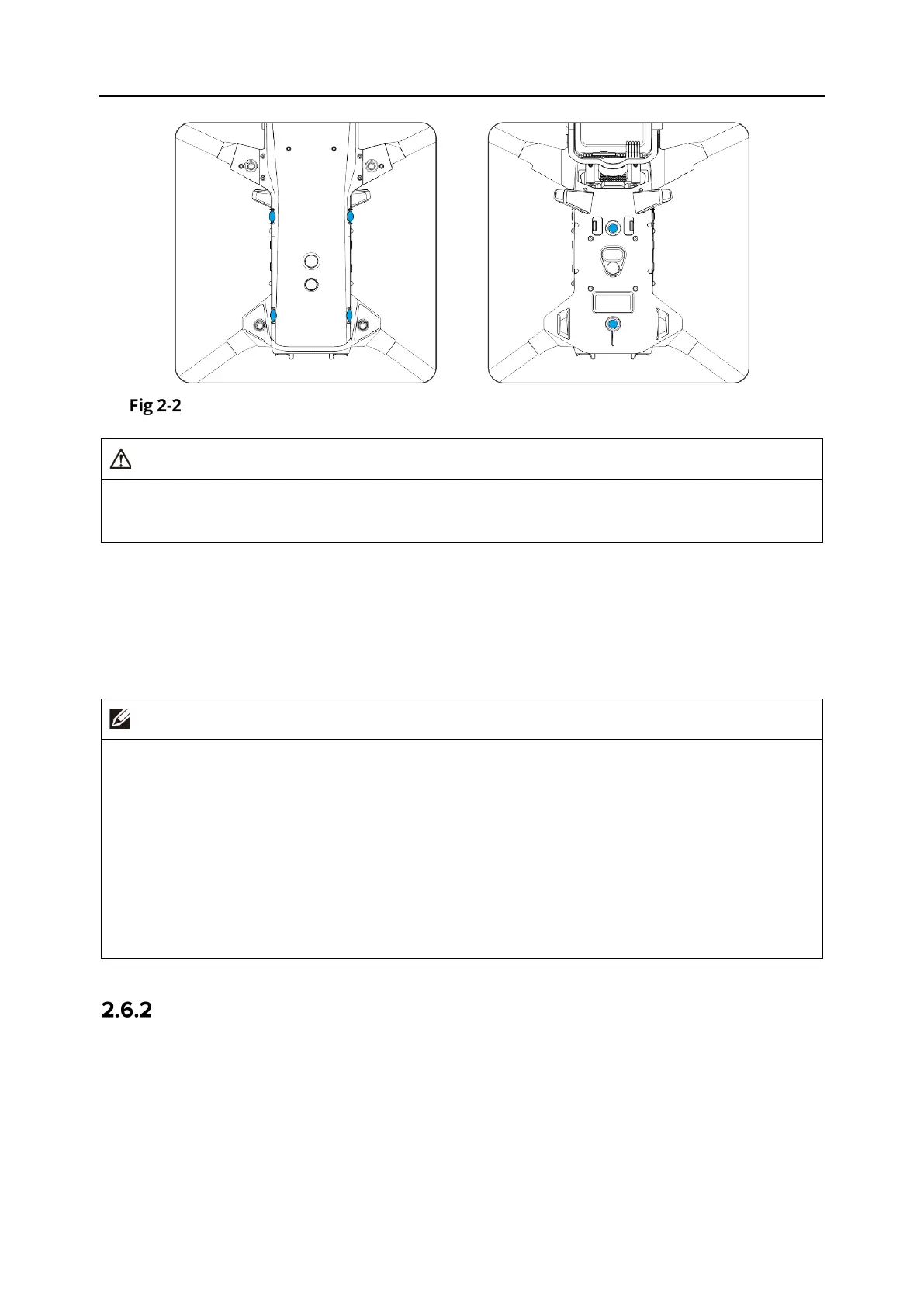
Upper left, upper right, and bottom visual lens modules of the aircraft
Do not block the lenses of the visual sensing system during flight, as it will affect the visual
obstacle avoidance performance of the aircraft, potentially leading to flight accidents.
The millimeter-wave radar sensing system senses the distances and positions of obstacles by
emitting electromagnetic waves. According to the regulations of different countries and regions,
the millimeter-wave radar sensing system of the aircraft can either integrate six 60 GHz
millimeter-wave radars inside the fuselage in six directions (front, rear, left, right, top, and
bottom) or integrate a 24 GHz millimeter-wave radar under the fuselage for sensing.
For detail frequency bands and Effective Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) data of the
millimeter-wave radar, see Appendix A “A.1 Aircraft”.
For the six millimeter-wave radars used in the Autel Alpha aircraft, the front, rear, left, right,
and top millimeter-wave radars use the 60 GHz frequency band, while the frequency band
used for the bottom millimeter-wave radar depends on local regulations.
Please be noted that the frequency band of the millimeter-
parameter, which cannot be adjusted through software. Autel Robotics ensures that the
millimeter-wave radar frequency band of the Autel Alpha aircraft complies with local legal
Observation Range
Observation Range of Visual Sensing System
By using fisheye lenses, the visual sensing system achieves a 360° field of view (FOV) in both
horizontal and vertical directions, allowing for 720° all-around observation.
 Loading...
Loading...