1-25
Catalyst 3750-X and 3560-X Switch Software Configuration Guide
OL-25303-03
Chapter 1 Configuring Network Security with ACLs
Configuring IPv4 ACLs
• Time Range Applied to an IP ACL, page 1-27
• Commented IP ACL Entries, page 1-28
• ACL Logging, page 1-28
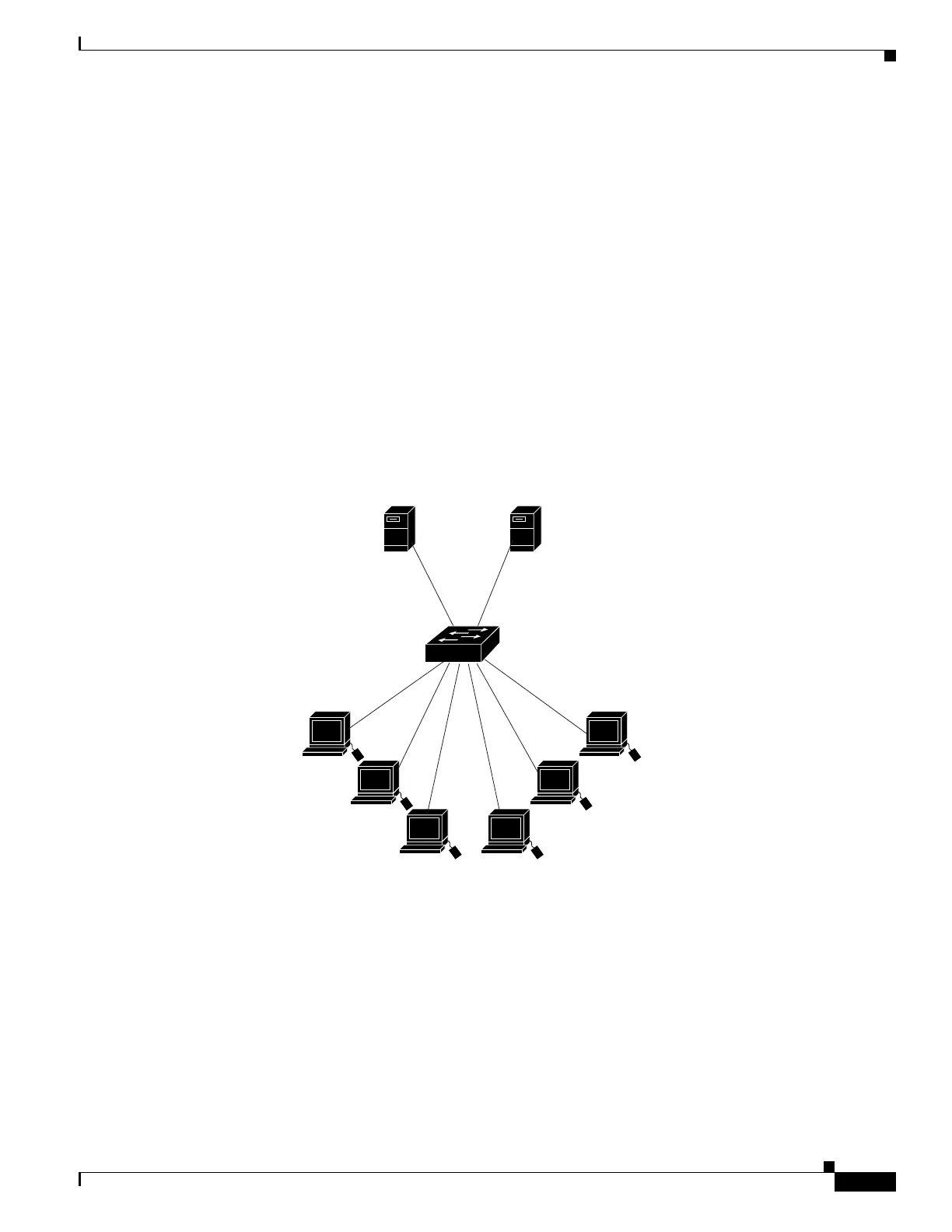
ACLs in a Small Networked Office
Figure 1-3 shows a small networked office environment with routed Port 2 connected to Server A,
containing benefits and other information that all employees can access, and routed Port 1 connected to
Server B, containing confidential payroll data. All users can access Server A, but Server B has restricted
access.
Use router ACLs to do this in one of two ways:
• Create a standard ACL, and filter traffic coming to the server from Port 1.
• Create an extended ACL, and filter traffic coming from the server into Port 1.
Figure 1-3 Using Router ACLs to Control Traffic
This example uses a standard ACL to filter traffic coming into Server B from a port, permitting traffic
only from Accounting’s source addresses 172.20.128.64 to 172.20.128.95. The ACL is applied to traffic
coming out of routed Port 1 from the specified source address.
Switch(config)# access-list 6 permit 172.20.128.64 0.0.0.31
Switch(config)# end
Switch# show access-lists
Standard IP access list 6
10 permit 172.20.128.64, wildcard bits 0.0.0.31
Switch(config)# interface gigabitethernet1/0/1
Switch(config-if)# ip access-group 6 out
Server A
Benefits
Server B
Payroll
Port 2 Port 1
Accounting
172.20.128.64-95
Human Resources
172.20.128.0-31
101354
 Loading...
Loading...











