492
Causes
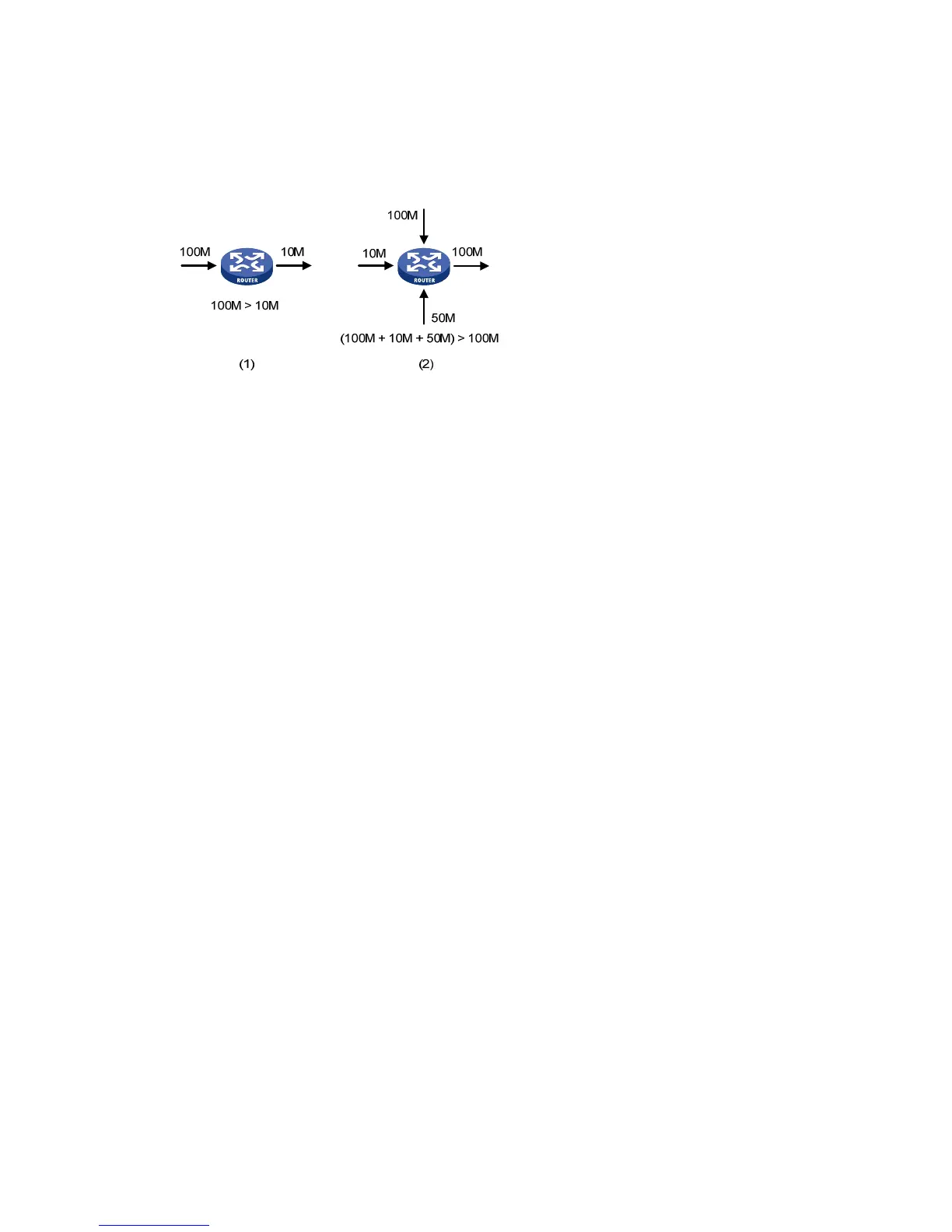
Congestion easily occurs in complex packet switching circumstances in the Internet. Figure 470 shows
two common cases:
Figure 470 Traffic congestion causes
• The traffic enters a device from a high speed link and is forwarded over a low speed link.
• The packet flows enter a device from several incoming interfaces and are forwarded out of an
outgoing interface, whose rate is smaller than the total rate of these incoming interfaces.
When traffic arrives at the line speed, a bottleneck is created at the outgoing interface causing
congestion.
Besides bandwidth bottlenecks, congestion can be caused by resource shortage in various forms such as
insufficient processor time, buffer, and memory, and by network resource exhaustion resulting from
excessive arriving traffic in certain periods.
Impacts
Congestion brings these negative results:
• Increased delay and jitter during packet transmission
• Decreased network throughput and resource use efficiency
• Network resource (memory in particular) exhaustion and even system breakdown
It is obvious that congestion hinders resource assignment for traffic and degrades service performance.
Congestion is unavoidable in switched networks and multi-user application environments. To improve the
service performance of your network, you must address the congestion issues.
Countermeasures
A simple solution for congestion is to increase network bandwidth, however, it cannot solve all the
problems that cause congestion because you cannot increase network bandwidth infinitely.
A more effective solution is to provide differentiated services for different applications through traffic
control and resource allocation. In this way, resources can be used more effectively. During resources
allocation and traffic control, the direct or indirect factors that might cause network congestion should be
controlled to reduce the probability of congestion. Once congestion occurs, resource allocation should
be performed according to the characteristics and demands of applications to minimize the effects of
congestion.
 Loading...
Loading...











