Static Electricity Precautions
XI
CBM-20A/20Alite
Static Electricity Precautions
A liquid chromatograph (LC) uses flammable organic solvent(s) as the mobile phase. LC systems are also
often used where large amount of flammable substances are present. Thus, an accident can produce large
scale damage. Operators must be constantly on guard against accidents involving fire or explosion.
The major cause of these accidents is static electricity. Devising preventative measures for static can be
difficult, because the symptoms before an accident vary and can be hard to detect, since such accidents
occur as a result of several simultaneous coincidences. Recommended methods for preventing static
electricity accidents are provided below. Take thorough safety measures based on this information.
Typical Cause of Static Electricity Accidents
Static electricity accidents are generally caused by this sequence of events:
Generation of static electricity
Accumulation of static electricity
Release of energy through
electrical discharge
Ignition of flammable substances
When liquid is passed through thin tubing at high flow rates, as in liquid
chromatograph, the electrostatic charges of the flowing matter generate
static electricity.
If electrostatically charged liquid is allowed to accumulate in an electrically
insulated container, the charge will gradually increase, and can eventually
reach several thousand volts. If this happens and an electrical conductor
is brought within a certain distance of the container, electrical discharge
will occur, releasing thermal energy which will ignite any flammable gas of
sufficient density in the vicinity.
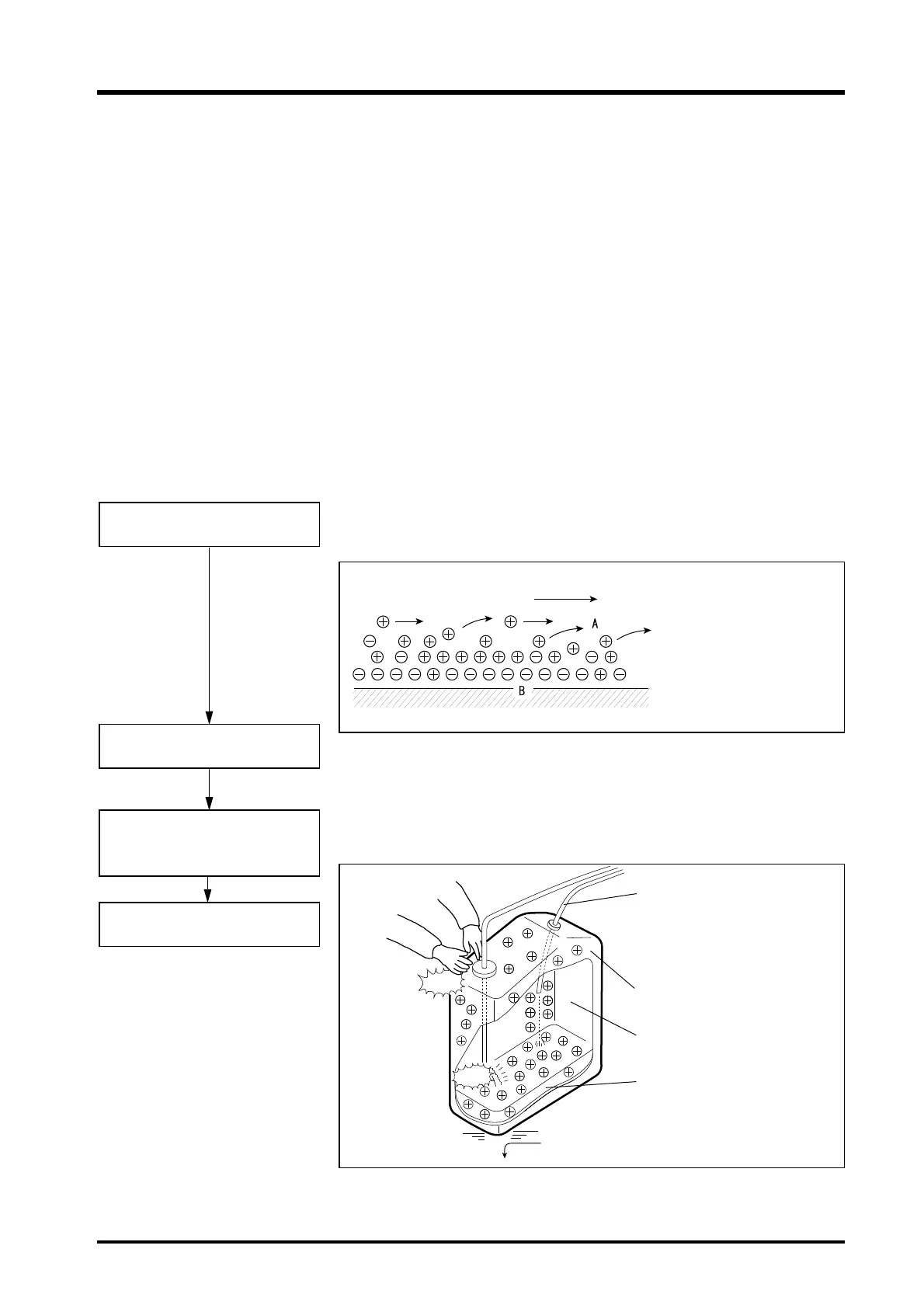
Generation of Static Electricity by a Liquid Flowing over a Solid
A: Charges move with
flow of liquid.
B: Immobile charges,
fixed to surface of
solid.
Solid
Flowing liquid
Potential accident situation
Dry air
Floor covered with rubber, etc.,
cannot conduct electricity away.
Liquid flowing through thin
tubing at high rate.
Air bubbles in liquid facilitate
generation of static electricity.
Insulated container of
polyethylene, etc.
Flammable gas present in
container.
Flammable organic solvent with
large electrostatic charge.
spark
spark

 Loading...
Loading...