restart. External device monitoring is then able to detect if one of the contactor’s con‐
t
acts is welded, for instance. In this case the external device monitoring places the sys‐
tem in a safe operational status and the OSSDs are not switched back to the ON state.
The table shows how the device reacts if the external device monitoring detects a con‐
tactor malfunction:
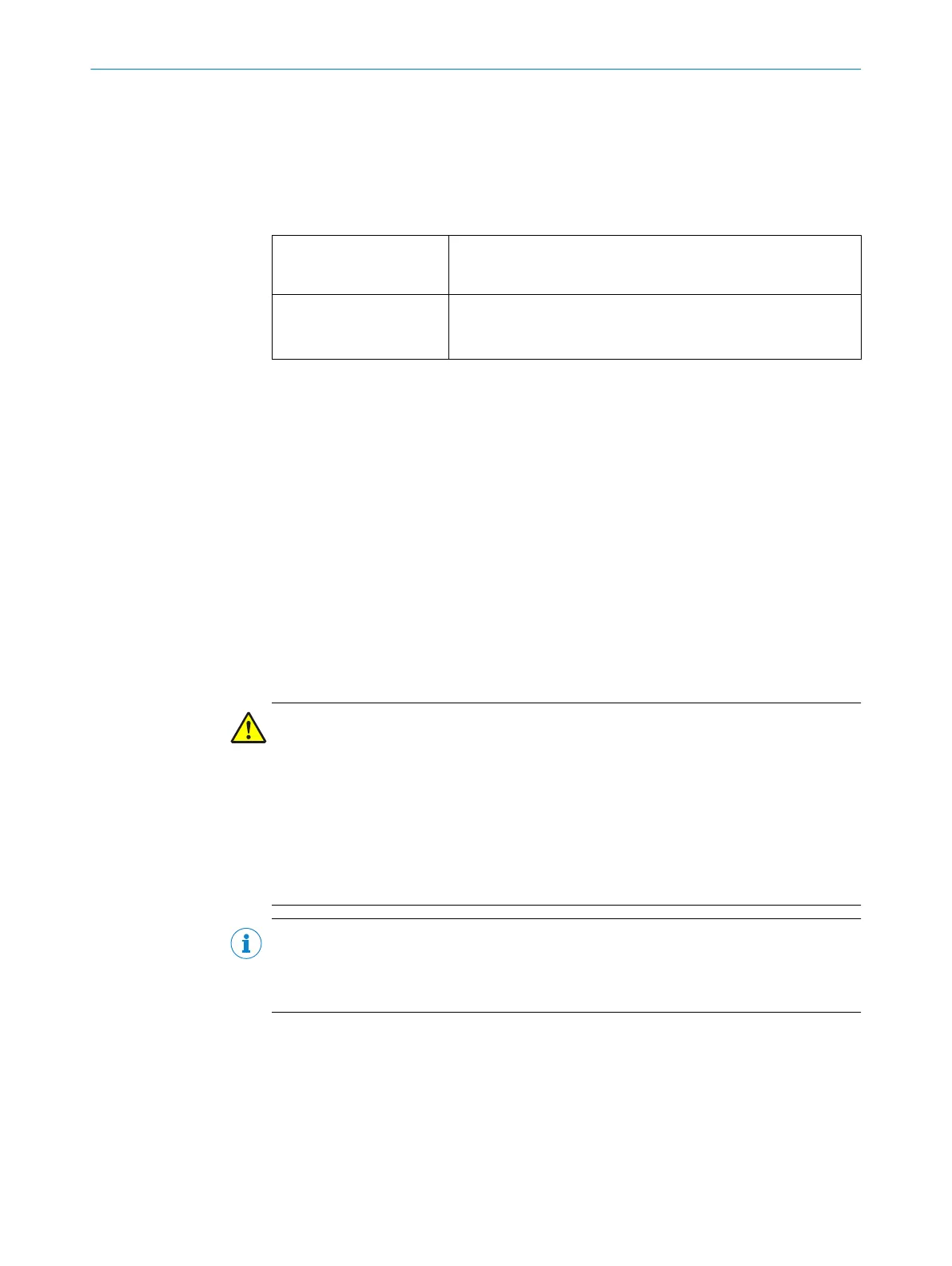
Table 16: Behavior of the device on a contactor malfunction
Without internal restart
int
erlock or with restart
delay
•
T
he system locks completely (lock-out).
•
The error message appears in the 7-segment display.
With restart interlock
•
T
he safety laser scanner switches its OSSDs to the OFF state.
•
The LED Ê is illuminated.
•
The error message appears in the 7-segment display.
External device monitoring can be configured in the CDS.
Further topics
•
"C
onnection diagrams", page 52
7.8 Restart
Overview
Y
ou can configure the restart behavior as follows:
•
Without restart interlock
•
With restart delay
•
With restart interlock
The type of restart can be configured in the CDS.
Important information
DANGER
H
azard due to unexpected starting of the machine
If the protective field can be exited in the direction of the hazardous point, e.g., to areas
that are unprotected due to the method of mounting or the near range of the safety
laser scanner, the machine could restart while a person is in the hazardous area.
b
It is imperative that you configure the safety laser scanner with restart interlock if
the protective field can be exited in the direction of the hazardous point or if a per‐
son cannot be detected by the safety laser scanner at every point in the hazardous
area.
NOTE
T
he S300 Mini Remote can only be operated on an S3000 / S300 safety laser scanner,
on a Flexi Soft safety controller, or on a sens:Control device via EFI. If a restart interlock
is needed, then it must be configured and installed on this device.
Configuration of the safety laser scanner without restart interlock
If t
here is an object in the protective field, the OSSDs on the safety laser scanner switch
to the OFF state. The OSSDs are re-enabled again immediately when there is no longer
an object in the active protective field.
7 C
ONFIGURATION
76
O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | S300 Mini 8014170/ZA23/2019-11-14 | SICK
Subject to change without notice
 Loading...
Loading...











