Chapter 7
111
UM10372_PCNC440_Manual_0221A
PROgRAMMiNg
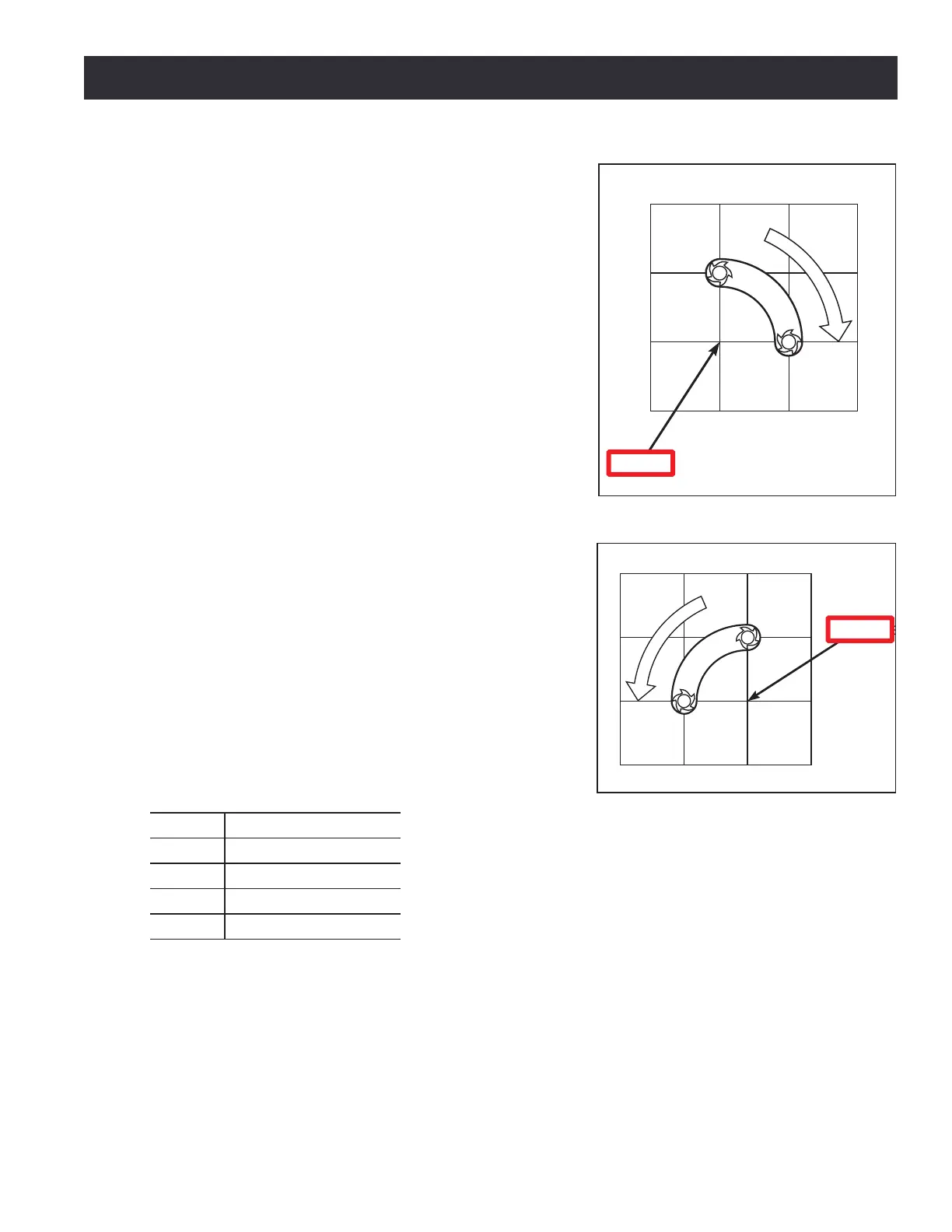
7.3.3 Arc at Feed Rate – G02, G03
A circular or helical arc is specied using either G02
(clockwise arc) or G03 (counterclockwise arc) as shown in
Figure 7.1 and Figure 7.2. The axis of the circle or helix
must be parallel to the X-, Y- or Z-axis of the mill coordinate
system. The axis (or equivalently, the plane perpendicular
to the axis) is selected with G17 (Z-axis, XY-plane), G18
(Y-axis, XZ-plane) or G19 (X-axis, YZ-plane). If the arc is
circular, it lies in a plane parallel to the selected plane.
If a line of code makes an arc and includes rotaonal axis
moon, the rotaonal axes turn at a constant rate so that
the rotaonal moon starts and nishes when the XYZ
moon starts and nishes. Lines of this sort are hardly
ever programmed.
If cuer radius compensaon is acve, the moon will
dier from the above; see Cuer Compensaon later in
this chapter.
Two formats are allowed for specifying an arc: the center
format and the radius format. In both formats the G02 or
G03 is oponal if it is the current moon mode.
7.3.3.1 Radius Format Arc
For an arc in radius format, program: G02 X~ Y~ Z~
A~ R~ (for a clockwise arc) or G03 X~ Y~ Z~ A~ R~
(for a counterclockwise arc).
Word Definition
X~ X-axis coordinate
Y~ Y-axis coordinate
Z~ Z-axis coordinate
A~ A-axis coordinate
R~ Radius of arc
In radius format, the coordinates of the end point of the arc in the selected plane are specied along
with the radius of the arc. R is the radius. The axis words are all oponal except that at least one of
the two words for the axes in the selected plane must be used. The R number is the radius. A posive
radius indicates that the arc turns through 180 degrees or less, while a negave radius indicates a turn
of 180 degrees to 359.999 degrees.
If the arc is helical, the value of the end point of the arc on the coordinate axis parallel to the axis of
the helix is also specied.
Center
Y
X
1
1
2
3
Figure 7.1
Center
X
1
1
2
2
3
3
Cent
Figure 7.2
Center

 Loading...
Loading...