Chapter 7
129
UM10372_PCNC440_Manual_0221A
PROgRAMMiNg
7.4 Canned Cycles
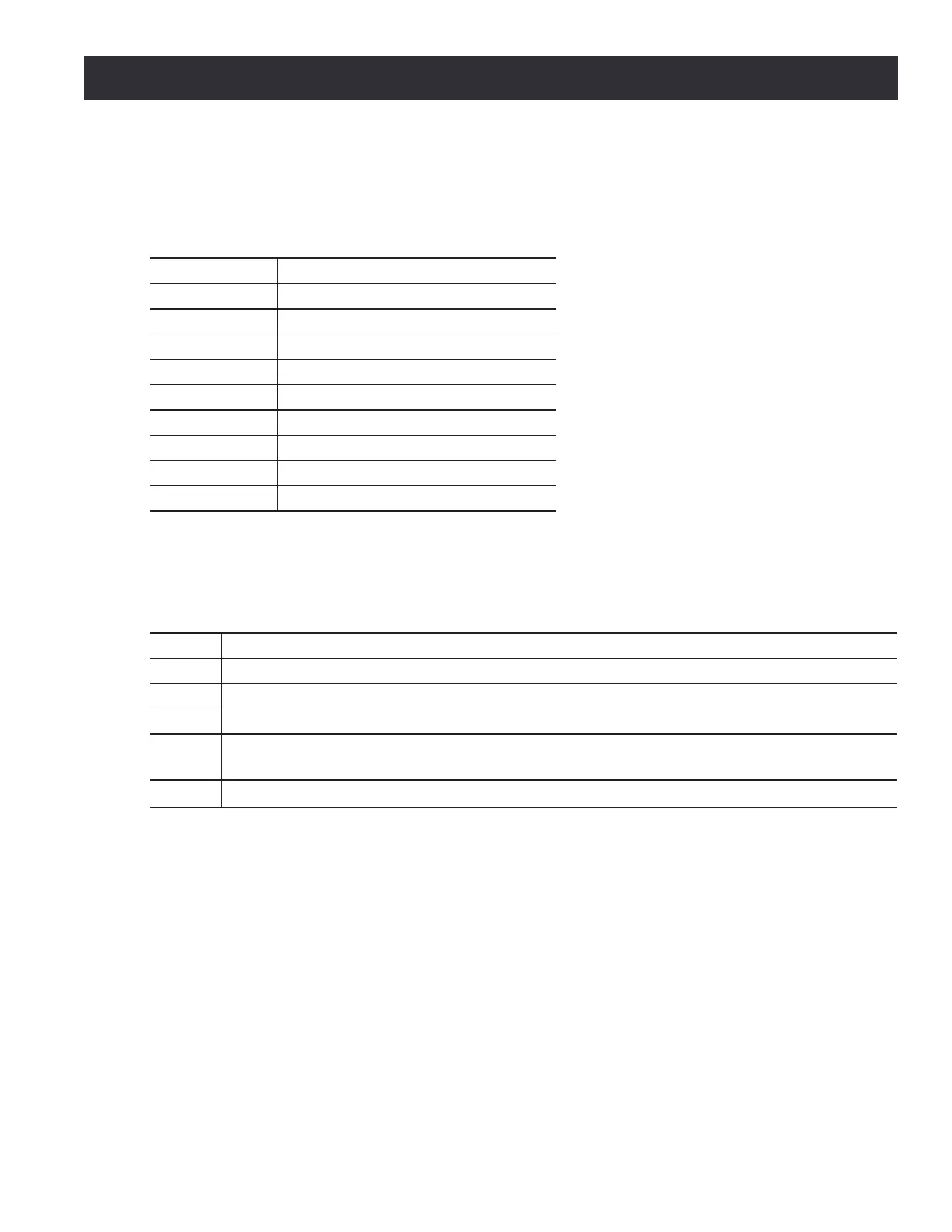
The canned cycles described in the table below are implemented in PathPilot.
Canned Cycle Description
G80 Cancel acve canned cycle
G81 Simple drilling cycle
G82 Simple drilling with dwell cycle
G83 Peck drilling cycle
G73 High speed peck drilling cycle
G84 Tapping cycle
G85 Boring cycle – feedrate out
G86 Boring cycle – stop, rapid out
G88 Boring cycle – stop, manual out
G89 Boring cycle – dwell, feedrate out
All canned cycles are performed with respect to the acve plane. The descripons in this secon assume
the XY-plane has been selected. The behavior is always analogous if the YZ or XZ-plane is selected.
Word Definition
X~ X-axis coordinate
Y~ Y-axis coordinate
Z~ Z-axis coordinate
A~ A-axis coordinate
R~
Retract posion along the axis perpendicular to the currently selected plane (Z-axis for XY-
plane, X-axis for YZ-plane, Y-axis for XZ-plane)
L~
L number is oponal and represents the number of repeats
All canned cycles use X, Y, Z, and R words. The R word sets the retract posion; this is along the axis
perpendicular to the currently selected plane (Z-axis for XY-plane, X-axis for YZ-plane, Y-axis for XZ-
plane). Some canned cycles use addional arguments.
Rotaonal axis (A-axis) words are allowed in canned cycles, but it is beer to omit them. If rotaonal
axis words are used, the numbers must be the same as the current posion numbers so that the
rotaonal axes do not move.
The R number is always scky. Scky numbers keep their value on subsequent blocks if they are not
explicitly programmed to be dierent.
 Loading...
Loading...