Z8 Microcontrollers
Address Space ZiLOG
2-12 UM001601-0803
2.7 Z8 STACKS
Stack operations can occur in either the Z8 MCU Standard Reg-
ister File or external data memory. Under software control, Port
0–1 Mode register (F8H) selects the stack location. Only the
General-Purpose Registers can be used for the stack when the in
-
ternal stack is selected.
The register pair FEH and FFH form the 16-bit Stack Pointer
(SP), that is used for all stack operations. The stack address is
stored with the MSB in FEH and LSB in FFH (Figure 2-9).
The stack address is decremented prior to a PUSH operation and
incremented after a POP operation. The stack address always
points to the data stored on the top of the stack. The Z8 stack is
a return stack for CALL instructions and interrupts, as well as a
data stack.
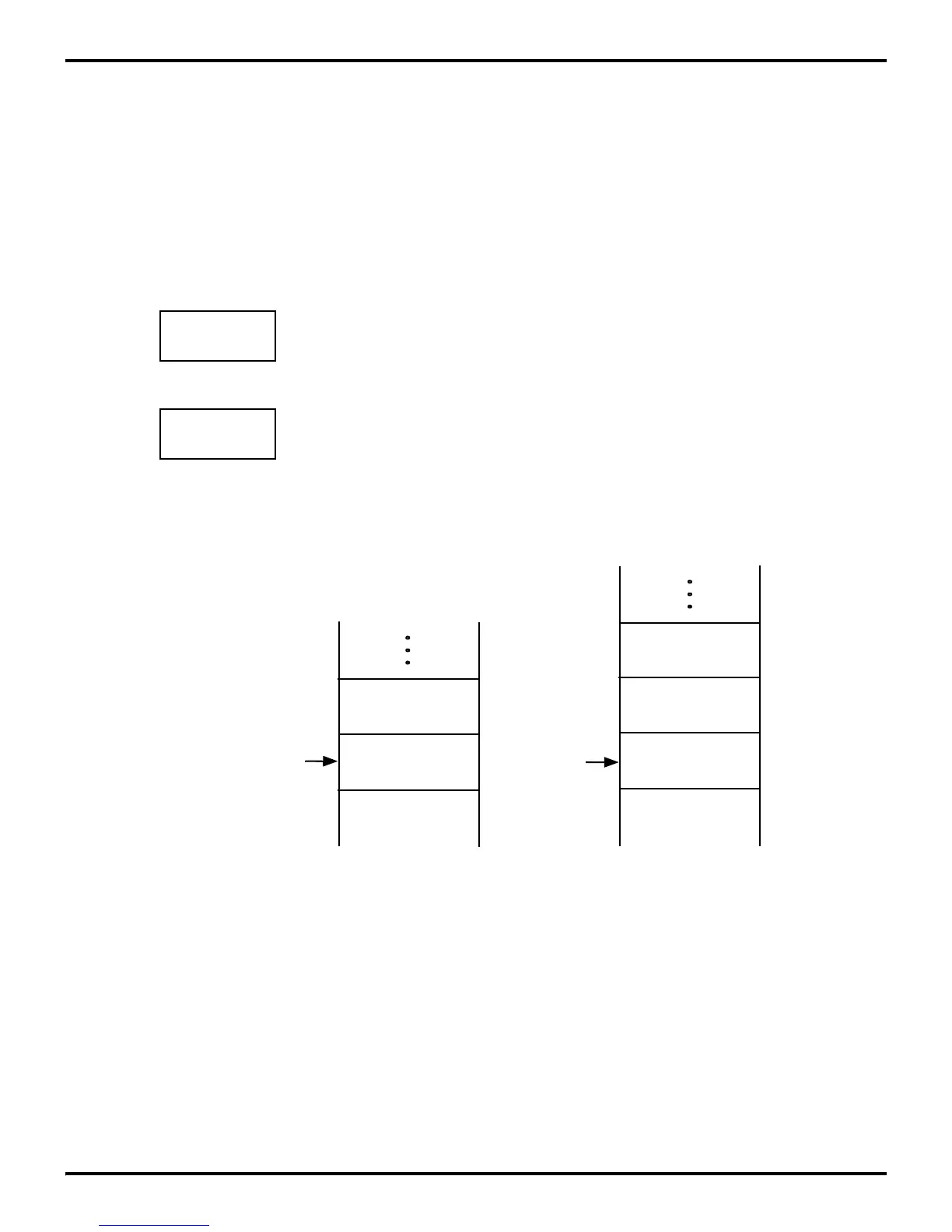
During a CALL instruction, the contents of the PC are saved on
the stack. The PC is restored during a RETURN instruction. In
-
terrupts cause the contents of the PC and Flag registers to be
saved on the stack. The IRET instruction restores them (Figure
2-10).
When the Z8 is configured for an internal stack (using the Z8
Standard Register File), register FFH serves as the Stack Pointer.
The value in FEH is ignored. FEH can be used as a general-pur
-
pose register in this case only.
An overflow or underflow can occur when the stack address is
incremented or decremented during normal stack operations.
The programmer must prevent this occurrence or unpredictable
operation will result.
Figure 2-9. Stack Pointer
UPPER Byte
LOWER Byte
Stack Pointer High
FFH
Stack Pointer Low
FEH
Figure 2-10. Stack Operations
PCL
Top of Stack
Stack Contents
PCH
PCL
PCH
FLAGS
After an
Interrupt Cycle
Stack Contents
After a Call
Instruction
Top of Stack

 Loading...
Loading...