MATHEMATICAL ALGORITHMS
Section 15, Page 9 October 2002
SCHLUMBERGER
mA = ½ (AB- Na)
mB = ½ (AB+Na)
nA = ½ (AB+Na)
nB = ½ (AB- Na)
Where: a = [A-SP] = a-spacing (size of receiver dipole) in meters
V = Received voltage in volts [Measured].
I = 4/π * [Tx Curr] = 4/π * Transmitter current in amperes
N = multiplier for potential dipole length. Used as N-spacing in other programs.
m,n = potential electrode locations.
A,B = current electrode locations. Ax and Bx are input in menu 1, in meters, and can
be coordinate locations.
AB = |Ax - Bx| in meters.
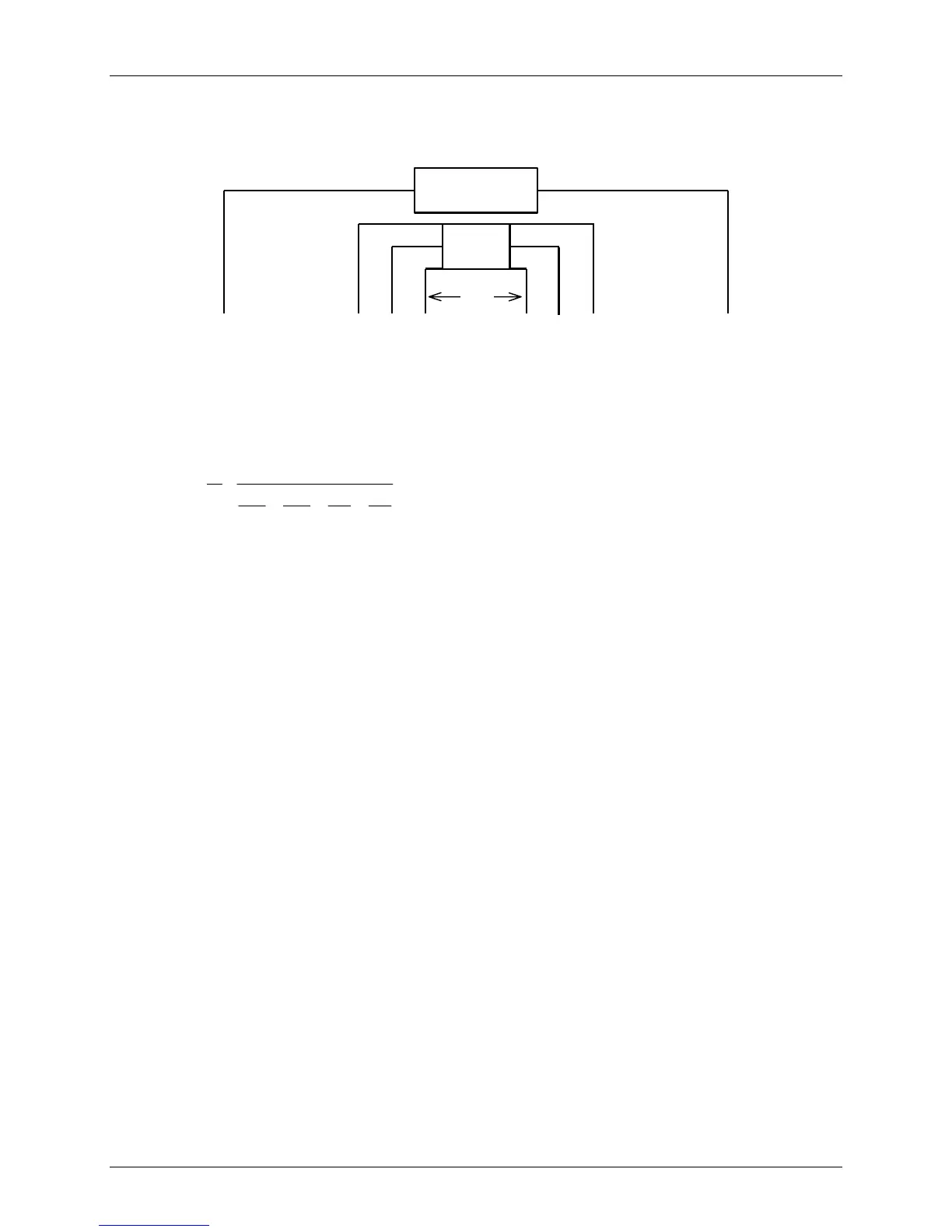
Assumption: Receiver dipoles are centered about the middle of the transmitter (AB) dipole.
Note that the Schlumberger and Wenner arrays are special cases of the Gradient array.
Input Parameters:
Ax, Bx : Menu 1, in meters.
A-SP : Menu 2, in meters. Shown as "a" in the equations.
N : Menus 3 and 4. The product of a * N = the potential dipole length.
Tx Curr : Menu 4, in amperes
In the above diagram, if the potential dipoles are 10, 20 and 30 meters long, with a = 10
m, and the 10 m dipole is connected to channel 1, the 20 m dipole to channel 2 and the 30
m dipole connected to channel 3, the operator would enter N=1 for channel 1, N=2 for
channel 2, and N=3 for channel 3.
RHO
I
mA mB nA nB
=
−−+
2
1
1111
π
**
Transmitter
Rcvr
Ax Bx
m
3
m
2
m
1
n
1
n
2
n
3
a
 Loading...
Loading...