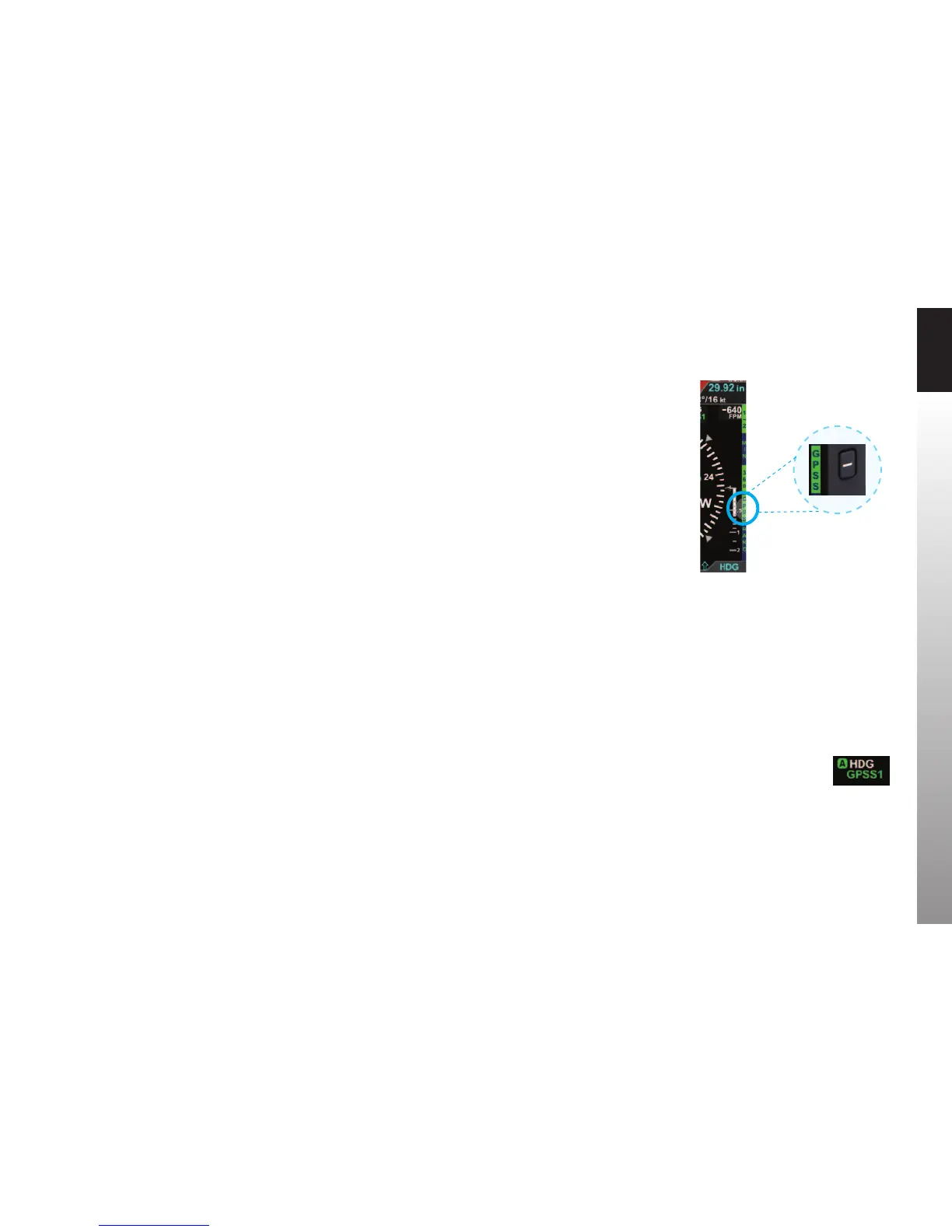CHAPTER 3 FLYING THE EFD1000 C3 PRO PFD
Page 3-18
091-00019-001 REV B
Page 3-19
091-00019-001 REV B EFD1000 C3 Pro PFD Pilot’s Guide
With GPS Steering (GPSS), a compatible GPS navigator (in this case, a Garmin 430W)
drives the autopilot directly via the autopilot’s HDG mode, telling it how to bank to
stay centered on course. GPSS can drive the autopilot far more accurately than the NAV
mode (which is based on course deviation indications) because the GPS always knows
the ground track and how to adjust to maintain that track, implicitly accounting for
changing wind conditions. The GPS also includes turn anticipation based on current
ground speed and track, enabling it to turn early and roll out centered on the new
course without overshooting. As we’ll soon see when ying an instrument approach, an
autopilot with a WAAS GPS and GPSS enabled can even y procedure turns and holding
patterns (see Chapter 4, Section 4.7.1. GPS Steering for more details).
Now that we’re established at our nal cruise altitude and in the enroute phase of our
ight, we’ll switch to the ARC Compass mode of the HSI to maximize a forward view.
1. Press the 360 Hot Key and observe that HSI changes to its ARC Compass
mode and the Hot Key label changes from 360 to ARC.
2. Press the RNG Buttons to adjust the map range to suit your preference.
Figure 3-28
GPSS Enabled legend in Green
Figure 3-29
GPSS Enabled

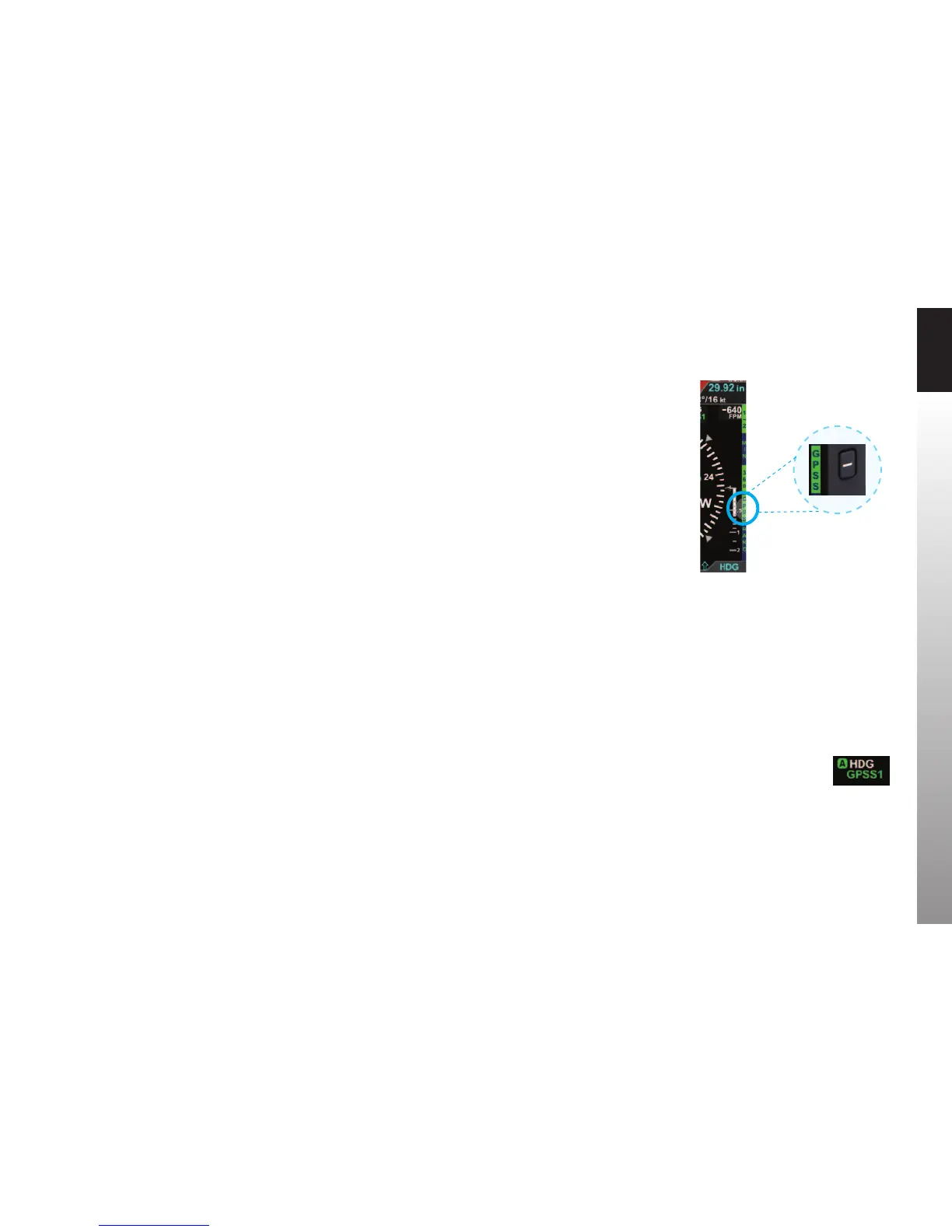 Loading...
Loading...