Installing under Windows
AX3000 Models 80 and 85 - User's Manual 89
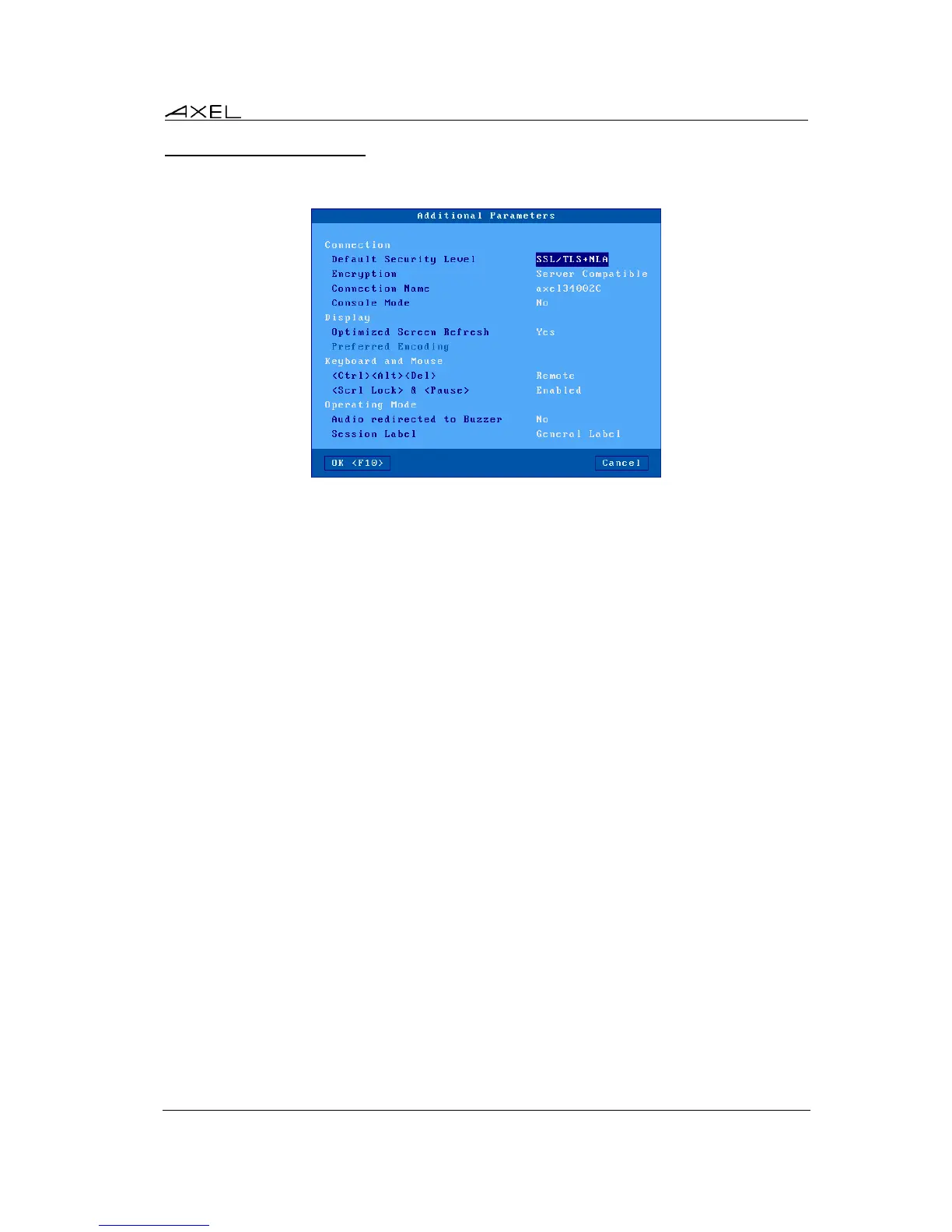
5.1.5 - Additional Parameters
The following box is displayed:
These parameters are:
- Default Security Level: values are:
- RDP: the thin client opens a connection with the standard RDP security layer. If this is
denied by the server, a new connection is opened with the SSL/TLS and
SSL/TLS+NLA security layers.
- SSL/TLS: the thin client opens a connection with the standard SSL/TLS security layer.
If this is denied by the server, a new connection is opened with the standard RDP
security layer.
- SSL/TLS+NLA: the thin client opens a connection with the SSL/TLS+NLA security
layer. If this is denied by the server, a new connection is opened with the standard
RDP security layer.
- Encryption: encryption levels are:
- Server Compatible: all the encryption capabilities are offered. This allows the
encryption method to be selected by the server.
- Low Level: only one-direction encrypted connections are accepted. (Data sent by
Windows is encrypted).
- Medium Level: both-direction and one-direction encrypted connections are accepted.
- High Level: only both-direction encrypted connections are accepted.
- Fips Compliant: both-direction encryption with FIPS method.
- Connection Name: this character string identifies the AX3000 within the Windows Operating
System. By default this name is the thin client name (see Chapter 3.1.1).
- Console Mode: when set to 'yes', the RDP connection will take remote control of the
Windows Server main console.
- Optimized Screen Refresh: smooth video playback especially for flash type content (ie
Youtube).
- Preferred Encoding: This option is only available for 32bpp connections. There are two
options but normally for best performance we advise using RDP (default):
- RemoteFX (20082R2): supported by 2008R2. And 2012R2 (according to GPOs)
- RDP: supported by all Windows Server versions.
- <Ctrl><Alt><Del>: the two modes for this keystroke are:
- Local: the keystroke is handled by the AX3000 and is used for shutdown the thin client
(see Chapter 4.9)
 Loading...
Loading...