1-4
Catalyst 3750-X and 3560-X Switch Software Configuration Guide
OL-25303-03
Chapter 1 Configuring Network Security with ACLs
Understanding ACLs
Port ACLs
Port ACLs are ACLs that are applied to Layer 2 interfaces on a switch. Port ACLs are supported only on
physical interfaces and not on EtherChannel interfaces and can be applied only on interfaces in the
inbound direction. These access lists are supported:
• Standard IP access lists using source addresses
• Extended IP access lists using source and destination addresses and optional protocol type
information
• MAC extended access lists using source and destination MAC addresses and optional protocol type
information
The switch examines ACLs associated with all inbound features configured on a given interface and
permits or denies packet forwarding based on how the packet matches the entries in the ACL. In this way,
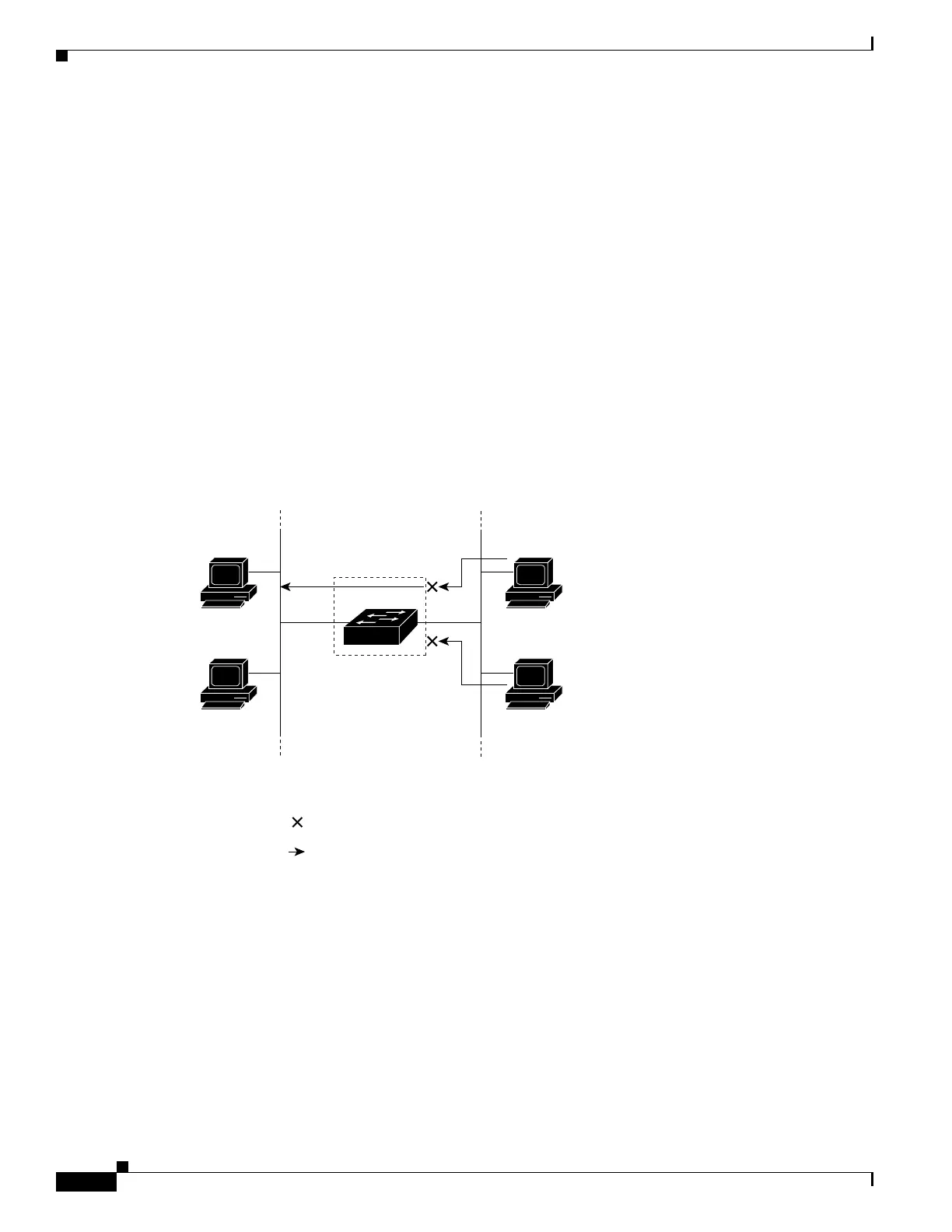
ACLs control access to a network or to part of a network. Figure 1-1 is an example of using port ACLs
to control access to a network when all workstations are in the same VLAN. ACLs applied at the Layer 2
input would allow Host A to access the Human Resources network, but prevent Host B from accessing
the same network. Port ACLs can only be applied to Layer 2 interfaces in the inbound direction.
Figure 1-1 Using ACLs to Control Traffic to a Network
When you apply a port ACL to a trunk port, the ACL filters traffic on all VLANs present on the trunk
port. When you apply a port ACL to a port with voice VLAN, the ACL filters traffic on both data and
voice VLANs.
With port ACLs, you can filter IP traffic by using IP access lists and non-IP traffic by using MAC
addresses. You can filter both IP and non-IP traffic on the same Layer 2 interface by applying both an IP
access list and a MAC access list to the interface.
Host A
Host B
101365
Research &
Development
network
= ACL denying traffic from Host B
and permitting traffic from Host A
= Packet
Human
Resources
network

 Loading...
Loading...











