2-34
Cisco ONS 15454 Troubleshooting Guide, R8.5
November 2009
Chapter 2 Alarm Troubleshooting
2.5.5 Service Effect
The far-end failure alarm hierarchy is shown in Table 2-12, as given in Telcordia GR-253-CORE.
2.5.5 Service Effect
Service-Affecting (SA) alarms—those that interrupt service—could be Critical (CR), Major (MJ), or
Minor (MN) severity alarms. Service-Affecting (SA) alarms indicate service is affected.
Non-Service-Affecting (NSA) alarms always have a Minor (MN) default severity.
2.5.6 States
The Alarms or History tab State (ST) column indicate the disposition of the alarm or condition as
follows:
• A raised (R) event is one that is active.
• A cleared (C) event is one that is no longer active.
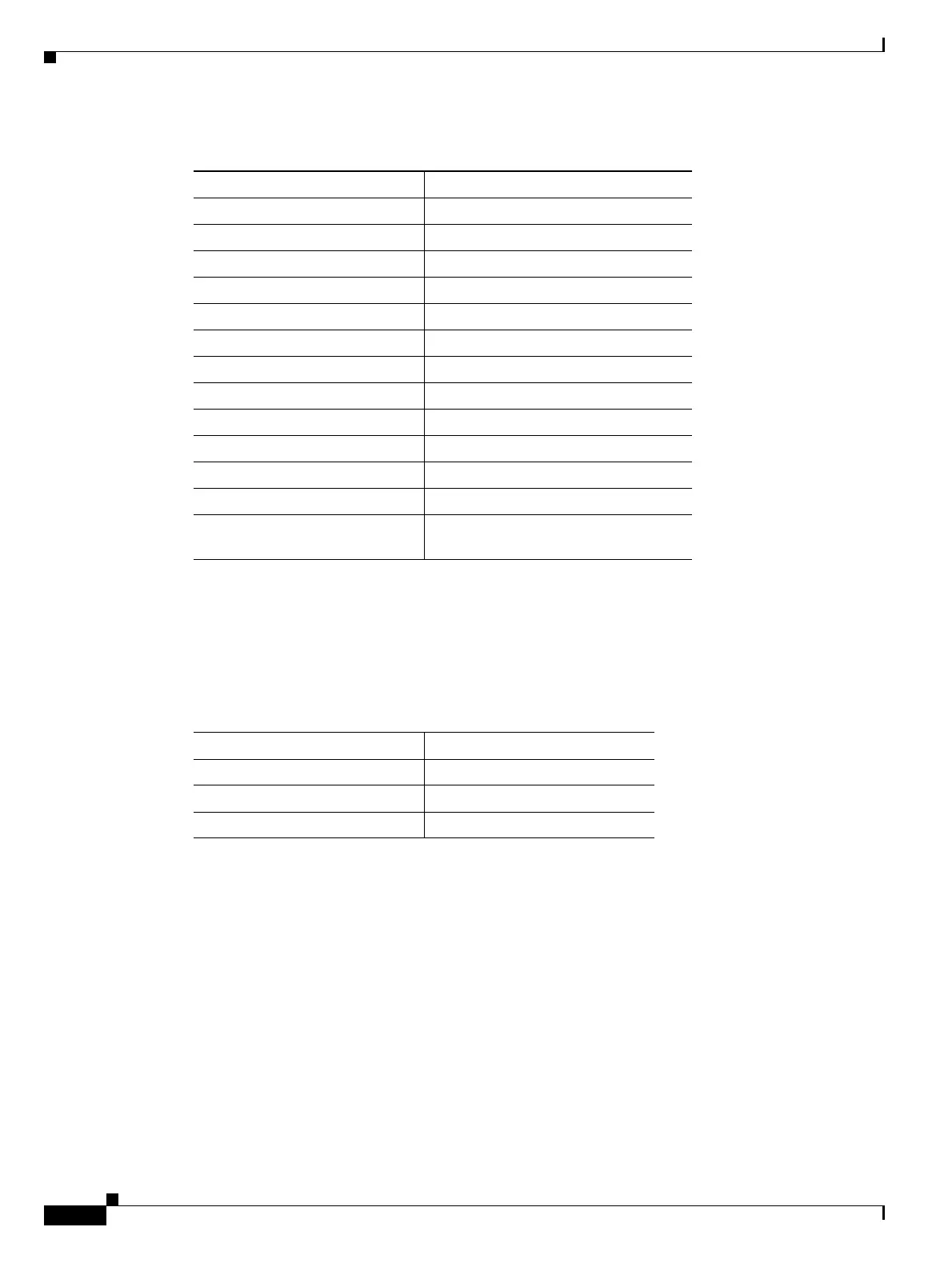
Table 2-11 Near-End Alarm Hierarchy
Priority Condition Type
Highest LOS
—LOF
—AIS-L
—AIS-P
1
1. Although it is not defined as a defect or failure, all-ones STS pointer relay is also higher
priority than LOP-P. Similarly, all-ones VT pointer relay is higher priority than LOP-V.
—LOP-P
2
2. LOP-P is also higher priority than the far-end failure RFI-P, which does not affect the
detection of any near-end failures. Similarly, LOP-V is higher priority than RFI-V.
—UNEQ-P
—TIM-P
—PLM-P
—AIS-V
1
—LOP-V
2
—UNEQ-V
—PLM-V
Lowest DS-N AIS (if reported for outgoing
DS-N signals)
Table 2-12 Far-End Alarm Hierarchy
Priority Condition Type
Highest RFI-L
—RFI-P
Lowest RFI-V
 Loading...
Loading...