Configuring IP
December 2000 15 - 53
The load sharing state for all the route sources is based on the state of IP load sharing. Since IP load sharing is
enabled by default on all Foundry Layer 3 Switches, load sharing for static IP routes, RIP routes, OSPF routes,
and BGP4 routes also is enabled by default.
How IP Load Sharing Works
When the Layer 3 Switch receives traffic for a destination and the IP route table contains multiple, equal-cost
paths to that destination, the device checks the IP forwarding cache for a forwarding entry for the destination. The
IP forwarding cache provides fast path for forwarding IP traffic, including load-balanced traffic. The cache
contains entries that associate a destination host or network with a path (next-hop router).
• If the IP forwarding sharing cache contains a forwarding entry for the destination, the device uses the entry to
forward the traffic.
• If the IP load forwarding cache does not contain a forwarding entry for the destination, the software selects a
path from among the available equal-cost paths to the destination, then creates a forwarding entry in the
cache based on the calculation. Subsequent traffic for the same destination uses the forwarding entry.
Foundry Layer 3 Switches support the following IP load sharing methods:
• Host-based – The Layer 3 Switch uses a simple round-robin mechanism to distribute traffic across the equal-
cost paths based on destination host IP address. This is the only method supported by stackable Layer 3
Switches and also is supported on chassis Layer 3 Switches.
• Network-based – The Layer 3 Switch distributes traffic across equal-cost paths based on destination network
address. The software selects a path based on a calculation involving the maximum number of load-sharing
paths allowed and the actual number of paths to the destination network. This method is available only on
chassis Layer 3 Switches and is the default.
In addition, on chassis Layer 3 Switches you can use network-based load sharing as the default while configuring
host-based load sharing for specific destination networks. When you configure host-based load sharing for a
specific destination network, the Layer 3 Switch distributes traffic to hosts on the network evenly across the
available paths. For other networks, the Layer 3 Switch uses a single path for all traffic to hosts on a given
network.
NOTE: Regardless of the method of load sharing that is enabled, the Layer 3 Switch always load shares paths
for default routes and the network default route based on destination host address.
Path Redundancy
If a path to a given destination becomes unavailable, the Layer 3 Switch provides redundancy by using another
available equal-cost path to the destination, as described in the following sections.
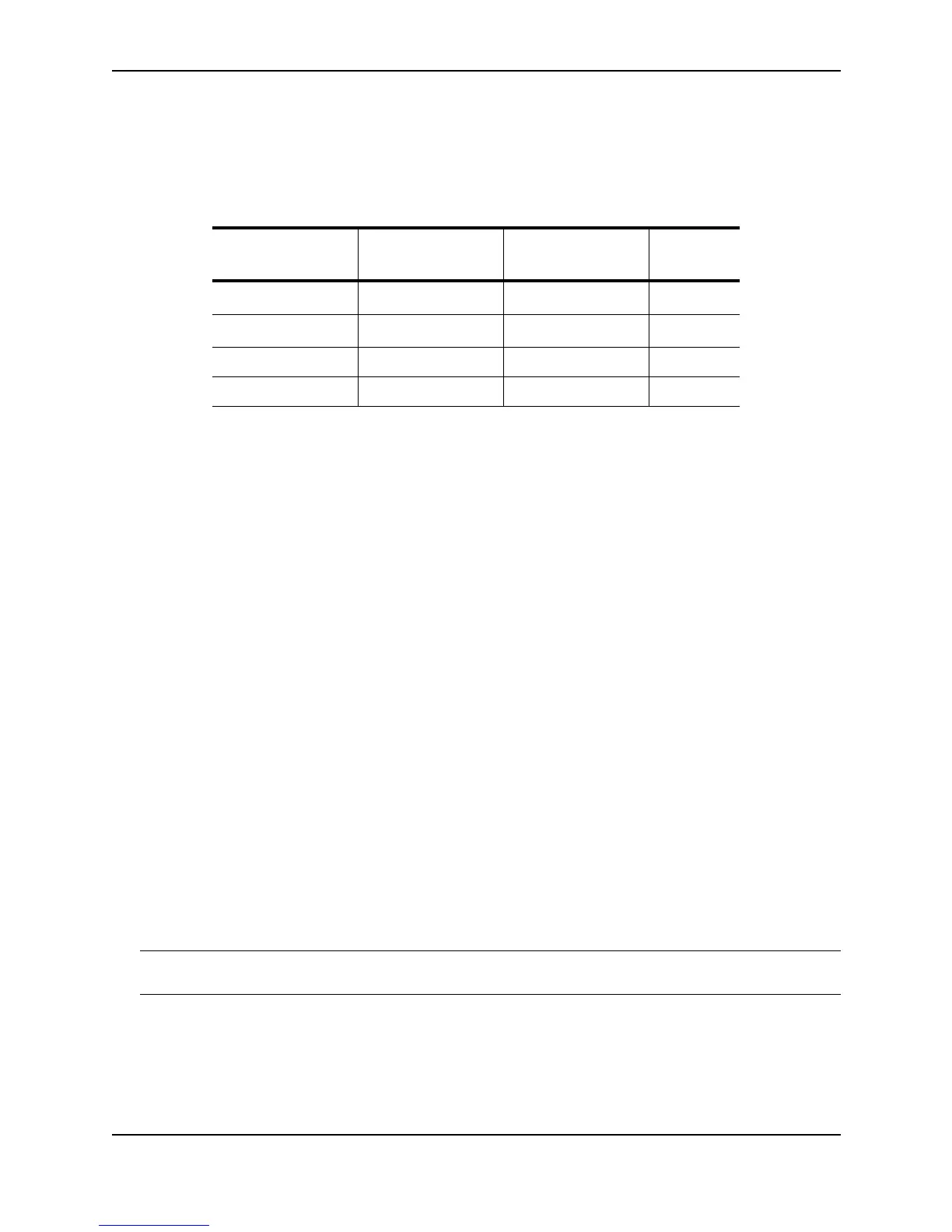
Table 15.6: Default Load Sharing Parameters for Route Sources
Route Source Default Maximum
Number of Paths
Maximum Number
of Paths
See...
Static IP route
4
a
a.This value depends on the value for IP load sharing, and is not separately
configurable.
8
a
15-62
RIP
4
a
8
a
15-62
OSPF 4 8 15-62
BGP4 1 4 19-28
 Loading...
Loading...