December 2000 A - 1
Appendix A
Protecting Against Denial of Service Attacks
In a Denial of Service (DoS) attack, a router is flooded with useless packets, hindering normal operation. Foundry
devices include measures for defending against two types of DoS attacks: Smurf attacks and TCP SYN attacks.
Protecting Against Smurf Attacks
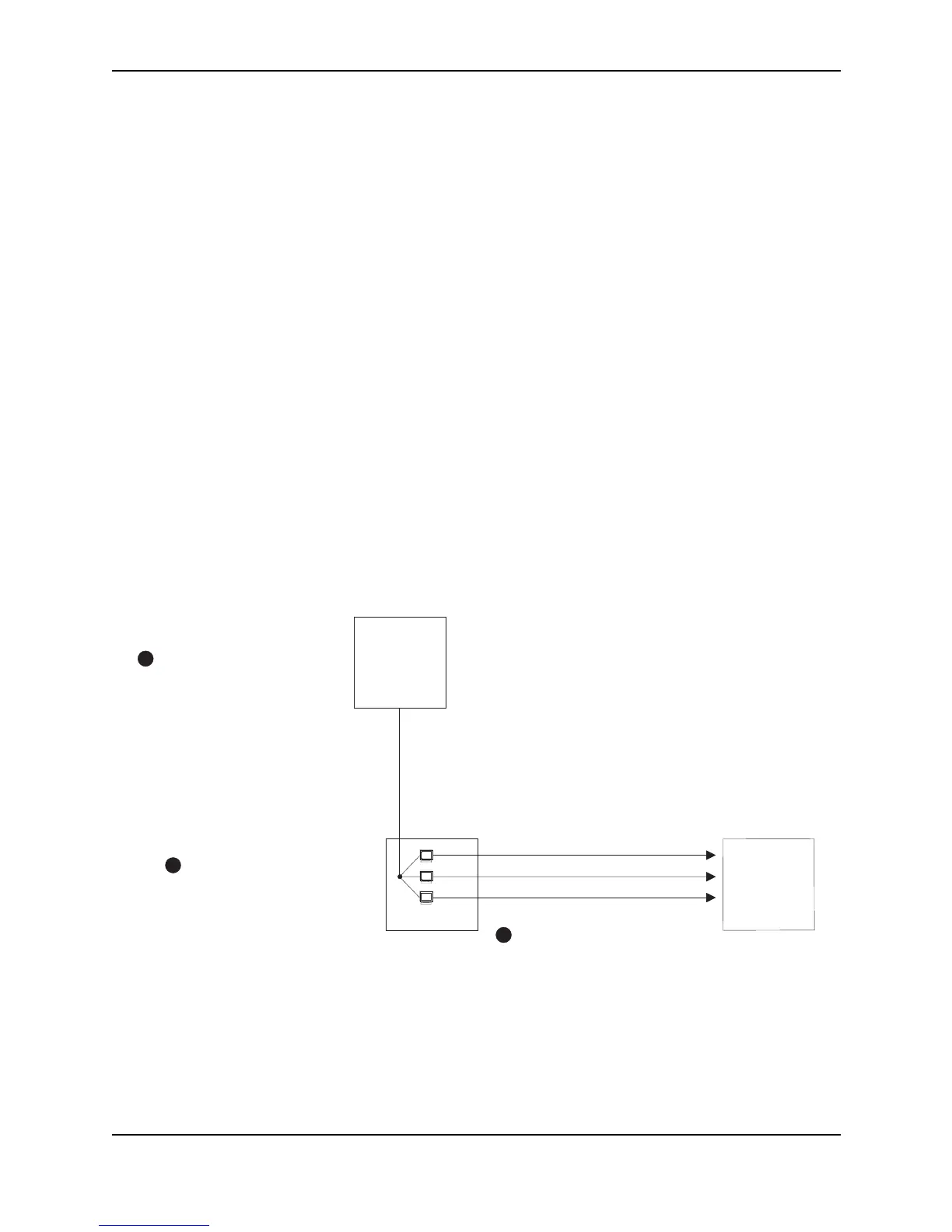
A Smurf attack is a kind of DoS attack where an attacker causes a victim to be flooded with ICMP echo (Ping)
replies sent from another network. Figure A.1 illustrates how a Smurf attack works.
Figure A.1 How a Smurf attack floods a victim with ICMP replies
The attacker sends an ICMP echo request packet to the broadcast address of an intermediary network. The ICMP
echo request packet contains the spoofed address of a victim network as its source. When the ICMP echo
request reaches the intermediary network, it is converted to a Layer 2 broadcast and sent to the hosts on the
intermediary network. The hosts on the intermediary network then send ICMP replies to the victim network.
Intermediary
Victim
1
Attacker sends ICMP echo requests to
broadcast address on Intermediary’s
network, spoofing Victim’s IP address
as the source
If Intermediary has directed broadcast
forwarding enabled, ICMP echo requests
are broadcast to hosts on Intermediary’s
network
2
The hosts on Intermediary’s network
send replies to Victim, Victim
with ICMP packets
inundating
3
Attacker
 Loading...
Loading...