Appendix 9 Definitions
A 14
Appendix 9 Definitions
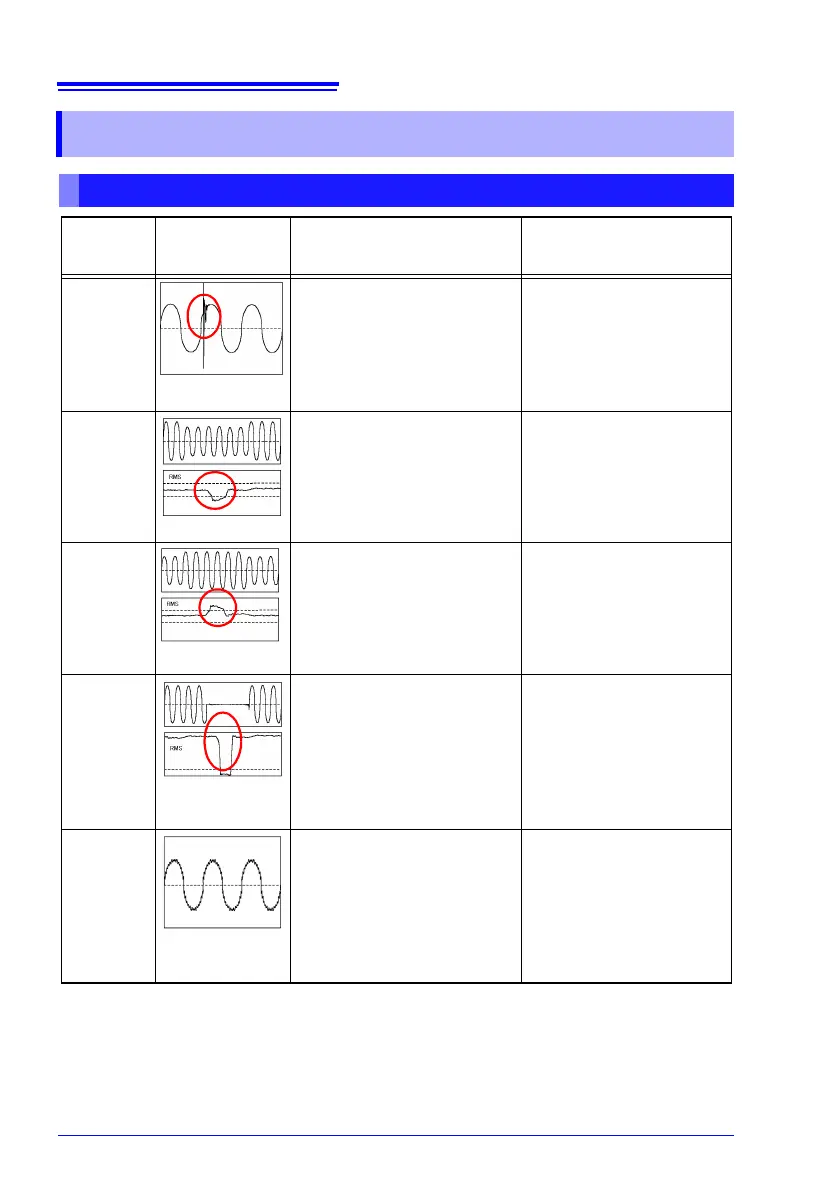
Detecting Anomalies and Phenomena Due to Drops in Power Quality
Power
Quality
Parameter
Waveform Display
Phenomenon Related Malfunctions
Transient
Overvoltage
(Impulse)
Occurs typically as a result of
lightning, circuit breaker trip-
ping, fouled relay contacts or
l
oad shutdown.
Many cases exhibit abrupt
v
oltage changes and high peak
voltage.
Near the source of the phe-
nomena, power devices may
s
ustain damage or opera-
tions reset abruptly because
of
the especially high volt-
age.
Voltage Dip
(Sag)
As a result of large inrush
current to a load such as a
motor starting up, a brief voltage
dip occurs.
Equipment may unexpected-
ly stop or reset due to low
su
pply voltage.
Voltage
Swell
(Surge)
Instantaneous voltage
increases that may occur as a
result of lightning strikes,
switching of heavily loaded
power lines and other loads.
Damage to the power or re-
set operations of equipment
ma
y result from rising supply
voltage.
Interruption
The power source may shut off
momentarily or for a short or
long term such as from tripping
of a circuit breaker, often as a
result of power company acci-
dent (electric supply interrupted
by
a lightning strike, etc.) or
from power system short circuit.
The recent popularity of UPS
(
uninterruptible power sup-
plies) has increased protec-
tion for computers and other
eq
uipment, although inter-
ruptions can still cause de-
vices to shut down or reset.
Harmonics
Cases commonly occur when a
semiconductor control system is
employed to power equipment,
where harmonics occur as a re-
uslt of distortion of voltage and
cu
rrent waveforms.
When harmonic contents be-
come large, major accidents
s
uch as resulting from abnor-
mal heating of motors and
tr
ansformers or burn out of
reactances connected to
leading-phase capacitors
may occur.

 Loading...
Loading...