252 N9030B PXA Signal Analyzer Service Guide
LO Synthesizer/Reference Troubleshooting
A14 LO Synthesizer Theory of Operation
synthesizer output drives the LO port of a mixer. The 1st LO from the A13A1
Front End drives the RF port of the mixer. The signal at the IF port, which
should be between 33 and 55 MHz (or between 78 and 88 MHz), drives the
phase/frequency detector.
The fractional-N divider drives the other input of the phase/frequency detector
which then feeds the loop integrator which then drives the YTO Main and FM
Coil Drivers.
Similar to the single-loop mode, there are two types of dual-loop modes;
dual-loop narrowband and dual-loop wideband. The dual-loop narrowband
mode provides lower phase noise at offsets greater than approximately 160
kHz.
To maintain the best span accuracy, dual loop spans between 2.5 MHz and 10
MHz are actually comprised of two to four individual spans that are then
“cut-and-pasted” together to yield the desired span.
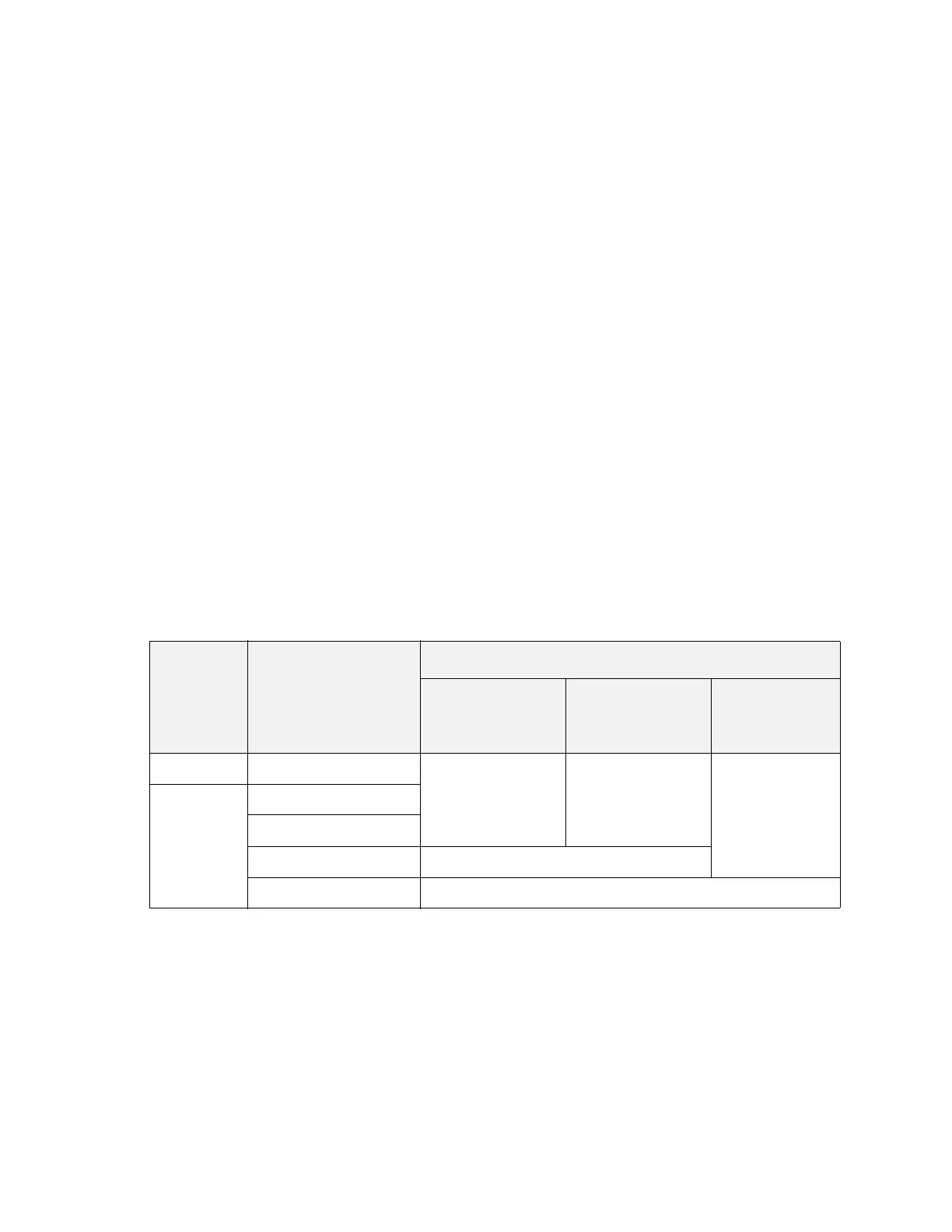
Manual Selection of Single versus Dual Loop Operation
The table below shows how the selections of Phase Noise Optimization, sweep
type, and span affects the selection of single-loop versus dual-loop operation.
Note that this table assumes the RBW is auto coupled. If the span is <= 10 MHz
(or zero span) and the RBW is manually set to >1.9 MHz, the synthesizer will be
set to single-loop operation.
Refer to the Phase Noise Optimization topic in the Spectrum Analyzer Mode
User's and Programmer's Reference for details on the autocoupled selections.
Table 8-1
Sweep Type Span
(with autocoupled RBW)
Phase Noise Optimization Setting
Best Close-In Phase
Noise
(offset < 140 kHz)
Best Wide-Offset
Phase Noise
(offset > 160 kHz)
Fast Tuning
FFT All Dual-Loop,
Wideband
a
Dual-Loop,
Narrowband
a
Single-Loop,
Wideband
Swept 0 Hz
≤ 10 MHz
>10 to ≤ 100 MHz Single-Loop, Narrowband
> 100 MHz Single-Loop, Wideband
a. Single-Loop, Narrowband if RBW is manually set to > 1.9 MHz

 Loading...
Loading...











