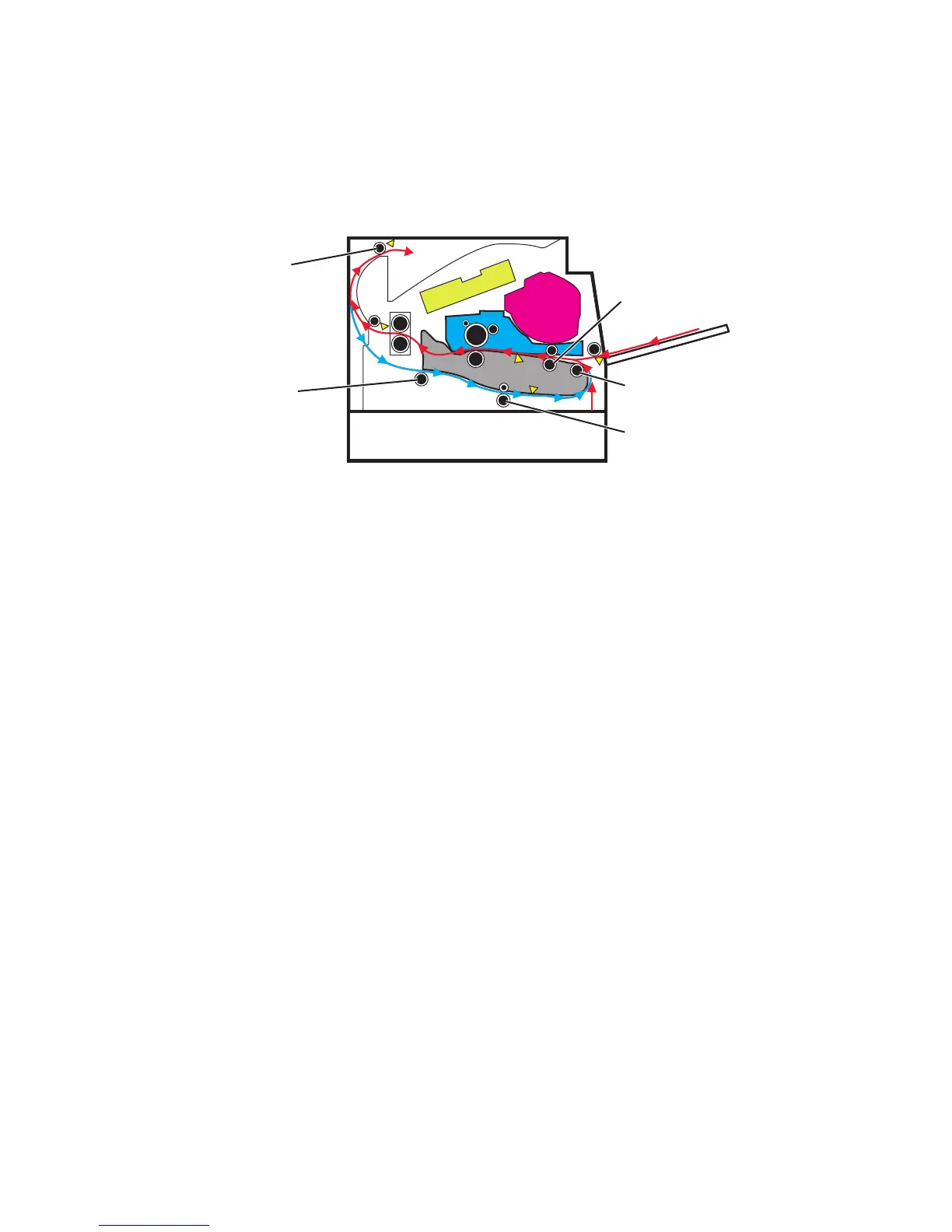
Duplex printing
After the first side of the media has been printed on and is partially fed out to the output bin, the duplex solenoid
activates. This causes the exit roller to reverse its rotation and feed the media, with its trailing edge first, back into the
redrive assembly and then to the duplex paper path. The duplex front and rear deliver rollers move the media through
the duplex paper path, the diverter, the first input roller, and back to the primary paper path. The same process for
printing on the first side of the media repeats, this time for the second side of the media.
Secondary input
roller
First input roller
Duplex front
deliver roller
Duplex rear
deliver roller
Paper exit
roller
Media handling components
Main drive gearbox
The gearbox supplies all mechanical power requirements of the printer. Its motor, through several gears, transfers
power to following paths: photoconductor drum, transfer roll, fuser, paper exit, input, duplex, and MPF.
Aside from providing rotational motion to rollers and feeders, the gearbox must also ensure that the print image is not
distorted during the whole process. It must also provide easy and effective means to cut or break the transfer of motion
when taking the cartridge unit out of the machine, or when clearing jammed sheets through its linkage system.
Autocompensator mechanism (ACM)
The fundamental function of the ACM is to pick and feed a single sheet of media and accurately deliver it to the
downstream paper path. The pick arm is counterbalanced to provide a priming force throughout the entire range of
paper levels in the tray. When media is picked, a subsequent sheet is not picked until the previous sheet's trailing edge
is detected by the trailing edge sensor. Once the trailing edge of the media is detected, and the minimum interpage
gap is satisfied, the next sheet will be picked.
4514-420, -430
Appendix C: Theory of operation
247

 Loading...
Loading...