5 Understanding Programming
5-58
CJ2 CPU Unit Software User’s Manual
When using CX-Programmer version 9.0 or higher with a CJ2 CPU Unit, you can create data structures
as user-defined data types.
z Data Structures
A data structure is a user-defined data type that groups more than one data type. Names can be
assigned to the data types. The name of the variable that uses a user-defined data type is specified
along with the name of one of the variables within the data structure. The overall data structure is
called a structure variable and the variables within the data structure are called members.
Additional Information
• Arrays can also be used to handle multiple pieces of data. An array data type, however, is dif-
ferent from a data structure in that it contains data with the same data type that is accessed by
specifying an offset from the beginning of the array. With a data structure, data with the same
or with different data types is accessed using member names. Also, with the CX-Programmer,
structure data types can be assigned names.
• Structure variables can be placed in arrays.
• Also, array variables can be used as members of data structures.
z Ladder Program Notation and Input for Structure Variables
In a Ladder Program, the structure variable name and member name are separated by a period.
z Applications of Data Structures
When you specify data that is grouped, you specify a member of a specific group. In other words,
you can specify data in a hierarchy in the form “main - sub.”
Using Data Structures without Arrays
User-defined Data Types (Data Structures)
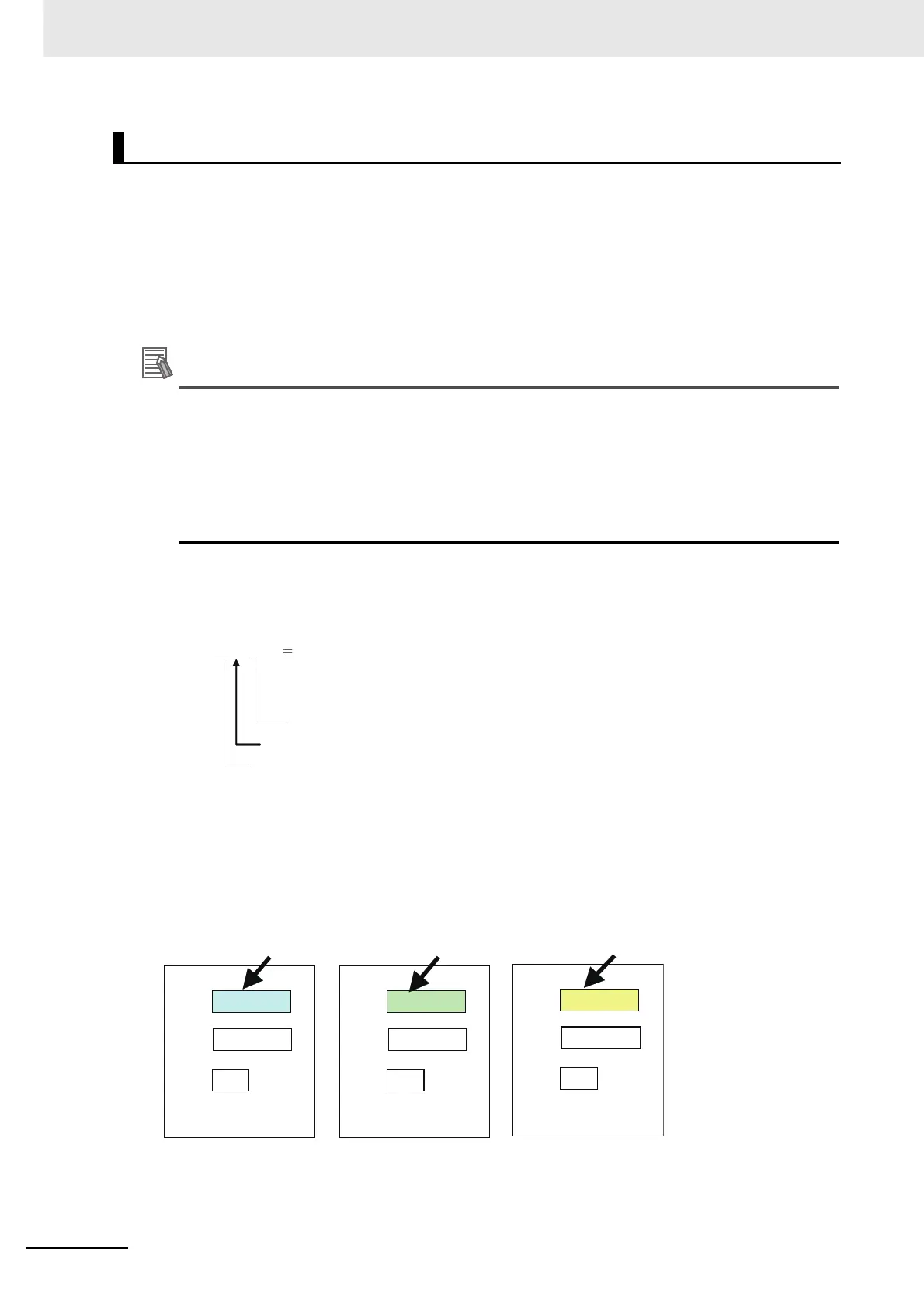
Example:
S1
. A
Structure variable name
Period
Member name
Means "member A of S1."
C
A
B
C
C
A
B
C
C
A
B
C
Example for Structure Variables S1, S2, and S3 Each with Members A, B, and C
Structure variable S1
Structure variable S2
Structure variable S3
A of S1 A of S2
A of S3
Member
Member
Member
 Loading...
Loading...











