4.35
ELECTRONIC FUEL INJECTION
4
9924096 - 2013 RANGER RZR XP 900 / RZR XP 4 900 Service Manual
© Copyright 2012 Polaris Sales Inc.
IGNITION COIL
Operation Overview
The ignition coil is used to provide high voltage to fire the
spark plugs. When the ignition key is on, DC voltage is
present in the primary side of the ignition coil windings.
During engine rotation, an AC pulse is created within the
crankshaft position sensor for each passing tooth on the
flywheel’s encoder ring. The encoder ring missing tooth
creates an “interrupt” input signal, corresponding to
specific crankshaft position. This signal serves as a
reference for the control of ignition timing. The ECU then
calculates the time interval between the consecutive
pulses, and determines when to trigger the voltage spike
that induces the voltage from the primary to the secondary
coil windings to fire the spark plugs.
Ignition Coil / HT Lead Replacement
IMPORTANT: The engine will misfire if the spark plug
wires are installed incorrectly. The spark plug wires
are marked with PTO and MAG from the factory and
should be installed to the corresponding cylinder and
ignition coil post.
1. Remove the seats and engine service panel to
access the ignition coil.
2. Disconnect the ignition coil harness and remove the
high tension leads from the coil.
3. Remove the fastener retaining the ignition coil and
remove it from the vehicle. If replacing the high
tension lead(s), remove the other end of the lead(s)
from the spark plug.
4. Install the new ignition coil and/or high tension lead(s).
Ignition Coil Tests
The ignition coil can be tested by using an ohm meter. Use
the following illustration and specification table to test the
ignition coil resistance.
Primary Test
Secondary Test
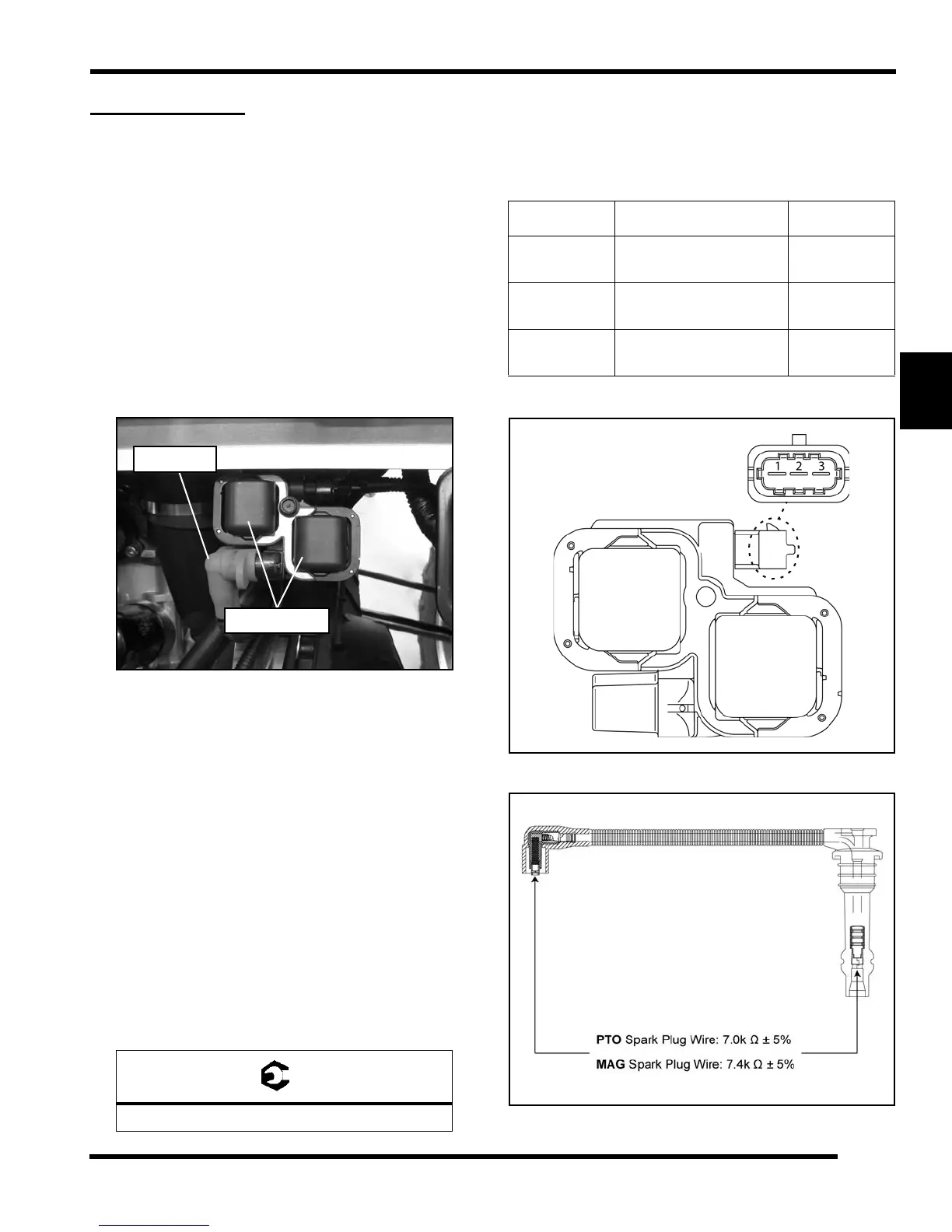
Ignition Coil Retaining Bolt: 75 in-lbs (8.5 Nm)
Test Pin Connection Resistance
Primary
Between 1 & 2
Between 2 & 3
0.4
Secondary
(PTO)
Between High Tension
Lead Caps
7.0k ± 5%
Secondary
(MAG)
Between High Tension
Lead Caps
7.4k ± 5%
Measure Between
Connector Pins
0.4

 Loading...
Loading...











