184 CHAPTER 5 Working with J-Link and J-Trace
J-Link / J-Trace (UM08001) ©
2004-2017 SEGGER Microcontroller GmbH & Co. KG
The target device is marked in blue.
5.3.4 JTAG Speed
There are basically three types of speed settings:
• Fixed JTAG speed.
•Automatic JTAG speed.
• Adaptive clocking.
These are explained below.
5.3.4.1 Fixed JTAG speed
The target is clocked at a fixed clock speed. The maximum JTAG speed the target can
handle depends on the target itself. In general CPU cores without JTAG synchroniza-
tion logic (such as ARM7-TDMI) can handle JTAG speeds up to the CPU speed, ARM
cores with JTAG synchronization logic (such as ARM7-TDMI-S, ARM946E-S,
ARM966EJ-S) can handle JTAG speeds up to 1/6 of the CPU speed.
JTAG speeds of more than 10 MHz are not recommended.
5.3.4.2 Automatic JTAG speed
Selects the maximum JTAG speed handled by the TAP controller.
Note: On ARM cores without synchronization logic, this may not work reliably,
because the CPU core may be clocked slower than the maximum JTAG speed.
5.3.4.3 Adaptive clocking
If the target provides the RTCK signal, select the adaptive clocking function to syn-
chronize the clock to the processor clock outside the core. This ensures there are no
synchronization problems over the JTAG interface.
If you use the adaptive clocking feature, transmission delays, gate delays, and syn-
chronization requirements result in a lower maximum clock frequency than with non-
adaptive clocking.
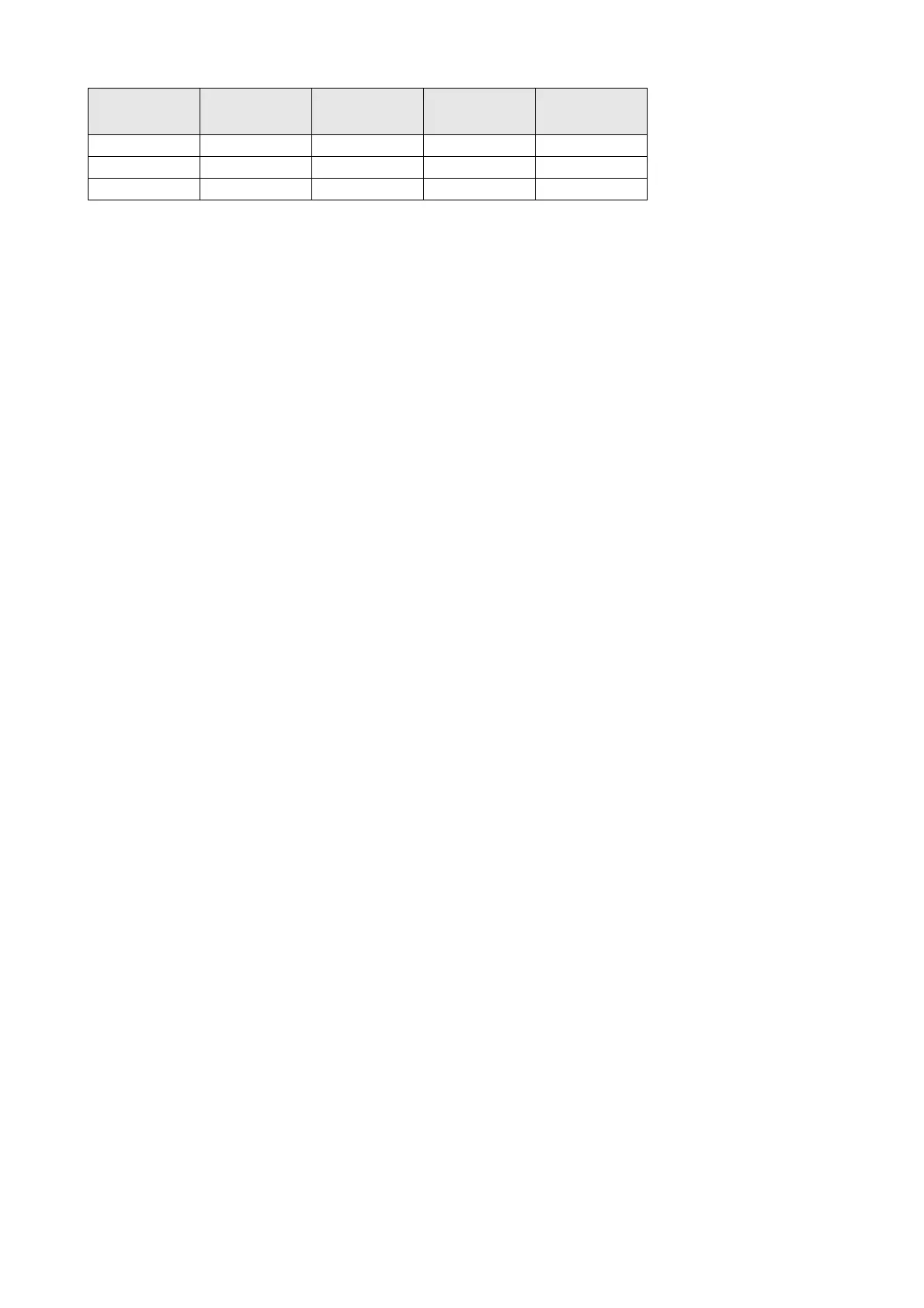
ARM(4) Xilinx(8) ARM(4) 0 0
ARM(4) Xilinx(8) ARM(4) 212
Xilinx(8) ARM(4) Xilinx(8) 1 8
Device 0
Chip(IR len)
Device 1
Chip(IR len)
Device 2
Chip(IR len)
Position IR len
Table 5.5: Example scan chain configurations
 Loading...
Loading...