3.2.2 Main Oscillator Fail Detection
VCOCLK
counter
(13bits)
Clear ResClear
OSCCLK
Clear
(7bits)
counter
Res Clear
OvfClk
XRS
PLL
Clk Ovf
Off
Clear
OSCCLK
Clock
switch
logic
VCOCLK
C28x
CPU
Missing
clock
reset
PLLCLK
/1,
/2
or
/4
PLLSTS
reg
PLLCR
reg
C28x
CPU
OSC and PLL Block
www.ti.com
Table 3-7. Possible PLL Configuration Modes
PLL Mode Remarks PLLSTS[DIVSEL]
(1)
SYSCLKOUT
PLL Off Invoked by the user setting the PLLOFF bit in the PLLSTS register. The 0, 1 OSCCLK/4
PLL block is disabled in this mode. This can be useful to reduce system 2 OSCCLK/2
noise and for low power operation. The PLLCR register must first be set 3 OSCCLK/1
to 0x0000 (PLL Bypass) before entering this mode. The CPU clock
(CLKIN) is derived directly from the input clock on either X1/X2, X1 or
XCLKIN.
PLL Bypass PLL Bypass is the default PLL configuration upon power-up or after an 0, 1 OSCCLK/4
external reset ( XRS). This mode is selected when the PLLCR register is 2 OSCCLK/2
set to 0x0000 or while the PLL locks to a new frequency after the 3 OSCCLK/1
PLLCR register has been modified. In this mode, the PLL itself is
bypassed but the PLL is not turned off.
PLL Enabled Achieved by writing a non-zero value n into the PLLCR register. Upon 0, 1 OSCCLK*n/4
writing to the PLLCR, the device will switch to PLL Bypass mode until 2 OSCCLK*n/2
the PLL locks.
(1)
PLLSTS[DIVSEL] must be 0 before writing to the PLLCR and should be changed only after PLLSTS[PLLLOCKS] = 1. See
Figure 3-10 .
Due to vibrations, it is possible for the external clock source to the DSP to become detached and fail to
clock the device. When the PLL is not disabled, the main oscillator fail logic allows the device to detect
this condition and default to a known state as described in this section.
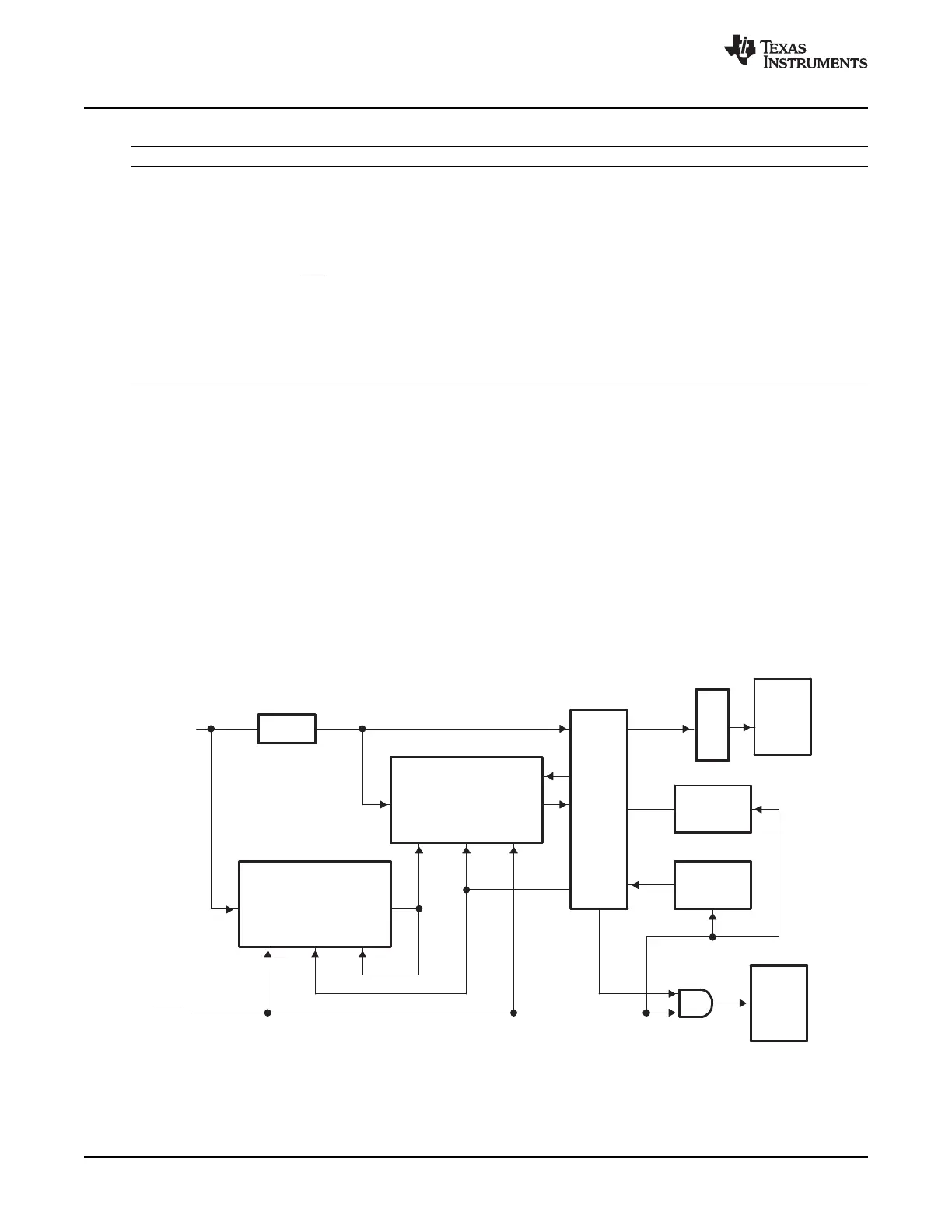
Two counters are used to monitor the presence of the OSCCLK signal as shown in Figure 3-8 . The first
counter is incremented by the OSCCLK signal itself either from the X1/X2 or XCLKIN input. When the PLL
is not turned off, the second counter is incremented by the VCOCLK coming out of the PLL block. These
counters are configured such that when the 7-bit OSCCLK counter overflows, it clears the 13-bit VCOCLK
counter. In normal operating mode, as long as OSCCLK is present, the VCOCLK counter will never
overflow.
Figure 3-8. Oscillator Fail-Detection Logic Diagram
46 Clocking SPRUFB0C – September 2007 – Revised May 2009
Submit Documentation Feedback

 Loading...
Loading...