Chapter 10
202
UM10350_PCNC770_Manual_0916A
Troubleshooting
Axes Drive Subsystem Checklist
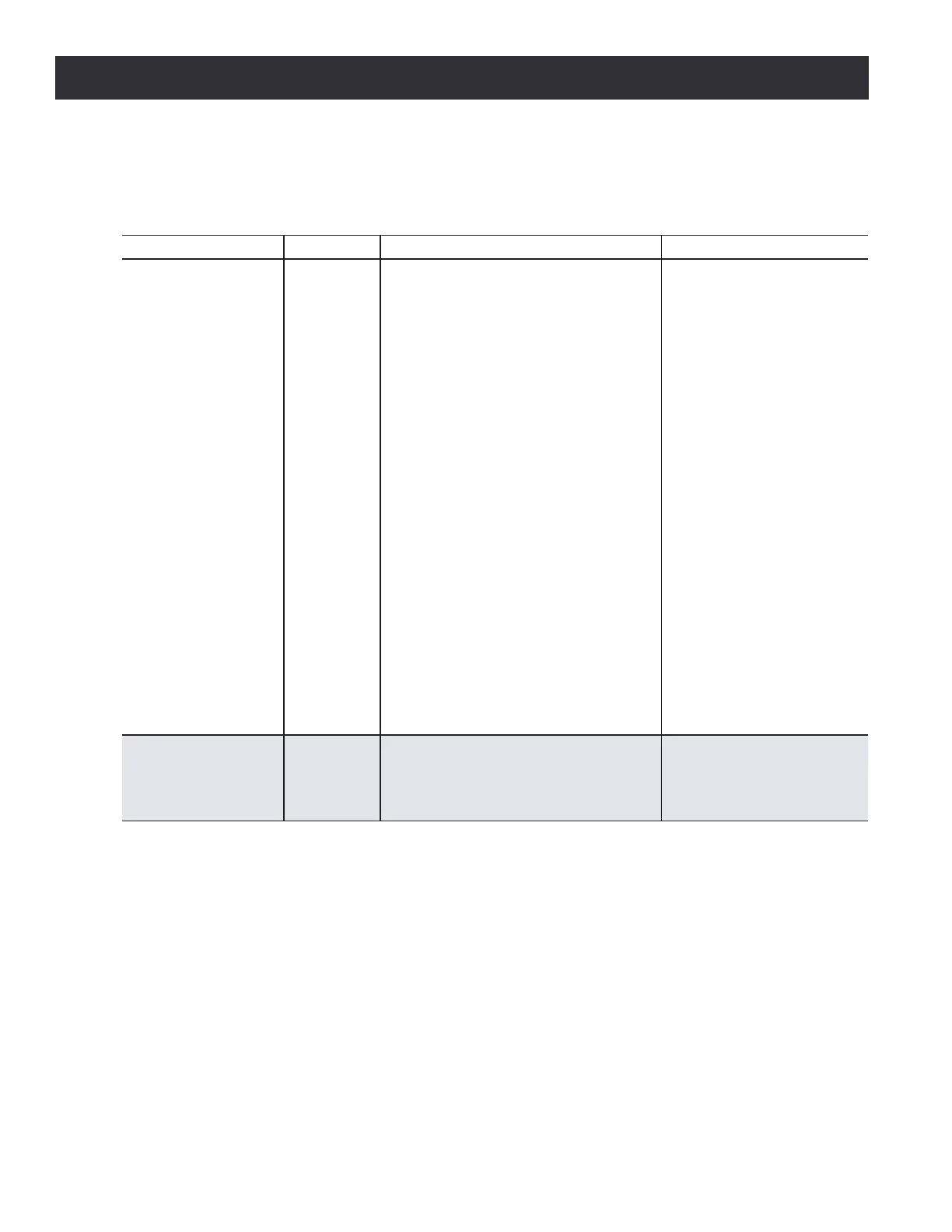
Table 4.8 — Steps are lost on axis travel
NOTE: Consult Table 4.2 and 4.5 for more information on lost steps.
Possible Cause Probability
Action to Identify Cause of Problem
Discussion
Obstruction or
excessive friction
(gibs not adjusted
properly or poor
lubrication) or
high load in the
mechanical system
Low
Jog the axis with the jog/shuttle control
and carefully observe the motion.
If you lose steps, it is
normally many steps. You
should be able to hear the
motor cogging; mechanical
issues most often result
in losing a large number
of steps or stalling. Typical
mechanical issues include
an increase in friction due
to lack of oil at the way
surfaces or ball screw and/
or improperly adjusted
gibs. They also come from
excessive load on the system
due to chips or debris on the
way surfaces or ball screw,
a sticking Z-axis brake, or
an end-of-travel bumper
wedged against the motor
mount casting. This occurs
sometimes after a limit
switch failure and is more
common on the Z-axis.
Axis drivers have
wrong DIP
switch settings
Low
See electrical schematic in the back of
this manual. Note that new axis drivers
will require the operator set these DIP
switches at installation.
—
10.5.4.2 Details of Axis Drive Subsystem
Axis drivers are mounted in the electrical cabinet le to right in the sequence X, Y, Z, A. Moon for
the X-, Y-, Z-, and oponally the A-axis are provided by DC axis motors. Each motor is powered by an
electronic driver module. The driver module receives nominal 65 VDC power from the DC bus board
and receives control signals from the control board which processes and formats informaon sent
by the controller. Find the relevant poron of the electrical schemac highligted in Figure 10.14 and
Figure 10.15. For more detail, view electrical schemac inside back cover.
When control power is on, contacts from contactor C1 pass the nominal 120 VAC input power to the
DC bus power transformer. The transformer reduces the voltage to a nominal 48VAC which is sent
to the DC bus board on wires 161 and 162.
(...connued)
 Loading...
Loading...