Theory of Operation
2-13
A read/write transaction consists of the following processes:
• The reader modulates a message to all tags until it receives a response from a sin-
gle tag that has been activated by the reader message
• The reader communicates with that individual tag by using the tag’s unique identi-
fication.
• The reader retrieves data from any of that tag’s memory location, and can also
write data to any of that tag’s memory locations.
This process is called read/write because the reader needs to write a message to the tag
to obtain a response. The reader can then write data to memory also, if required.
A read/write transaction is more complicated because not only does it entail commu-
nication between the tag and a reader, but the reader can also modify information that
is stored in the tag memory.
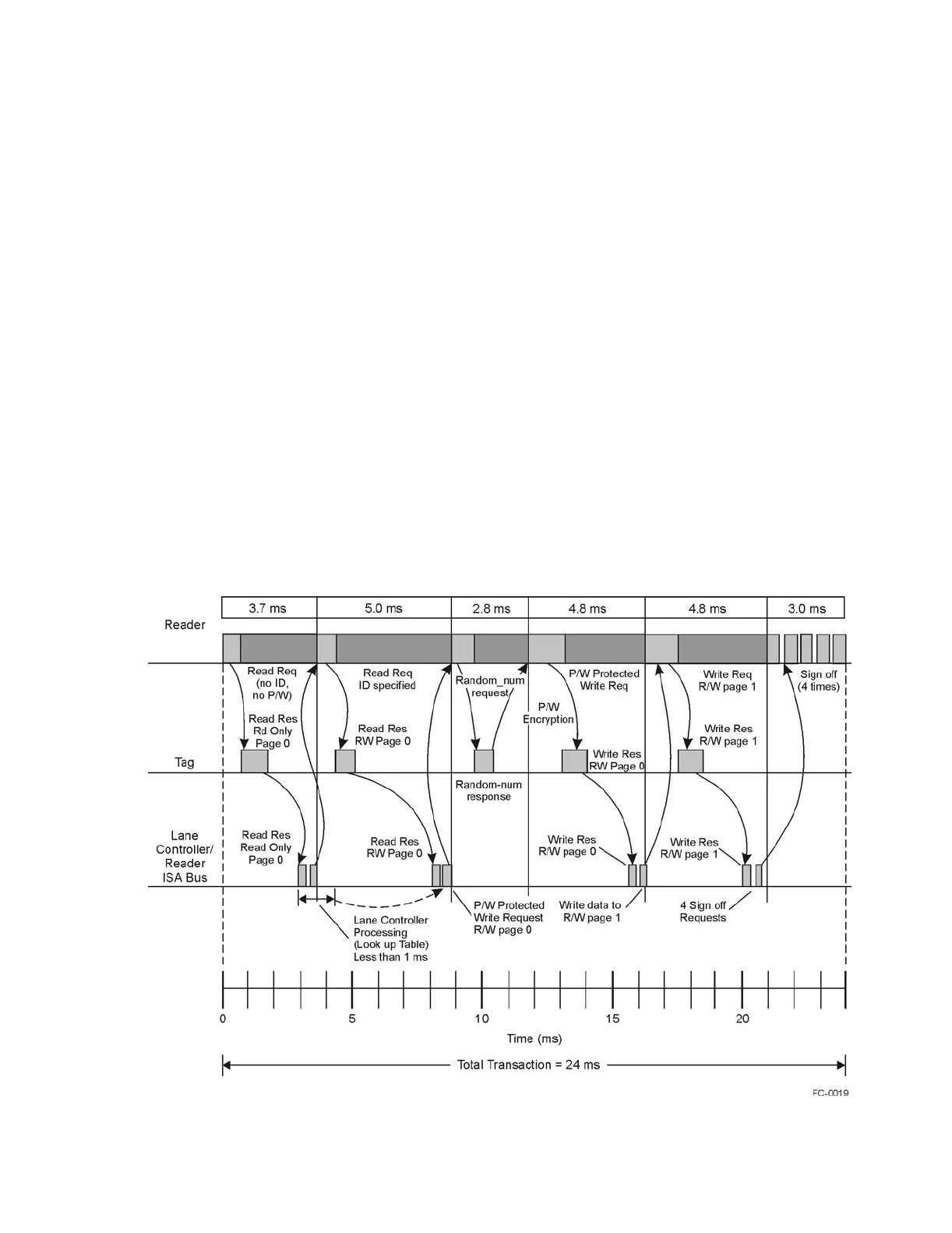
The total transaction time for this RFID system is less than one-tenth of a second.
Within that timeframe, a number of transactions occur. Figure 2-5 shows a timeline
for a representative read/write transaction using the IT2200 Reader System with Mul-
timode Capability and an IT2200-series tag that is controlled by an IT2200 reader
with multimode capability housed in a lane controller.
Figure 2-5 Typical Read/Write Transaction Using the IT2200 Reader System and
an IT2200-series Tag
 Loading...
Loading...