Rockwell Automation Publication 1769-UM022C-EN-P - June 2018 77
Communicate Over Networks Chapter 5
EtherNet/IP Network Connections
Compact GuardLogix 5370 controllers use connections to manage
communication on the EtherNet/IP network. A connection is a point-to-point
communication mechanism that is used to transfer data between a transmitter
and a receiver. Connections can be logical or physical.
You indirectly determine the number of connections the controller uses by
configuring the controller to communicate with other devices in the system.
Connections are allocations of resources that provide more consistent
communication between devices than unconnected messages.
All EtherNet/IP connections are unscheduled. An unscheduled connection is a
message transfer between controllers that the requested packet interval (RPI)
or the program, such as a MSG instruction, triggers. Unscheduled messaging
lets you send and receive data when needed.
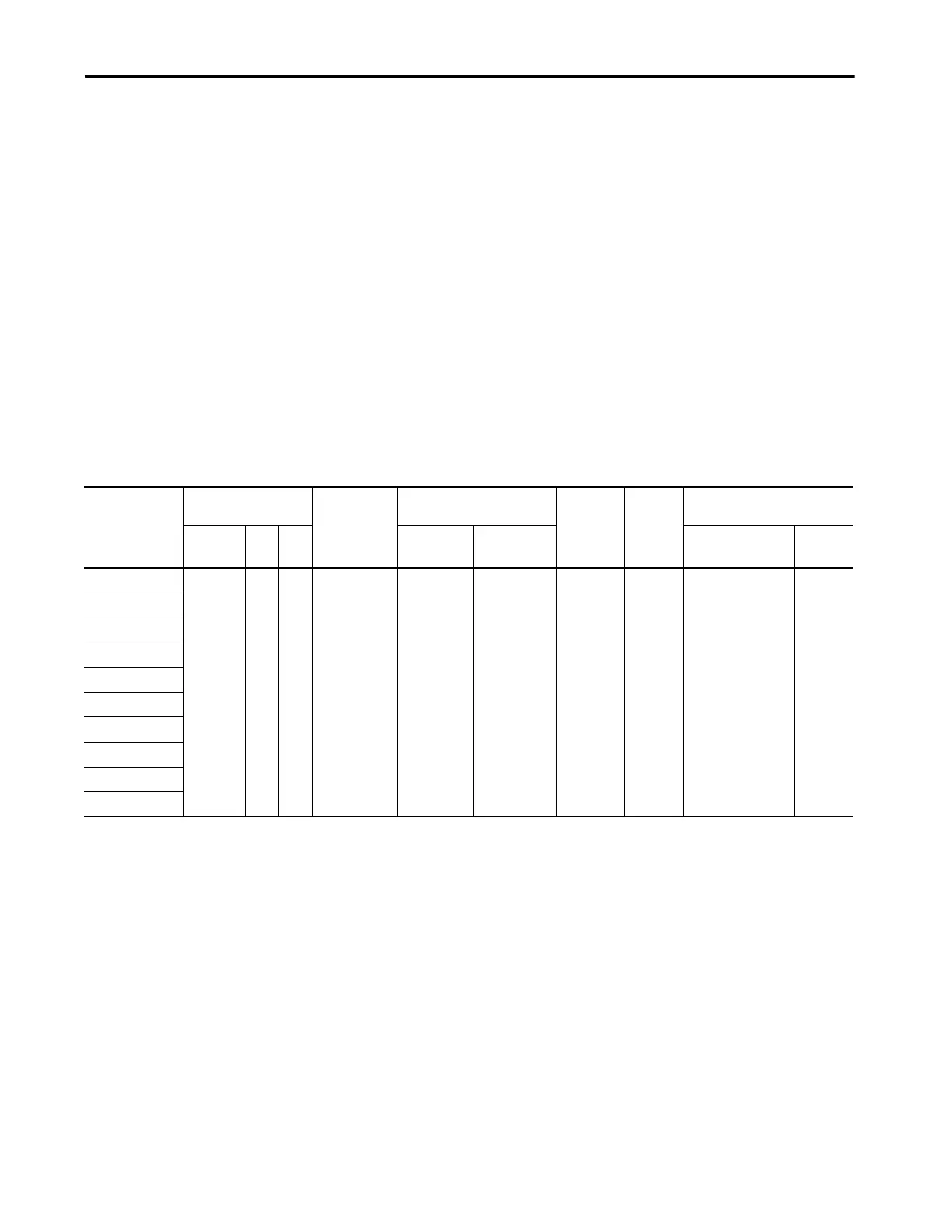
Table 8 - Compact GuardLogix 5370 Controller EtherNet/IP Network Port Specifications
Socket Interface
The Compact GuardLogix 5370 controller can use socket interfaces to
communicate with Ethernet devices that do not support the EtherNet/IP
application protocol.
Examples of devices that do not support the EtherNet/IP application protocol
but can be used in a Compact GuardLogix 5370 controller application include
the following:
•Modbus TCP/IP device
Cat. No.
Connections
CIP
Unconnected
Messages
(backplane +
Ethernet)
Packet Rate Capacity
(packets/second)
(2)
SNMP
Support
(password
required)
Media
Support
Produced/Consumed Tags
Controller TCP CIP I/O HMI/MSG
Number of Multicast
Tags, max
(3)
Unicast
Available
1769-L30ERMS 256 120 256 256 6000 @ 500
bytes/packet
400 messages/
second @ 20%
comm. timeslice
Yes Twi sted
pair
•32 multicast
produced tags
•128 unicast
produced tags
Yes
1769-L33ERMS
1769-L33ERMSK
1769-L33ERMOS
1769-L36ERMS
1769-L36ERMOS
1769-L37ERMS
(1)
1769-L37ERMOS
(1)
1769-L38ERMS
(1)
1769-L38ERMOS
(1)
(1) Available at firmware revision 31.
(2) Total packet rate capacity = I/O Produced Tag, max + HMI/MSG, max Packet rates vary depending on packet size. For more detailed specifications, see the capacity section of the EDS file for the
catalog number.
(3) These are the maximum numbers of CIP I/O connections.

 Loading...
Loading...











