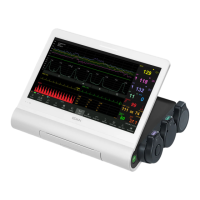
F15 Series Fetal & Maternal Monitor User Manual After Monitoring
- 107 -
deflates from above systolic pressure. The amplitude suddenly increases as the pulse breaks through
the occlusion in the artery. As the cuff pressure decreases further, the pulsations increase in amplitude,
reach a maximum (which approximates to the mean artery pressure), and then diminish.
There are two modes available: Manual and Auto. In manual mode, NIBP is measured once on each
demand. In auto mode, NIBP is measured repeatedly after a preset time interval. This interval is
adjustable. You can perform a manual measurement during an Auto measurement interval.
In both modes, systolic pressure (SYS), diastolic pressure (DIA), mean artery pressure (MAP) and
pulse rate (PR) (optional) are measured and displayed.
The blood pressure measurements determined with this device comply with the American National
Standard for Electronic or Automated Sphygmomanometers (ANSI/AAMI/ISO 81060-2:2013) in
relation to mean error and standard deviation.
In clinical investigation method with a reference sphygmomanometer, the fifth Korotkoff sound was
used to determine adult diastolic pressure, and the fourth Korotkoff sound was used to determine
pediatric diastolic pressure.
WARNING
1 Check for any fault of the cuff before start monitoring.
2 Do not perform NIBP measurements on patients with sickle-cell disease or under any
condition where the skin is damaged or expected to be damaged, such as on the arm on the
side of a mastectomy.
3 Pressurization of the cuff can temporarily cause loss of function of simultaneously used
monitor on the same limb.
4 If liquid is splashed on or into the main unit inadvertently, or enters the conduit, stop using
the monitor and contact the manufacturer for service immediately.
5 For a thrombasthemia patient, it is important to determine whether the measurement of
blood pressure shall be done automatically. The determination should be based on clinical
evaluation.
6 Do not apply the cuff to a limb that has an intravenous infusion or catheter in place
frequently. This could cause tissue damage around the catheter when infusion is slowed or
blocked during cuff inflation.
7 Do not apply the cuff to a limb where intravascular access or therapy, or an arterio-venous
(A-V) shunt is present, otherwise, it may result in injury to the patient.
8 NIBP readings can be affected by the measurement site, the position of the patient,
exercise, or the patient's physiologic conditions.
9 Continuous cuff pressure due to connection tubing kinking can block the blood flow, and
may result in injury to the patient.
10 Make sure that the air conduit connecting the blood pressure cuff and the monitor is
neither blocked nor tangled.
NOTE:
1 The monitor is intended to measure NIBP for adults only.
2 NIBP measurement can be affected by extremes of temperature, humidity and altitude.
3 Continuous use of the automatic measuring mode for short intervals may lead to the
discomfort of the patient.
4 If a NIBP measurement is suspected, repeat the measurement. If you are still uncertain
about the reading, use another method to measure the blood pressure.
Measurement Limitations -
Traditional 510(k) of Fetal & Maternal Monitor
014_14.1_F15_Series_User_Manual
 Loading...
Loading...