Foundry Configuration Guide for the FESX, FSX, and FWSX
11 - 54 © Foundry Networks, Inc. December 2005
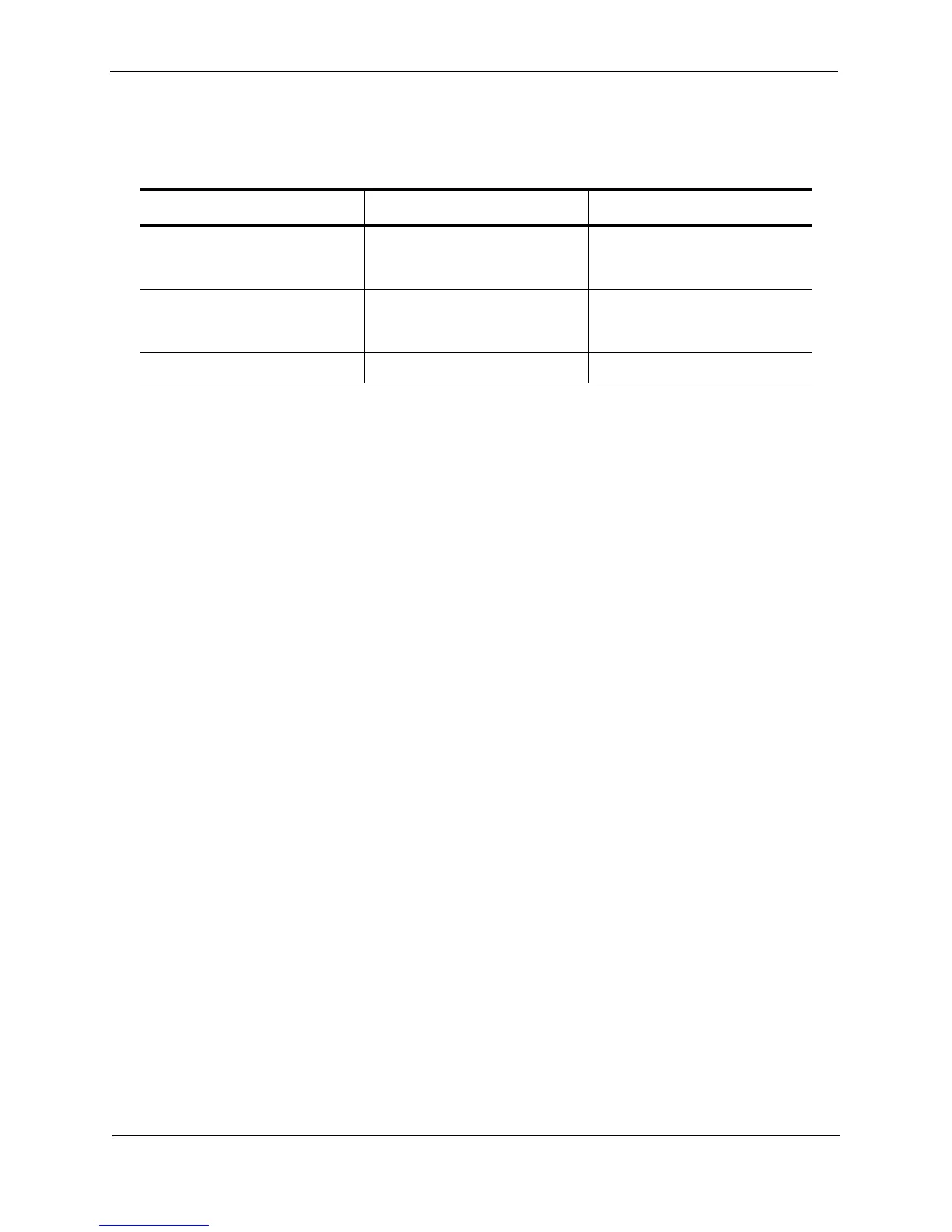
Table 11.3 list the differences between private VLANs and standard VLANs.
Implementation Notes
• Private VLANs are supported starting in software release 02.4.00. Releases 02.4.00 and later support
private VLANs on untagged ports only. You cannot configure isolated, community, or primary VLANs on
802.1Q tagged ports.
• The private VLAN implementation in the current release uses the CPU for forwarding packets on the primary
VLAN’s “promiscuous” port. Other forwarding is performed in the hardware. Support for the hardware
forwarding in this feature sometimes results in multiple MAC address entries for the same MAC address in the
device’s MAC address table. In this case, each of the entries is associated with a different VLAN. The
multiple entries are a normal aspect of the implementation of this feature and do not indicate a software
problem.
• By default, the primary VLAN does not forward broadcast or unknown unicast packets into the private VLAN.
You also can use MAC address filters to control traffic forwarded into and out of the private VLAN. If you are
implementing the private VLAN on a Layer 2 Switch, you also can use ACLs to control the traffic into and out
of the private VLAN.
Command Syntax
To configure a private VLAN, configure each of the component VLANs (isolated, community, and public) as a
separate port-based VLAN.
• Use standard VLAN configuration commands to create the VLAN and add ports.
• Identify the private VLAN type (isolated, community, or public)
• For the primary VLAN, map the other private VLANs to the port(s) in the primary VLAN
Configuring an Isolated or Community Private VLAN
To configure a community private VLAN, enter commands such as the following:
FastIron SuperX Router(config)# vlan 901
FastIron SuperX Router(config-vlan-901)# untagged ethernet 3/5 to 3/6
FastIron SuperX Router(config-vlan-901)# pvlan type community
These commands create port-based VLAN 901, add ports 3/5 and 3/6 to the VLAN as untagged ports, then
specify that the VLAN is a community private VLAN.
Syntax: untagged ethernet [<slotnum>/]<portnum> [to [<slotnum>/]<portnum> | ethernet [<slotnum>/]<portnum>]
Syntax: [no] pvlan type community | isolated | primary
The untagged command adds the ports to the VLAN.
The pvlan type command specifies that this port-based VLAN is a private VLAN.
• community – Broadcasts and unknown unicasts received on community ports are sent to the primary port
Table 11.3: Comparison of Private VLANs and Standard Port-Based VLANs
Forwarding Behavior Private VLANs Standard VLANs
All ports within a VLAN constitute
a common Layer broadcast
domain
No Yes
Broadcasts and unknown
unicasts are forwarded to all the
VLAN’s ports by default
No (isolated VLAN)
Yes (community VLAN)
Ye s
Known unicasts Yes Yes
 Loading...
Loading...