Configuring BGP4
December 2005 © Foundry Networks, Inc. 21 - 3
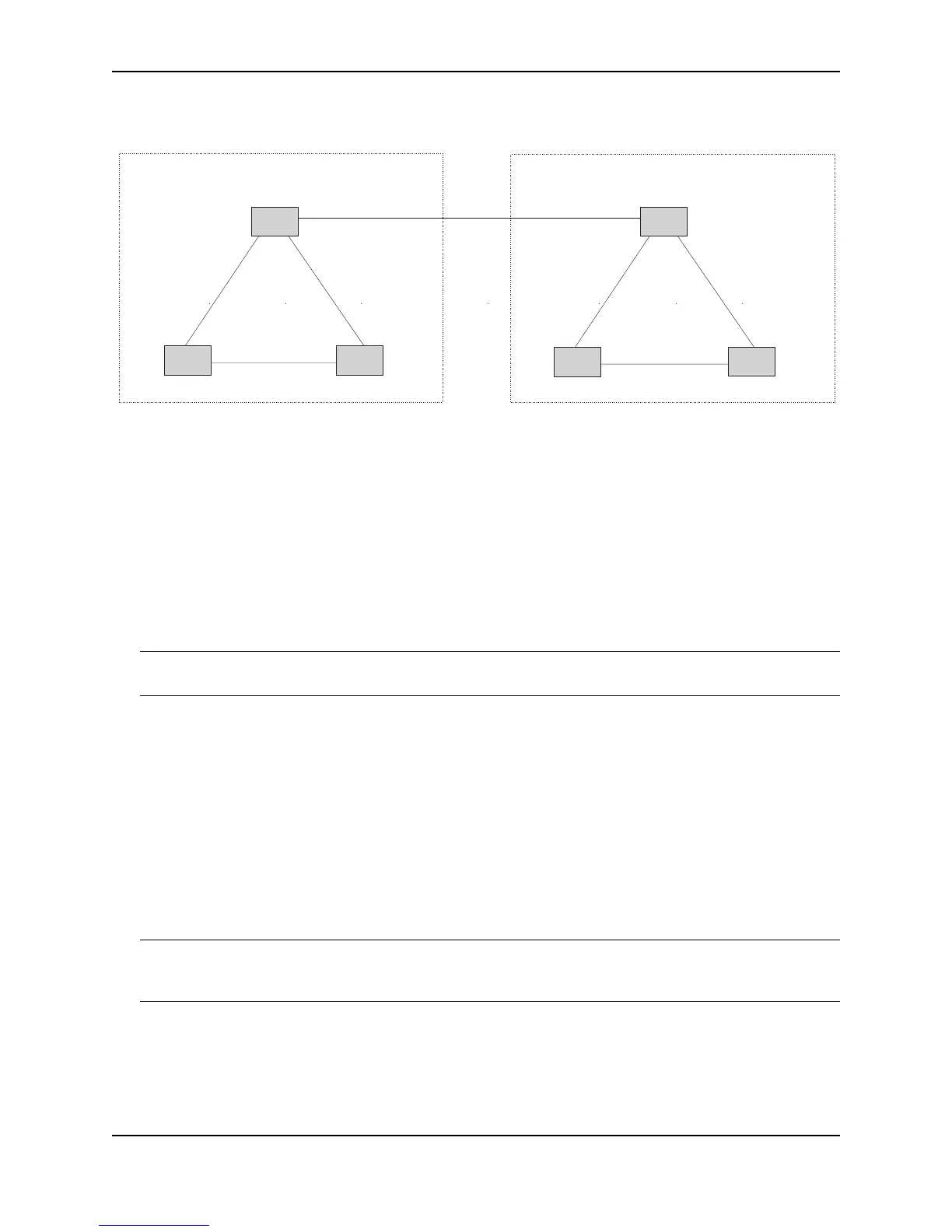
Figure 21.1 Example BGP4 ASs
Relationship Between the BGP4 Route Table and the IP Route Table
The Foundry Layer 3 Switch’s BGP4 route table can have multiple routes to the same destination, which are
learned from different BGP4 neighbors. A BGP4 neighbor is another router that also is running BGP4. BGP4
neighbors communicate using Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port 179 for BGP communication. When you
configure the Foundry Layer 3 Switch for BGP4, one of the configuration tasks you perform is to identify the Layer
3 Switch’s BGP4 neighbors.
Although a router’s BGP4 route table can have multiple routes to the same destination, the BGP4 protocol
evaluates the routes and chooses only one of the routes to send to the IP route table. The route that BGP4
chooses and sends to the IP route table is the preferred route and will be used by the Foundry Layer 3 Switch. If
the preferred route goes down, BGP4 updates the route information in the IP route table with a new BGP4
preferred route.
NOTE: If IP load sharing is enabled and you enable multiple equal-cost paths for BGP4, BGP4 can select more
than one equal-cost path to a destination.
A BGP4 route consists of the following information:
• Network number (prefix) – A value comprised of the network mask bits and an IP address (<IP address>/
<mask bits>); for example, 192.215.129.0/18 indicates a network mask of 18 bits applied to the IP address
192.215.129.0. When a BGP4 Layer 3 Switch advertises a route to one of its neighbors, the route is
expressed in this format.
• AS-path – A list of the other ASs through which a route passes. BGP4 routers can use the AS-path to detect
and eliminate routing loops. For example, if a route received by a BGP4 router contains the AS that the router
is in, the router does not add the route to its own BGP4 table. (The BGP4 RFCs refer to the AS-path as
“AS_PATH”.)
• Additional path attributes – A list of additional parameters that describe the route. The route origin and next
hop are examples of these additional path attributes.
NOTE: The Layer 3 Switch re-advertises a learned best BGP4 route to the Layer 3 Switch’s neighbors even
when the software does not select that route for installation in the IP route table. The best BGP4 route is the route
that the software selects based on comparison of the BGP4 route path’s attributes.
After a Foundry Layer 3 Switch successfully negotiates a BGP4 session with a neighbor (a BGP4 peer), the
Foundry Layer 3 Switch exchanges complete BGP4 route tables with the neighbor. After this initial exchange, the
Foundry Layer 3 Switch and all other RFC 1771-compliant BGP4 routers send UPDATE messages to inform
neighbors of new, changed, or no longer feasible routes. BGP4 routers do not send regular updates. However, if
configured to do so, a BGP4 router does regularly send KEEPALIVE messages to its peers to maintain BGP4
EBGP
RIP
IBGP
IBGP
IBGP
IBGP
AS 2
AS 1
IBGP
IBGP
OSPF
RIP
OSPF OSPF
RIP
BGP4
Router
BGP4
Router
BGP4
Router
BGP4
Router
BGP4
Router
BGP4
Router

 Loading...
Loading...