Foundry Configuration Guide for the FESX, FSX, and FWSX
22 - 2 © Foundry Networks, Inc. December 2005
NOTE: You can use a Foundry Layer 3 Switch configured for VRRP with another Foundry Layer 3 Switch or a
third-party router that is also configured for VRRP. However, you can use a Foundry Layer 3 Switch configured for
VRRPE only with another Foundry Layer 3 Switch that also is configured for VRRPE.
For a summary of how these two router redundancy protocols differ, see “Comparison of VRRP and VRRPE” on
page 22-7.
Overview
The following sections describe VRRP and VRRPE. The protocols both provide redundant paths for IP
addresses. However, the protocols differ in a few important ways. For clarity, each protocol is described
separately.
Overview of VRRP
VRRP is a protocol that provides redundancy to routers within a LAN. VRRP allows you to provide alternate router
paths for a host without changing the IP address or MAC address by which the host knows its gateway. Consider
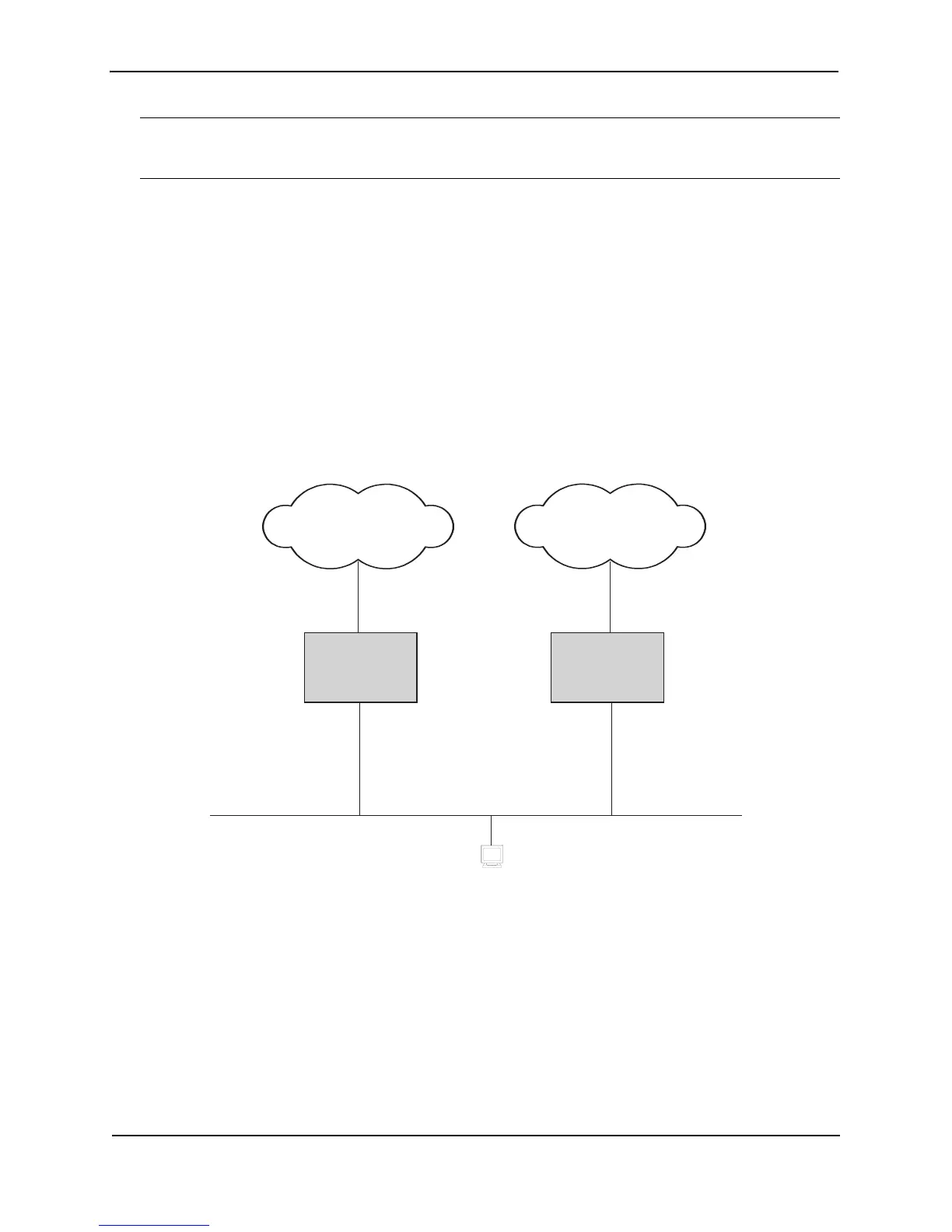
the situation shown in Figure 22.1.
Figure 22.1 Router1 is Host1’s default gateway but is a single point of failure
As shown in this example, Host1 uses 192.53.5.1 on Router1 as the host’s default gateway out of the sub-net. If
this interface goes down, Host1 is cut off from the rest of the network. Router1 is thus a single point of failure for
Host1’s access to other networks.
If Router1 fails, you could configure Host1 to use Router2. Configuring one host with a different default gateway
might not require too much extra administration. However, consider a more realistic network with dozens or even
hundreds of hosts per sub-net; reconfiguring the default gateways for all the hosts is impractical. It is much
simpler to configure a VRRP virtual router on Router1 and Router2 to provide a redundant path for the host(s).
Figure 22.2 shows the same example network shown in Figure 22.1, but with a VRRP virtual router configured on
Router1 and Router2.
Default Gateway
192.53.5.1
Host1
Internet
or
enterprise Intranet
e 3/2
192.53.5.1
e 1/6
e 1/5
e 2/4
Internet
or
enterprise Intranet
Router1 Router2
 Loading...
Loading...