22
You can use one of the following methods to enable IP FRR:
• Configure an IGP to automatically calculate a backup next hop.
• Configure an IGP to specify a backup next hop by using a routing policy.
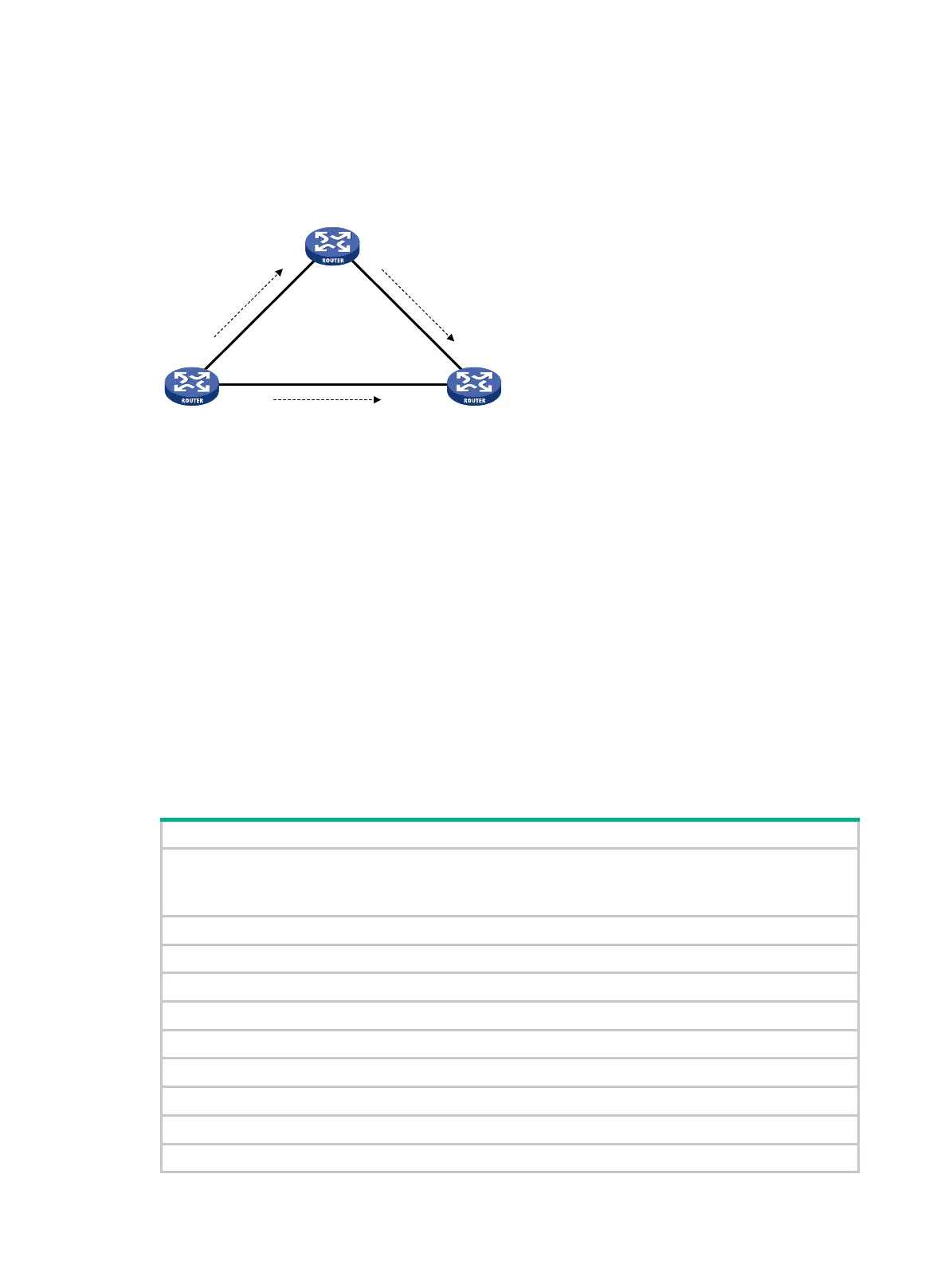
Figure 14 Network diagram for LDP FRR
As shown in Figure 14, configure IP FRR on LSR A. The IGP automatically calculates a backup next
hop or it specifies a backup next hop through a routing policy. LDP creates a primary LSP and a
backup LSP according to the primary route and the backup route calculated by IGP. When the
primary LSP operates correctly, it forwards the MPLS packets. When the primary LSP fails, LDP
directs packets to the backup LSP.
When packets are forwarded through the backup LSP, IGP calculates the optimal path based on the
new network topology. When IGP route convergence occurs, LDP establishes a new LSP according
to the optimal path. If a new LSP is not established after IGP route convergence, traffic forwarding
might be interrupted. To reduce the traffic interruption time, enable LDP IGP synchronization to work
with LDP FRR as a best practice.
Protocols
RFC 5036, LDP Specification
LDP configuration task list
Enable LDP:
1. (Required.) Enabling LDP globally
(Required.) Enabling LDP on an interface
(Optional.) Configuring Hello parameters
(Optional.) Configuring LDP session parameters
(Optional.) Configuring LDP backoff
(Optional.) Configuring LDP MD5 authentication
(Optional.) Configuring an LSP generation policy
(Optional.) Configuring the LDP label distribution control mode
(Optional.) Configuring a label advertisement policy
(Optional.) Configuring a label acceptance policy
(Optional.) Configuring LDP loop detection
LSR
A
LSR C
LSR B
Primary LSP
Backup LSP
Backup LSP

 Loading...
Loading...



















