54
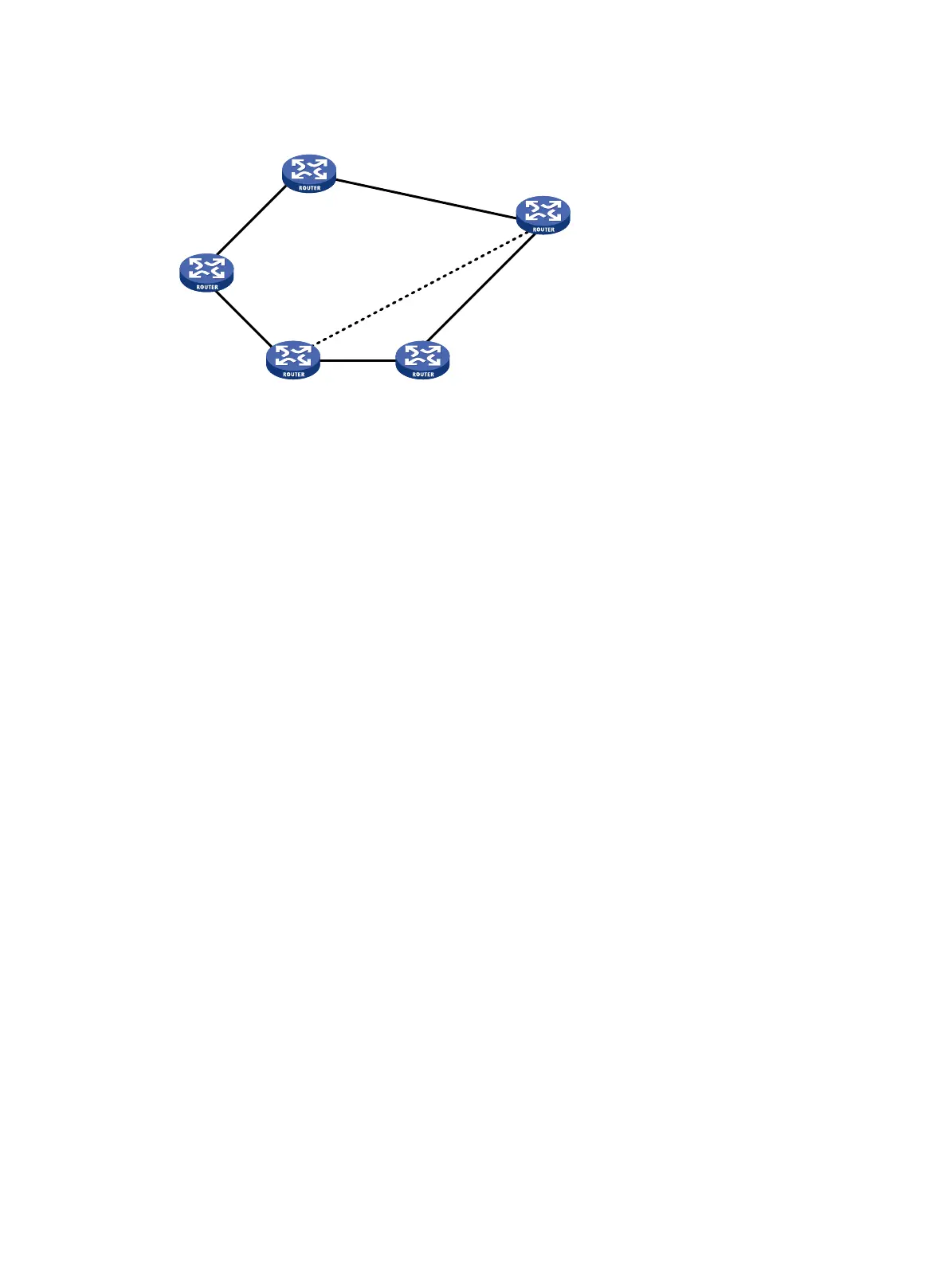
Figure 21 IGP shortcut and forwarding adjacency diagram
As shown in Figure 21, an MPLS TE tunnel is present from Router D to Router C. IGP shortcut
enables only the ingress node Router D to use the MPLS TE tunnel in the IGP route calculation.
Router A cannot use this tunnel to reach Router C. With forwarding adjacency enabled, Router A can
also know the existence of the MPLS TE tunnel, so it can use this tunnel to transfer traffic to Router
C by forwarding the traffic to Router D.
Make-before-break
Make-before-break is a mechanism to change an MPLS TE tunnel with minimum data loss and
without using extra bandwidth.
In cases of tunnel reoptimization and automatic bandwidth adjustment, traffic forwarding is
interrupted if the existing CRLSP is removed before a new CRLSP is established. The
make-before-break mechanism makes sure that the existing CRLSP is removed after the new
CRLSP is established and the traffic is switched to the new CRLSP. However, this wastes bandwidth
resources if some links on the old and new CRLSPs are the same. It is because you need to reserve
bandwidth on these links for the old and new CRLSPs separately. The make-before-break
mechanism uses the SE resource reservation style to address this problem.
The resource reservation style refers to the style in which RSVP-TE reserves bandwidth resources
during CRLSP establishment. The resource reservation style used by an MPLS TE tunnel is
determined by the ingress node, and is advertised to other nodes through RSVP.
The device supports the following resource reservation styles:
• FF—Fixed-filter, where resources are reserved for individual senders and cannot be shared
among senders on the same session.
• SE—Shared-explicit, where resources are reserved for senders on the same session and
shared among them. SE is mainly used for make-before-break.
Router D
Router A
Router B
Router C
Router E
10
20
10
10
10
20

 Loading...
Loading...



















