57
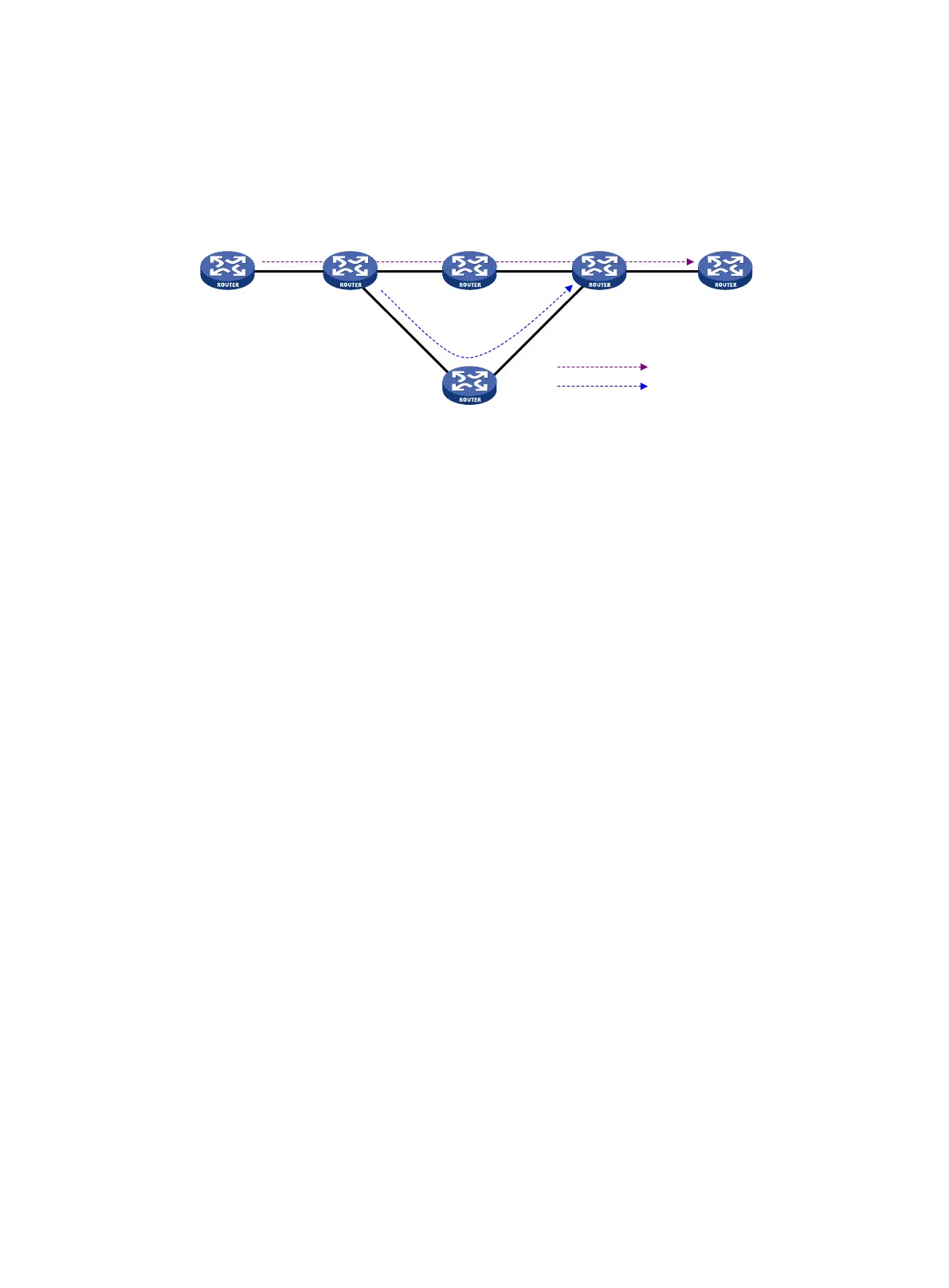
• Node protection—The PLR and the MP are connected through a device and the primary
CRLSP traverses this device. When the device fails, traffic is switched to the bypass tunnel. As
shown in
Figure 24, the primary CRLSP is Router A—Router B—Router C—Router D—Router
E, and the bypass tunnel is Router B—Router F—Router D. Router C is the protected device.
This mode is also called next-next-hop (NNHOP) protection.
Figure 24 FRR node protection
DiffServ-aware TE
DiffServ is a model that provides differentiated QoS guarantees based on class of service. MPLS TE
is a traffic engineering solution that focuses on optimizing network resources allocation.
DiffServ-aware TE (DS-TE) combines DiffServ and TE to optimize network resources allocation on a
per-service class basis. DS-TE defines different bandwidth constraints for class types. It maps each
traffic class type to the CRLSP that is constraint-compliant for the class type.
The device supports these DS-TE modes:
• Prestandard mode—Proprietary DS-TE mode of Hewlett Packard Enterprise.
• IETF mode—Complies with RFC 4124, RFC 4125, and RFC 4127.
Basic concepts
• CT—Class Type. DS-TE allocates link bandwidth, implements constraint-based routing, and
performs admission control on a per class type basis. A given traffic flow belongs to the same
CT on all links.
• BC—Bandwidth Constraint. BC restricts the bandwidth for one or more CTs.
• Bandwidth constraint model—Algorithm for implementing bandwidth constraints on different
CTs. A BC model comprises two factors, the maximum number of BCs (MaxBC) and the
mappings between BCs and CTs. DS-TE supports two BC models, Russian Dolls Model (RDM)
and Maximum Allocation Model (MAM).
• TE class—Defines a CT and a priority. The setup priority or holding priority of an MPLS TE
tunnel for a CT must be the same as the priority of the TE class.
The prestandard and IETF modes of DS-TE have the following differences:
• The prestandard mode supports two CTs (CT 0 and CT 1), eight priorities, and up to 16 TE
classes. The IETF mode supports four CTs (CT 0 through CT 3), eight priorities, and up to eight
TE classes.
• The prestandard mode does not allow you to configure TE classes. The IETF mode allows for
TE class configuration.
• The prestandard mode supports only RDM. The IETF mode supports both RDM and MAM.
• A device operating in prestandard mode cannot communicate with devices from some vendors.
A device operating in IETF mode can communicate with devices from other vendors.
Router A Router B Router C Router D
Router F
PLR MP
Router E
Primary CRLSP
Bypass tunnel

 Loading...
Loading...



















