4.5 Integration into the network
4.5.1 Network topology
The device is suitable for the following network topologies:
•
St
ar
•
Line
•
Ring
•
Tree
4.5.2 Network services and ports
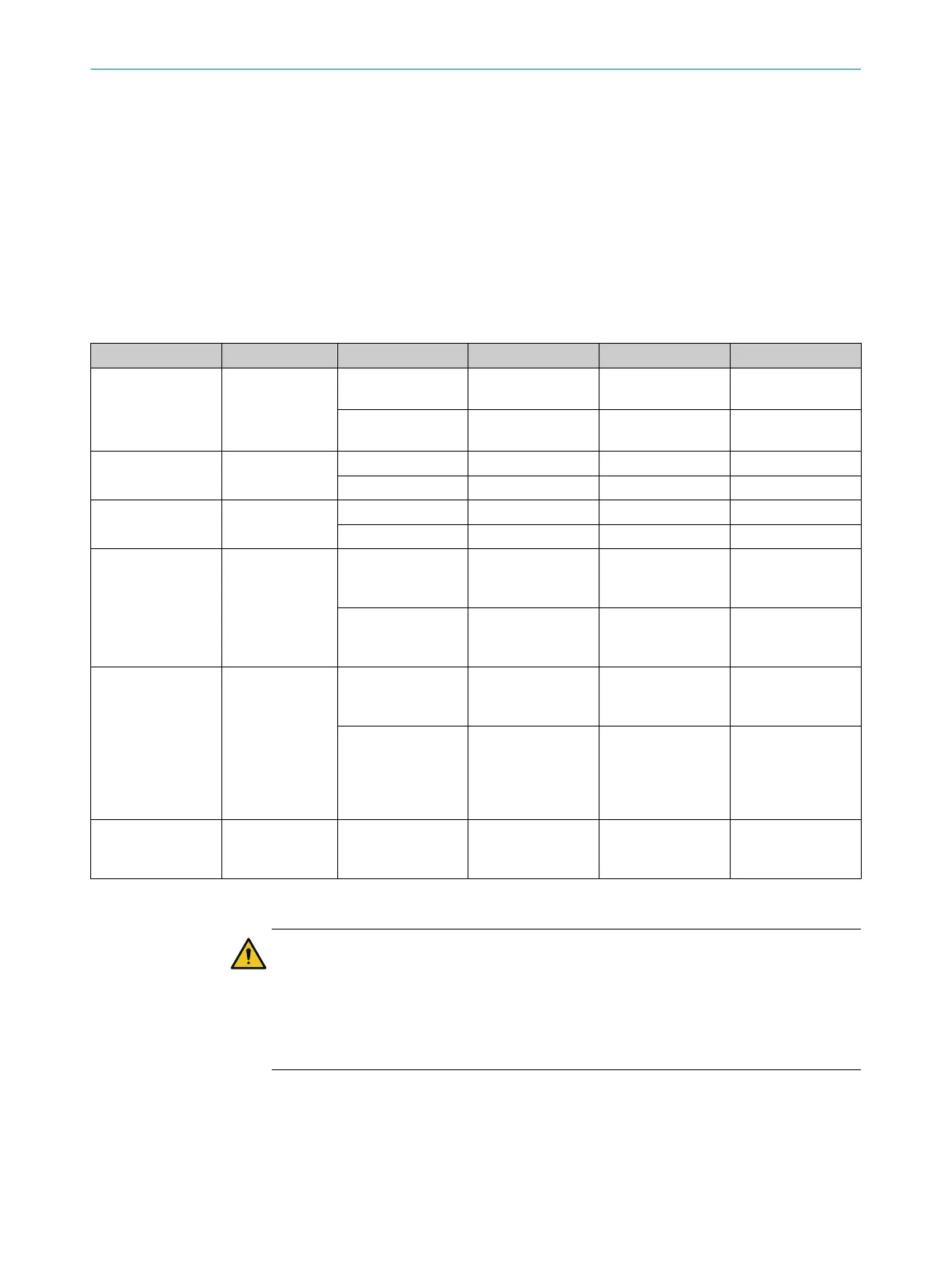
Table 3: Network services and ports
Use Protocol Source Source port Target Destination port
SNMP UDP SNMP client Selected by SNMP
c
lient
microScan3 161
microScan3 161 SNMP client Selected by SNMP
c
lient
DHCP UDP microScan3 68 DHCP server 67
DHCP server 67 microScan3 68
SNTP UDP microScan3 123 NTP server 123
NTP server 123 microScan3 123
CoLa2 (protocol
fr
om SICK, configu‐
ration and diagnos‐
tics)
TCP CoLa2 client, e.g.
computer with
Safety Designer
Selected by CoLa2
client
microScan3 2122
microScan3 2122 CoLa2 client, e.g.
com
puter with
Safety Designer
Selected by CoLa2
client
CoLa2 (protocol
from SICK, device
search)
UDP Computer with
Safety Designer
30718 … 30738 microScan3 or Lim‐
ited Broadcast or
Directed Broadcast
30718
microScan3 30718 Computer with
Safety Designer (if
in the same subnet)
or Broadcast (if in a
different subnet)
30718 … 30738
Data output in
transmit mode con‐
tinuous
UDP microScan3 Randomly selected Target computer Configurable
4.5.3 Integration of the safety laser scanner into the network
DANGER
D
anger due to unintended use of SIL 2 data of the safety laser scanner in SIL 3
applications
b
Ensure that the safety-related data of the safety laser scanner is only used in
applications which do not exceed safety integrity level SIL 2 (IEC 61508) of the
safety laser scanner.
b
Be
fore integrating an already-configured safety laser scanner into a safety-related
network: reset the safety laser scanner to its factory settings, see "Factory set‐
tings", page 129.
4 P
ROJECT PLANNING
66
O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | microScan3 – PROFINET 8021219/1ELL/2022-01-21 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

 Loading...
Loading...











