Advanced commissioning
6.5 Motor control
Converter with the CU240B-2 and CU240E-2 Control Units
250 Operating Instructions, 01/2016, FW V4.7 SP6, A5E34259001B AC
Advanced settings
K
P
- and T
I
adaptation
K
p
and T
I
adaptation suppress speed control oscillations that may occur. The "rotating
measurement" of the motor data identification optimizes the speed controller. If you have
performed the rotating measurement, then the K
p
- and T
n
adaptation has been set.
You can find additional information in the List Manual:
● Vector control with speed controller: Function diagram 6050
● Vector control after presetting the application class Dynamic Drive Control Function
diagram 6824
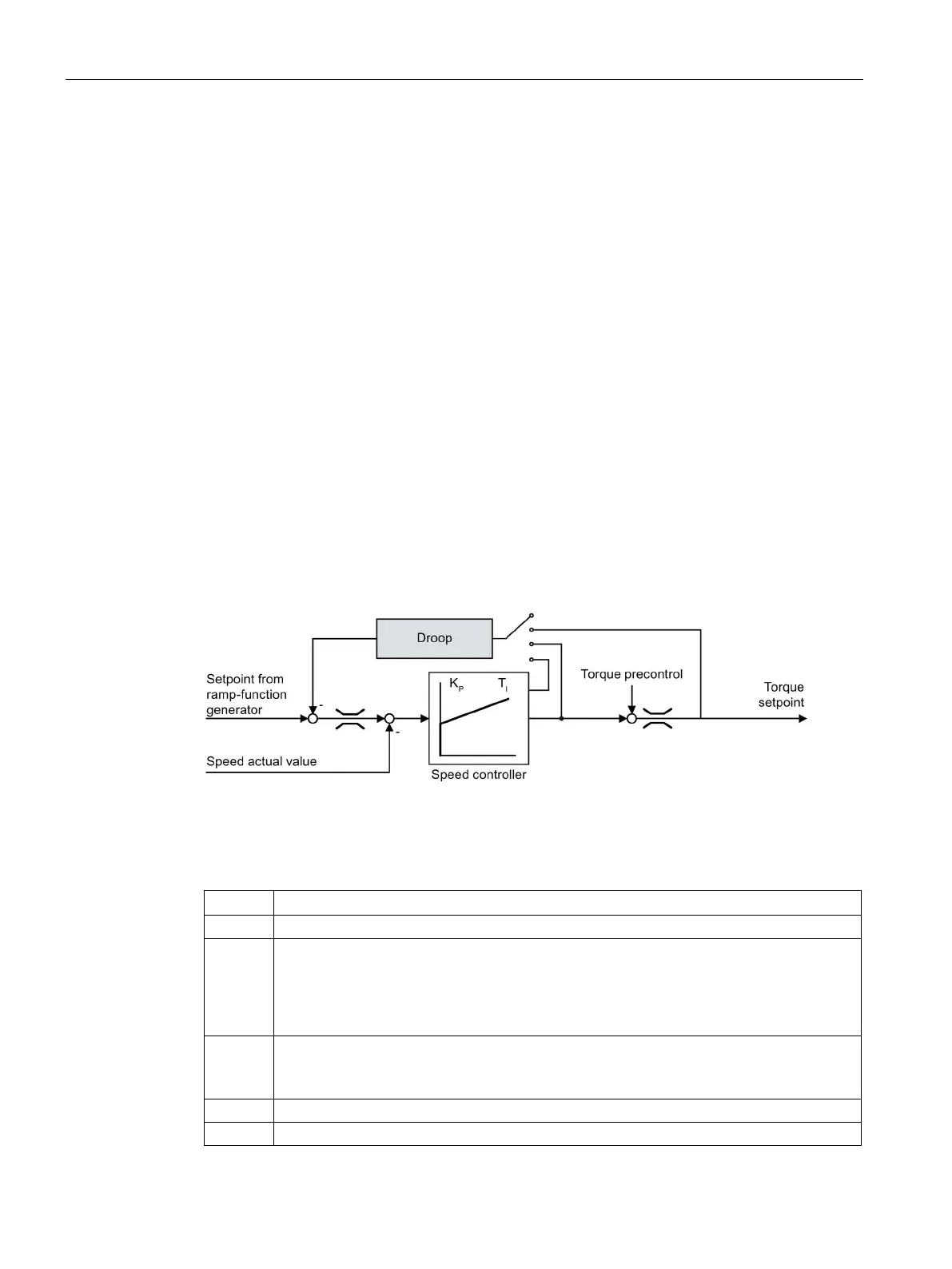
For mechanically coupled drives, there is the risk that the drives oppose one another: Small
deviations in the speed setpoint or actual value of the coupled drives can mean that the
drives are operated with significantly different torques.
The droop function ensures even torque distribution between several mechanically coupled
drives.
The droop function reduces the speed setpoint as a function of the torque setpoint.
Image 6-35 Effect of droop in the speed controller
When droop is active, the ramp-function generators of all of the coupled drives must be set
to have identical ramp-up and ramp-down times as well as rounding-off.
Speed controller I torque output
p1488
(factory setting: 0)
0: Droop feedback not connected
1: Droop from the torque setpoint
2: Droop from the speed control output
3: Droop from the integral output, speed controller
p1489
(factory setting: 0.05)
A value of 0.05 means: At the rated motor torque, the inverter reduces the speed by 5% of
the rated motor speed.
Droop feedback speed reduction
Droop feedback enable (factory setting: 0)
 Loading...
Loading...















