Reference Point Approach (R1)
18.3 Referencing with distancecoded reference markers
Turning, Milling, Nibbling
Function Manual, 11/2012, 6FC5397-1CP10-5BA0
323
Referencing methods
Referencing with distance-coded reference marks can be performed in one of two ways:
● Evaluation of two consecutive reference marks:
MD34200 ENC_REFP_MODE (referencing mode) = 3
Advantage:
– Short travel path
● Evaluation of four consecutive reference marks:
MD34200 ENC_REFP_MODE = 8
Advantage:
– Plausibility check by NC is possible
– Increase in reliability of referencing result
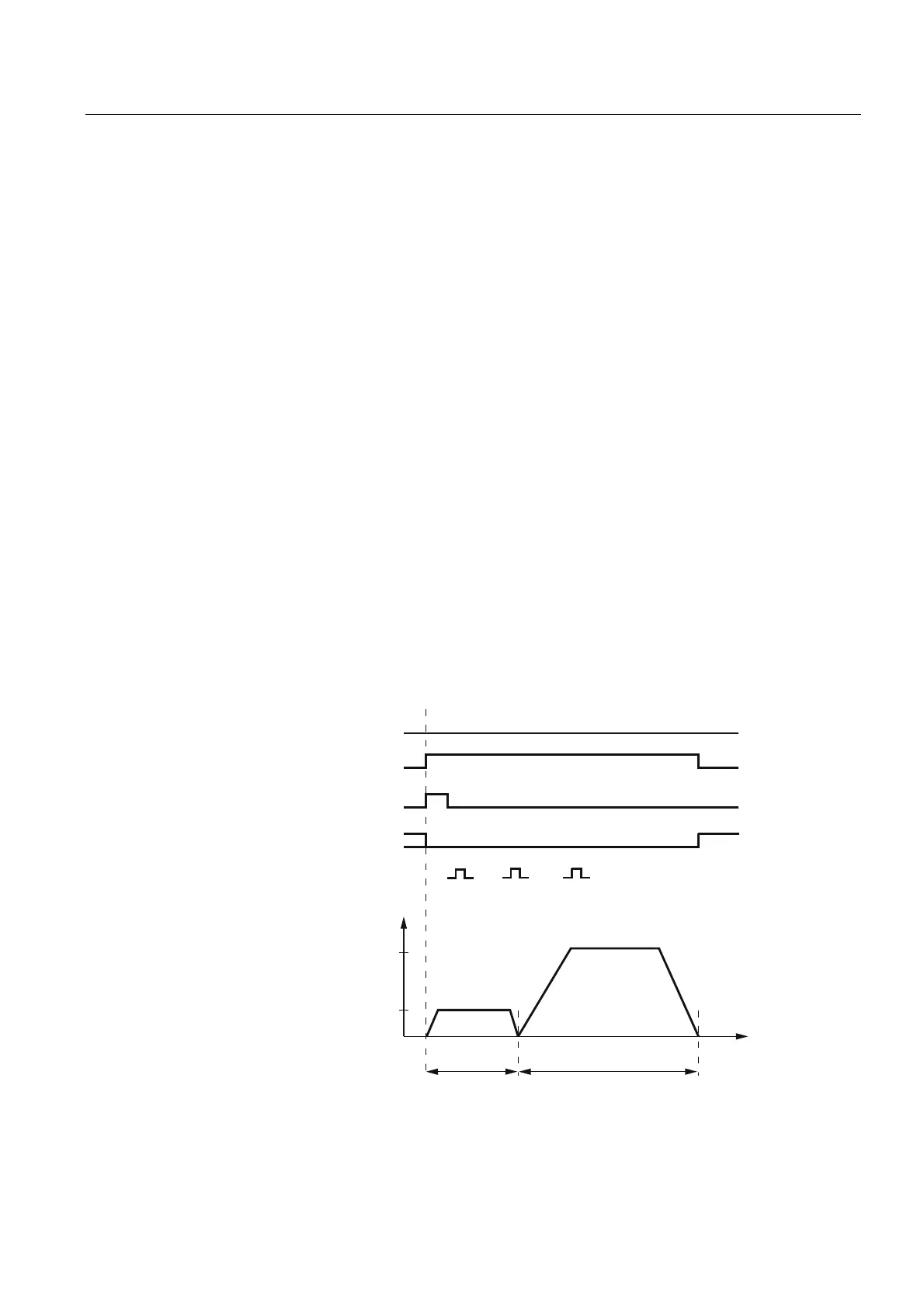
18.3.3 Chronological sequence
Chronological sequence
Referencing with distance-coded reference marks can be divided into two phases:
● Phase 1: Travel across the reference marks with synchronization
● Phase 2: Traveling to a fixed destination point
9[UHISRLQWDSSURDFKGHOD\
9[WUDYHUVHFRPPDQGPLQXV
9[DQGWUDYHUVLQJNH\SOXVPLQXV
9[UHIHUHQFHGV\QFKURQL]HG
9HORFLW\
UHIHUHQFHSRLQWFUHHSYHORFLW\
UHIHUHQFHSRLQWSRVLWLRQLQJYHORFLW\
3KDVH3KDVH
/LQHDUPHDVXULQJV\VWHPUHIHUHQFHPDUNHUV
W
0'5()3B9(/2B326
0'5()3B9(/2B6($5&+B0$5.(5
Figure 18-3 Distance-coded reference markers

 Loading...
Loading...

















