[anlaufbeispiele-b-260602-kn, 1, en_US]
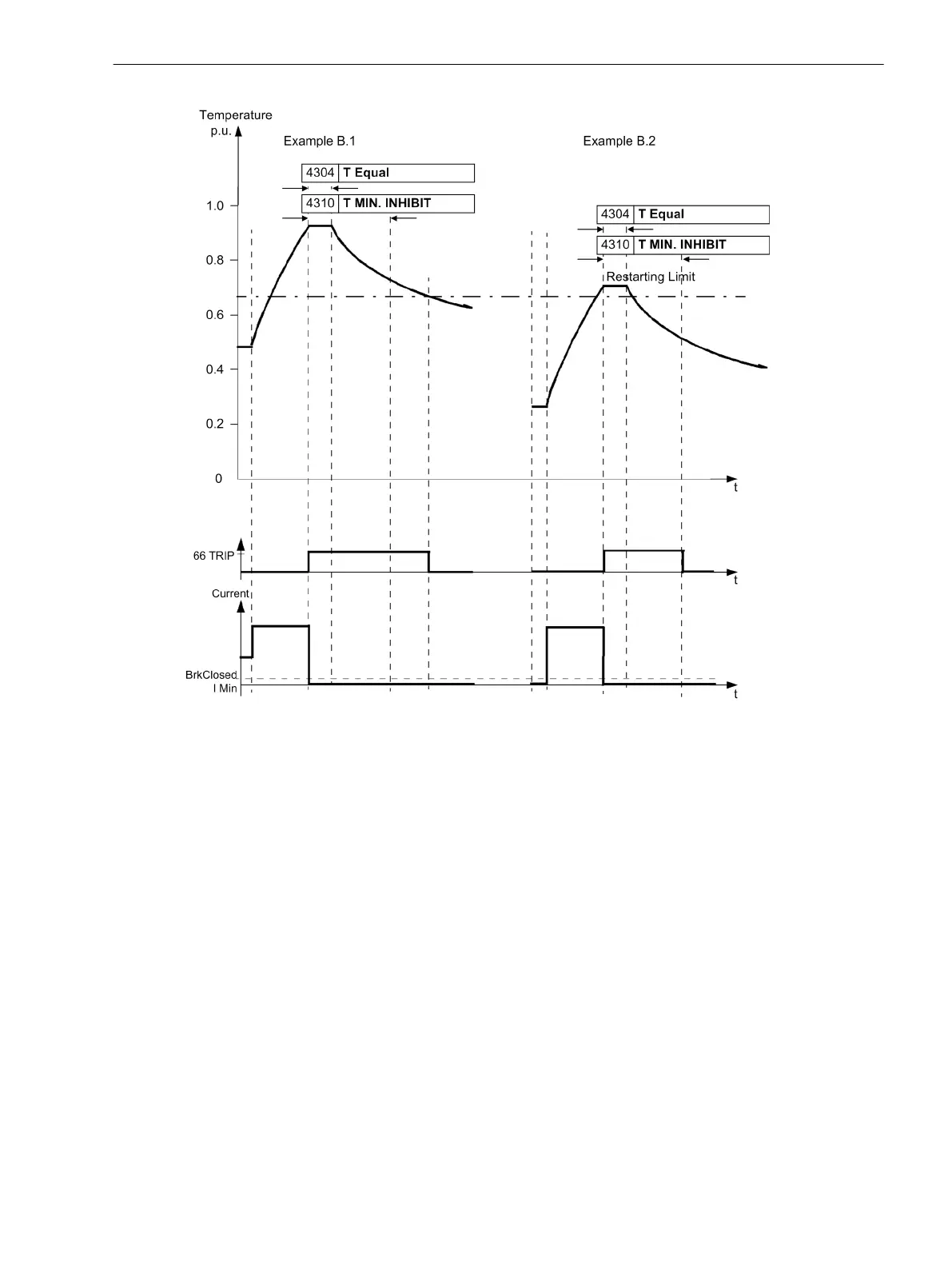
Figure 2-60
Starting up according to examples B.1 and B.2
Load Jam Protection (51M)
The load jam protection serves to protect the motor during sudden rotor blocking. Damage to drives, bearings
and other mechanic motor components can be avoided or reduced by means of quick motor shutdown.
The blocking results in a current jump in the phases. This is detected by the function as a recognition criteria.
The thermal overload protection would of course also pickup as soon as the configured threshold values of the
thermal replicas are exceeded. The load jam protection, however, is able to detect a locked rotor quicker, thus
reducing possible damage to the motor and powered equipment.
Description
Principle of Operation
Figure 2-61 illustrates a typical characteristic curve of an asynchronous cage motor. Nominal current is flowing
at normal load. If the load is increased, the current flow also increases and the speed decreases. Above a
certain load, however, the motor is no longer able to adjust the speed by increasing the torque. The motor
comes to standstill in spite of an increase in current to a multiple of its nominal value (see Figure 2-62). Other
types of induction motors have similar characteristics. Apart from the thermal heating of the motor, a locked
rotor causes substantial mechanical strain on coils and bearings.
2.8.3
2.8.3.1
Functions
2.8 Motor Protection
SIPROTEC 4, 7SJ62/64, Manual 157
C53000-G1140-C207-8, Edition 08.2016

 Loading...
Loading...











