• 10/100-TX xl module ports
• 100/1000-T xl module ports
• 10/100/1000-T xl module ports
Using the above ports:
• If you connect a copper port using a straight-through cable on a switch to a port on another switch or hub that
uses MDI-X ports, the switch port automatically operates as an MDI port.
• If you connect a copper port using a straight-through cable on a switch to a port on an end node—such as a
server or PC—that uses MDI ports, the switch port automatically operates as an MDI-X port.
Auto-MDIX was developed for auto-negotiating devices, and was shared with the IEEE for the development of the
IEEE 802.3ab standard. Auto-MDIX and the IEEE 802.3ab Auto MDI/MID-X feature are completely compatible.
Additionally, Auto-MDIX supports operation in forced speed and duplex modes.
For more information on this subject, see the IEEE 802.3ab standard reference. For more information on MDI-X,
the installation and getting started guide for your switch.
Manual override
If you require control over the MDI/MDI-X feature, you can set the switch to either of these non-default modes:
• Manual MDI
• Manual MDI-X
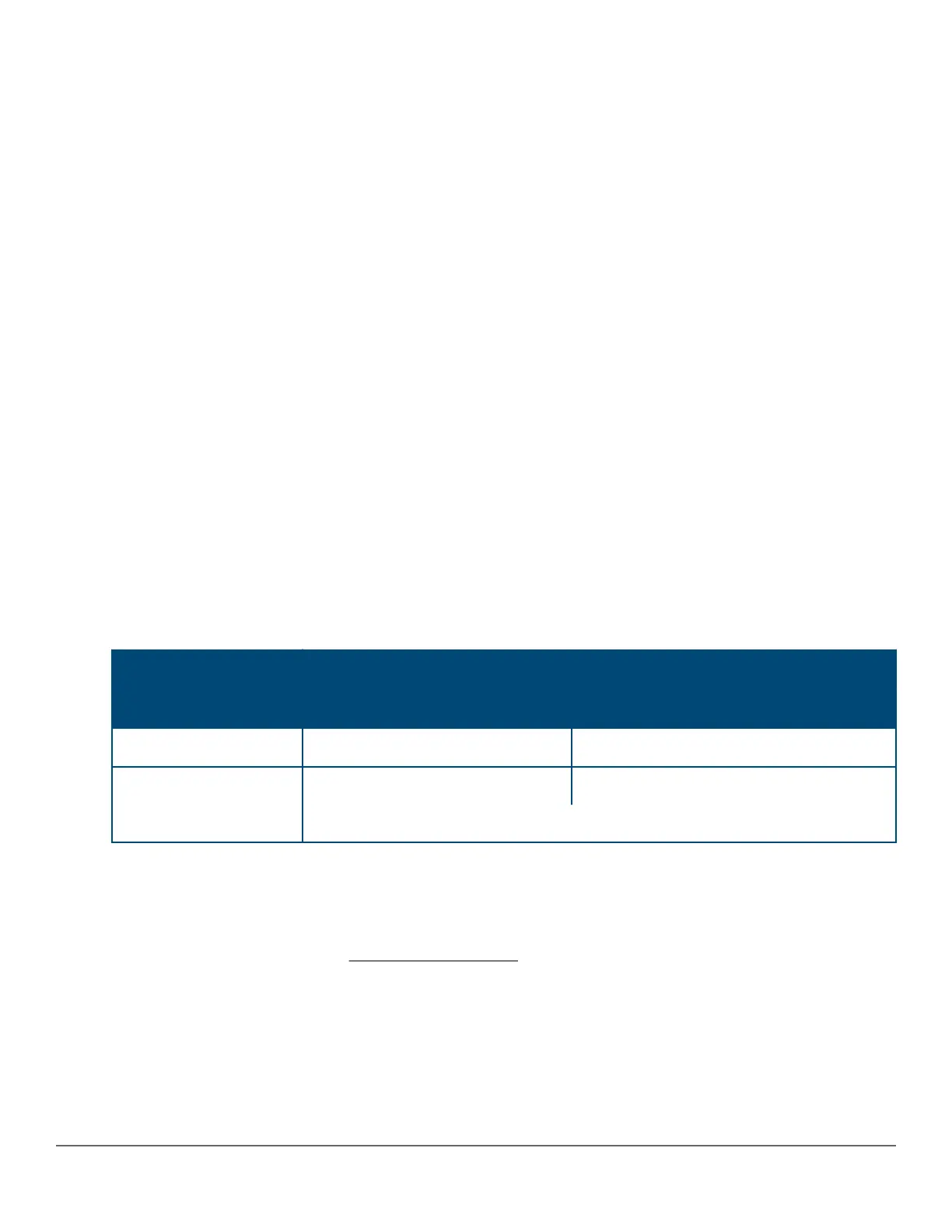
The table below shows the cabling requirements for the MDI/MDI-X settings.
Table 7: Cable types for auto and manual MDI/MDI-X settings
Setting MDI/MDI-X device type
PC or other MDI device type Switch, hub, or other MDI-X device
Manual MDI Crossover cable Straight-through cable
Manual MDI-X Straight-through cable Crossover cable
Auto-MDI-X (the default) Either crossover or straight-through cable
The AutoMDIX features apply only to copper port switches using twisted-pair copper Ethernet cables.
Configuring auto-MDIX (CLI)
The auto-MDIX features apply only to copper port switches using twisted-pair copper Ethernet cables. For
information about auto-MDIX, see Configuring auto-MDIX on page 71.
Syntax:
interface <port-list> mdix-mode < {auto-mdix | mdi | mdix>}
72 Aruba 2530 Management and Configuration Guide for
ArubaOS-Switch 16.05
 Loading...
Loading...











