10/1
Chapter 10: The Laser Box
Operators & Maintenance Manual GENIUS Compact Version UK 0.1 © BESTnv
BESTnv Industrial Research BV, Marinus van Meelweg 20, 5657 EN, EINDHOVEN, THE NETHERLANDS
General tel. +31 (40) 292 2622 - Service tel. +31 (40) 292 2620 - Fax. +31 (40) 292 2633 - Email: service.BESTnv@bestnv.com
X. The Laser Box
10.1. Introduction
Only the GENIUS Compact-L and the GENIUS Compact-D confi gurations are equipped with a Laser
Box system. In these confi gurations Lasers are used as light sources instead of high frequency light
tubes, and special sensitive light receivers are used instead of - or in addition to - cameras to capture
the light and generate a signal for the electronics to use in separating good and bad product.
The laser box system is always located in the third detection zone of the GENIUS Compact sorting
system (see chapter 3: theory).
The major advantage of laser over camera technology is that it can see differences in structure as well as
differences in colour. This is especially interesting when trying to remove defects that have almost/exactly
the same colour as the good product.
10.2. Theory
10.2.1. Laser Light Illumination
Laser light is quite different from normal white light that is used for camera sorting:
- Laser light is emitted in a very tight and focused beam, which means that it stays constant even at a
longer distance from the light source, making it possible to place the light source further away from the
detection zone.
- Laser light is also emitted in a very small spectrum (specifi c frequency/colour), unlike white light, which
consists of a very wide spectrum containing all visible colours. This means that different lasers (specifi c
colours) will be used depending on the product that is to be sorted.
Thanks to these special properties of laser light, two different techniques can be used to “see” the
difference between defects and good product:
- Direct refl ection: all products refl ect and absorb a certain amount of light, and depending on the colour
of the product, and the colour of the light, more or less light will be refl ected.
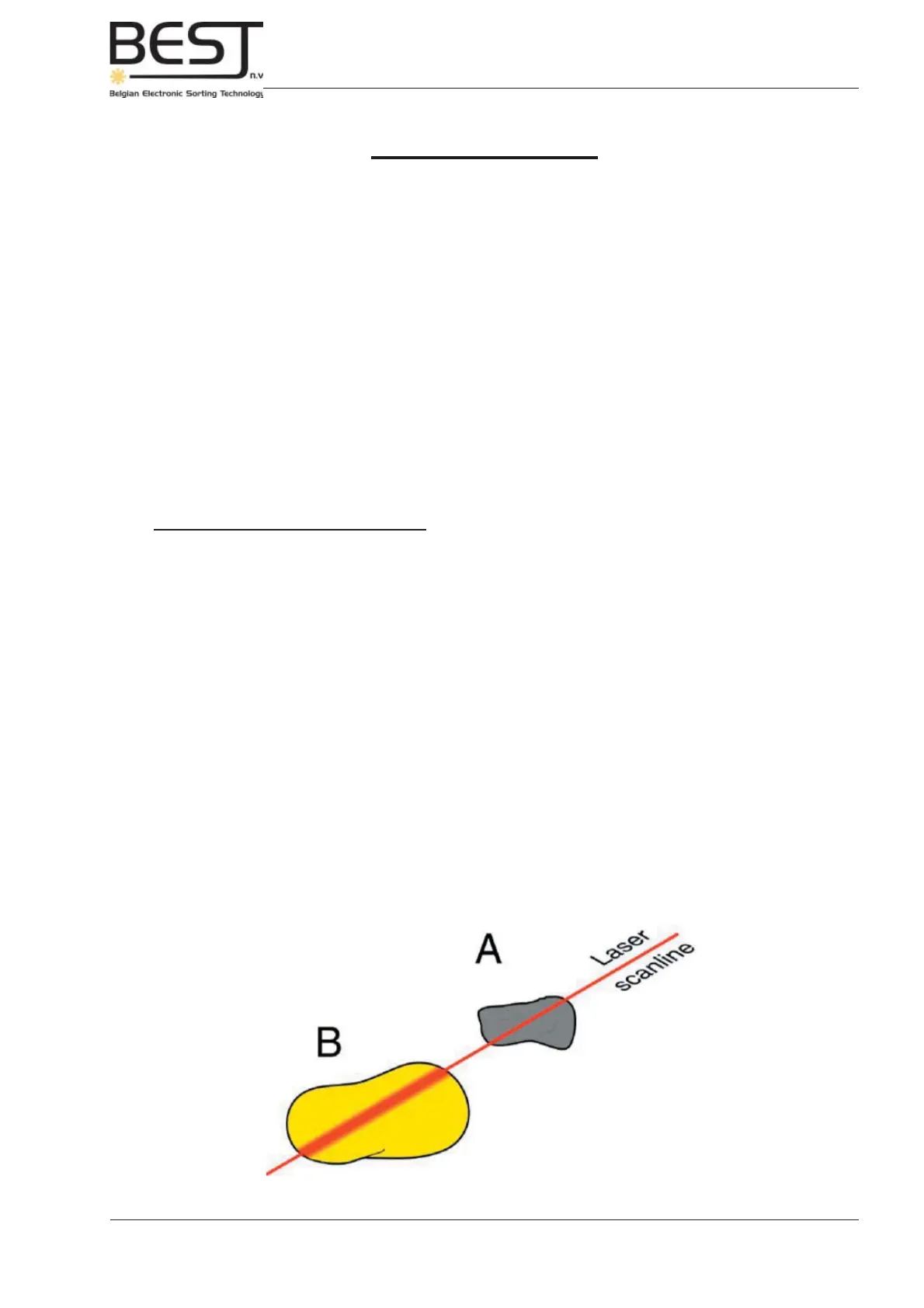
- Scattered refl ection: not only the amount of light, but also the way the light s refl ected can differ from
object to object: a hard object will refl ect light directly, while a softer object will scatter the light, which
means that the light is able to enter the product before it gets refl ected, which changes the intensity and
shape of the refl ected light (see image below).

 Loading...
Loading...