Cameras Section
The Cameras section in the System Configuration widget is where noise filter settings are activated and
configured.
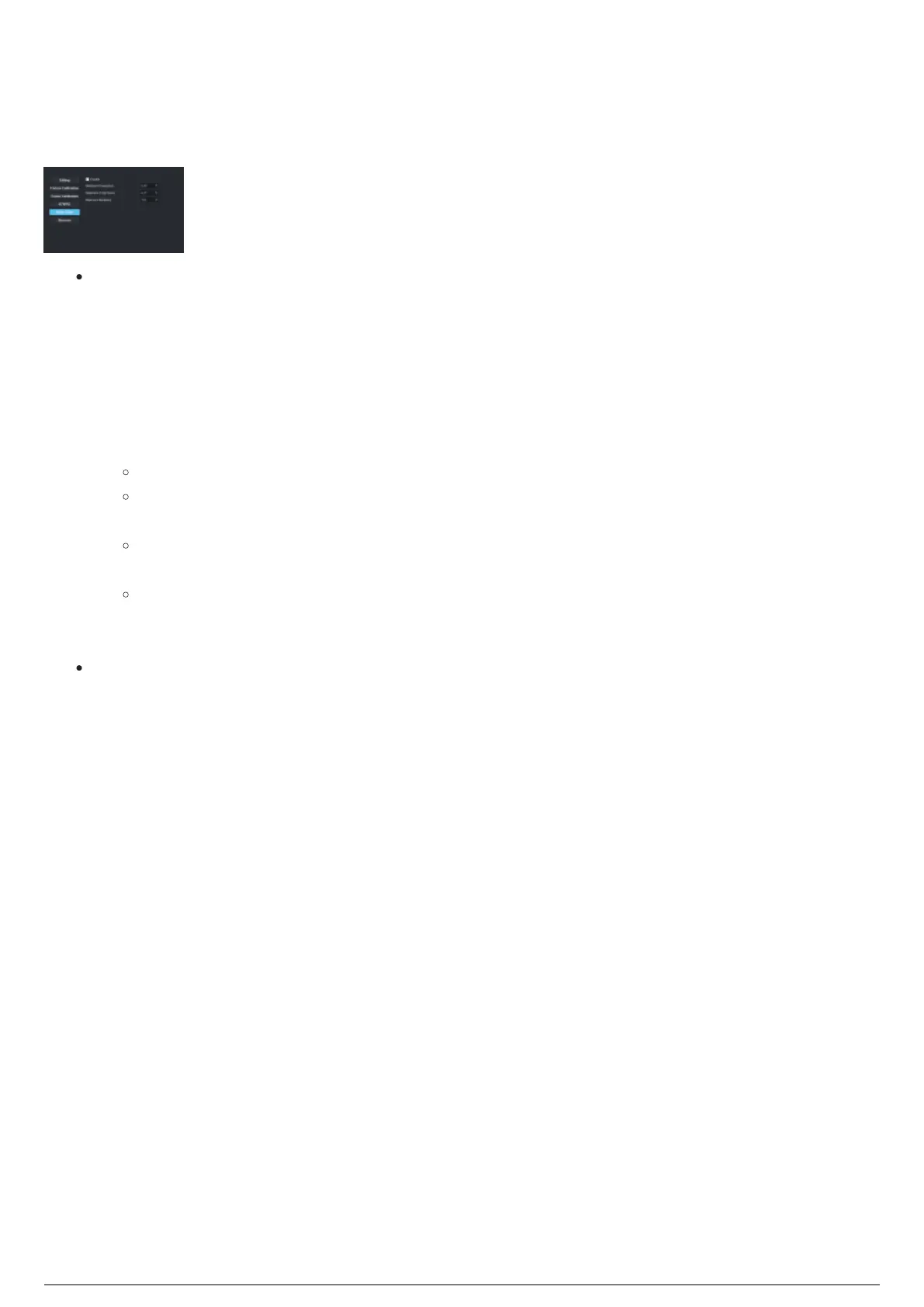
Cameras section
Noise Filter: Determines if the point is valid or not by using a probability algorithm to determine
how likely a point would be. For example, if Beacon 1, LED 2 is seen in the same spot for 100
frames, but it then appears for one frame 10m away (typically caused by IR noise), then the filter
tosses that single frame away and continues to track the real LED. As the system does not have a
concept of 'real' and 'fake', the system uses a history to determine the 'real' LED. This means that
in rare cases, noise may pass through the outlier filter if the noise is consistent, such as a
reflection. There are other tricks to mask out reflections and to trim out extra parts of the tracking
area. Please see Motive reconstruction bound settings for more information.
Enable: Select this checkbox to activate the noise filter.
Minimum Covariance: Click this scroll box to set how 'wide' or 'narrow' the range of noise
suppression. Minimum Covariance affects a higher tolerance of points in a given spectrum.
Maximum Z-Sqr Score: Click this scroll box to set how 'wide' or 'narrow' the range of noise
suppression. Maximum Z-Sqr Score affects a wider tolerance of points in a given spectrum.
Maximum Iterations: Click this scroll box to set the maximum number of repetitions per frame
the same data point is analyzed to determine the noise level. There is no range to this field,
but the default is 150.
Tip: The easiest way to adjust the outlier filter is to increase or decrease the Min Covariance and
then click Apply Changes. There is a large range that you may use, so it is best to step the field by
either +0.1 or -0.1 each time to see if the noise becomes better or worse.
 Loading...
Loading...