10-13
Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers SIP and SPA Software Configuration Guide
OL-14127-08
Chapter 10 Configuring the Ethernet SPAs
Configuration Tasks
To configure a SPA subinterface on a VLAN, use the following commands beginning in global
configuration mode:
VLAN Classification
Note When the hw-module subslot ethernet vlan unlimited command is configured, the default
classification of CoS bits 6-7 as high priority is still supported. However, other user-defined CoS values
for high and low priority classification using the plim qos input map cos queue command are not
supported.
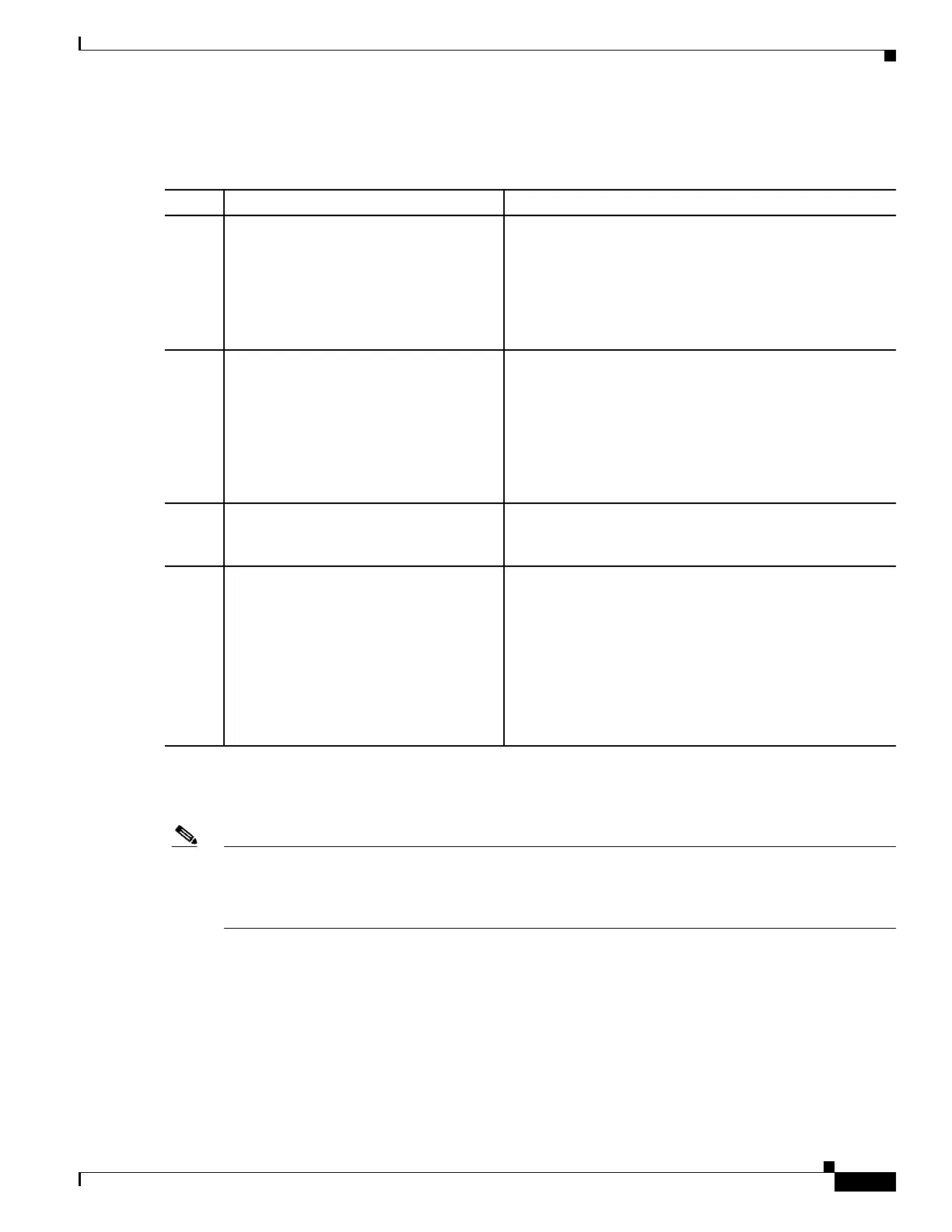
Command Purpose
Step 1
Router(config)# hw-module subslot
slot/subslot ethernet vlan unlimited
(Optional) Enables configuration of up to 4094 dot1q
VLANs per port per Ethernet SPA, where:
• slot—Specifies the chassis slot number where the SIP
is installed.
• subslot—Specifies the slot of the SIP where the SPA is
installed.
Step 2
Router(config)# interface
gigabitethernet
slot/subslot/port.subinterface-number
or
Router(config)# interface
tengigabitethernet
slot/subslot/port.subinterface-number
Specifies the Gigabit Ethernet interface to configure,
where:
• slot/subslot/port—Specifies the location of the
interface. See the
“Specifying the Interface Address on
a SPA” section on page 10-4.
• .subinterface-number—Specifies a secondary
interface (subinterface) number.
Step 3
Router(config-subif)# encapsulation
dot1q vlan-id
Defines the encapsulation format as IEEE 802.1Q
(“dot1q”), where vlan-id is the number of the VLAN
(1–4094).
Step 4
Router(config-if)# ip address ip-address
mask [secondary]
Sets a primary or secondary IP address for an interface,
where:
• ip-address—Specifies the IP address for the interface.
• mask—Specifies the mask for the associated IP subnet.
• secondary—(Optional) Specifies that the configured
address is a secondary IP address. If this keyword is
omitted, the configured address is the primary IP
address.

 Loading...
Loading...











