27-5
Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers SIP and SPA Software Configuration Guide
OL-14127-08
Chapter 27 Classifying and Scheduling Packets for ASR 1000 Series
Information About Ingress Classification
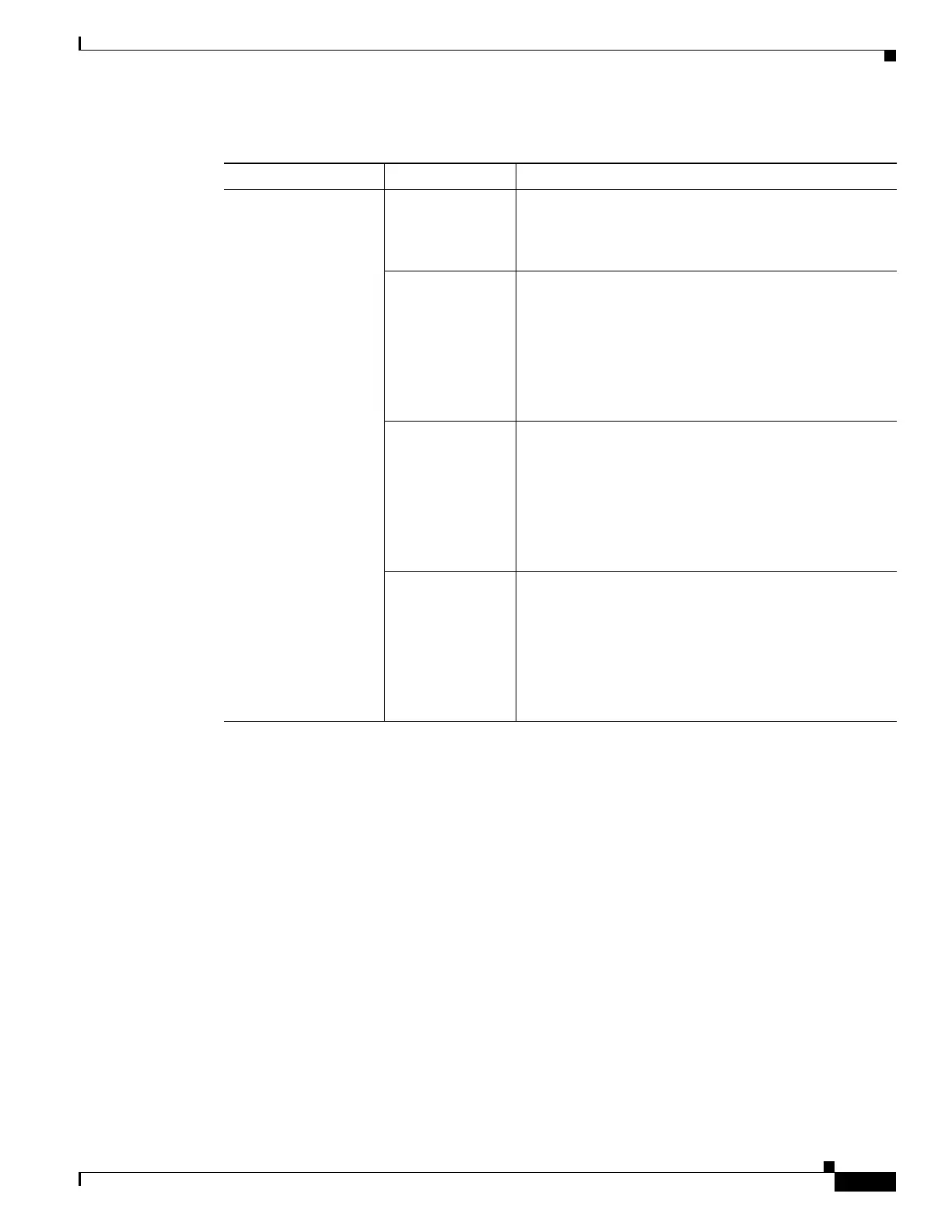
Ta b l e 27-4 SIP-40 Oversubscription Details
Resolving Oversubscription
Following are the two high-level tasks which need to performed to resolve the bandwidth
oversubscription on the ingress side:
• Classifying the incoming traffic as high priority and low priority. Depending on the SPA type, the
classification is done by either a SIP or a SPA.
• Scheduling the high-priority packets first and then processing the low-priority traffic. Depending on
the scheduling configuration, weight can be assigned to low-priority packets.
Ingress Classification Overview
To solve the bandwidth oversubscription issue, packets must be classified as high-priority data traffic
and control traffic, and guarantee their trasmit to the QFP. Ingress Classification can be broadly divided
into two:
• SPA-based classification—Some of the SPAs support the classification performed within the SPA
hardware.
ASR 1000 Chassis Type ESP Type Oversubscription State
• ASR1000-SIP40G
• Incoming rate
from SPAs.
Maximum 4
multiplied by 11.2
Gbps
• Outgoing rate
towards ESP
depends on the
ESP type
Conclusion: SIP40G
oversubscription
depends on the ESP
type.
ESP-2.5 G and
ESP-5 G
(Supported only
on ASR-1002)
Not supported.
ESP-10G ASR1000-SIP40G operates as ASR1000-SIP10G.
Example:
Input rate from (example) 3 carrier cards is 3 multiplied
by 11.2 Gbps
Output rate towards QFP=12.8 Gbps
ESP is oversubscribed.
ESP-20G ASR1000-SIP40G operates as ASR1000-SIP10G.
Example:
Input rate from (example) 3 carrier cards is 3 multiplied
by 11.2 Gbps
Output rate towards QFP=25.6 Gbps
ESP is oversubscribed.
ESP-40G ASR1000-SIP40G operates as ASR1000-SIP40G.
Example:
Input rate from (example) 3 carrier cards is 3 multiplied
by 23 Gbps
Output rate towards QFP=51.2 Gbps
ESP is oversubscribed.

 Loading...
Loading...











