A desirable characteristic of an integrating analog-to-digital (A/D) converter is its ability to reject spurious
signals. Integrating techniques reject power-line related noise present with DC signals on the input. This is
called normal mode rejection or NMR. Normal mode noise rejection is achieved when the internal DMM
measures the average of the input by “integrating” it over a fixed period. If you set the integration time to a
whole number of power line cycles (PLCs) of the spurious input, these errors (and their harmonics) will aver-
age out to approximately zero.
When you apply power to the internal DMM, it measures the power-line frequency (50 Hz or 60 Hz), and
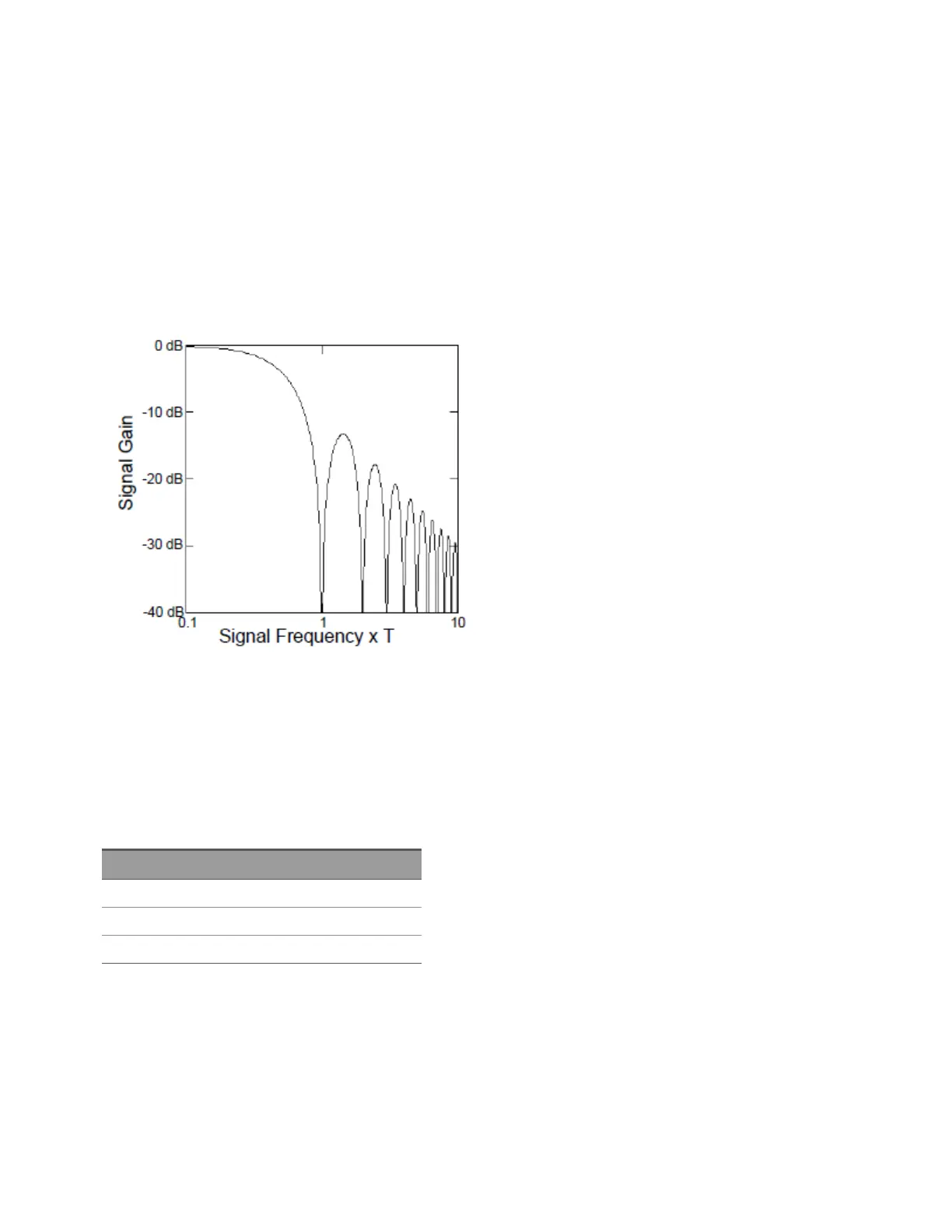
uses this measurement to determine the integration time. The following graph shows the attenuation of AC
signals measured in the DC voltage function for various A/D integration time settings. Note that signal fre-
quencies at multiples of 1/T exhibit high attenuation.
Temperature Measurements
A temperature transducer measurement is typically either a resistance or voltage measurement converted
to an equivalent temperature by software conversion routines inside the instrument. The mathematical con-
version is based on specific properties of the various transducers. The mathematical conversion accuracy
(not including the transducer accuracy) for each transducer type is shown below:
Transducer Conversion Accuracy
Thermocouple 0.05 °C
RTD 0.02 °C
Thermistor 0.05 °C
Errors associated with temperature measurements include all of those listed for DC voltage and resistance
measurements elsewhere in this chapter. The largest source of error in temperature measurements is gen-
erally the transducer itself.
Your measurement requirements will help you to determine which temperature transducer type to use.
Each transducer type has a particular temperature range, accuracy, and cost. The table below summarizes
some typical specifications for each transducer type. Use this information to help select the transducer for
4Measurement Tutorials
184 Keysight DAQ970A User's Guide
 Loading...
Loading...