LAN Configuration Procedure
There are several parameters that you might need to set to establish network communication using the
LAN interface. Primarily, you will need to establish an IP address. You might need to contact your network
administrator for help in establishing communication with the LAN interface.
If Secure mode is enabled, the instrument must be unlocked with the correct security code to per-
form many of these actions. See Security for more information.
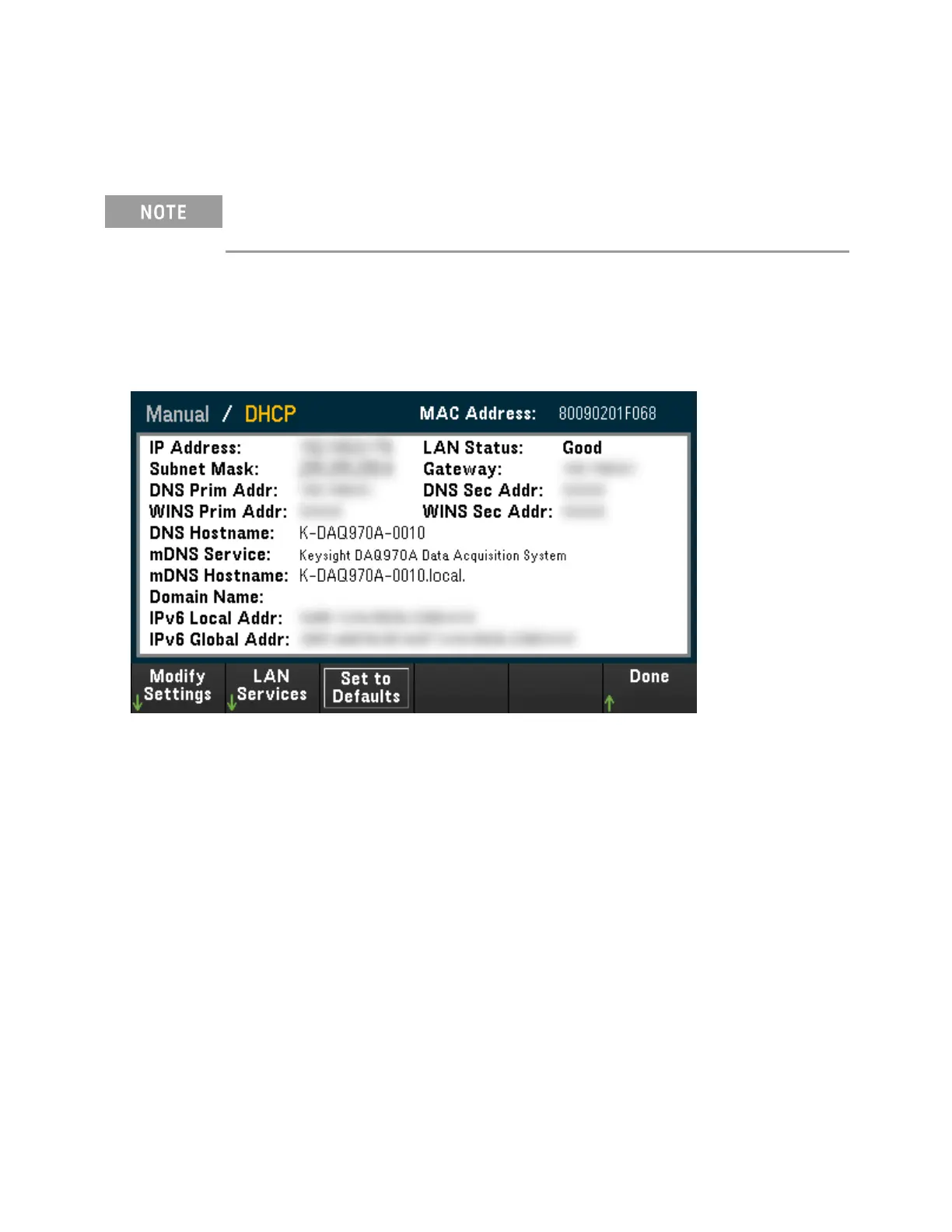
1. Press [Home] > User Settings > I/O > LANSettings.
2. You can select Modify Settings to change the LAN settings, select LANServices to enable (On) or dis-
able (Off) LANservices on the instrument, or select Set to Defaults to restore the LAN settings to its
factory default settings.
3. To change settings, press Modify Settings. To access most items on this screen, use the first softkey to
switch from DHCP to Manual. With DHCP on, an IP address will automatically be set by the DHCP
(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) when you connect the instrument to the network; provided
that the DHCP server is found and is able to do so. The DHCP also automatically deals with the subnet
mask, gateway address, DNS, WINS, and domain name, if required. This is typically the easiest way to
establish LAN communication for your instrument; all you need to do is leave the DHCP on. Contact
your LAN administrator for details.
4. Establish an "IPSetup"
If you are not using DHCP (the first softkey is set to Manual), you must establish an IP setup, including
an IP address, and possibly a subnet mask and gateway address. The IP Address and Subnet Mask
softkeys are on the main screen. Press More to configure other settings.
Contact your network administrator for the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway to use. All IP
addresses take the dot-notation form "nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn" where "nnn" in each case is a byte value in
the range 0 through 255. You can enter a new IP address using the knob or the front panel arrow keys.
Do not enter leading zeros.
Keysight DAQ970A User's Guide 33
1 Introduction to the Instrument
 Loading...
Loading...