AC current measurements are very similar to DC current measurements. The output of the current-to-
voltage sensor is measured by an AC voltmeter. The input terminals are direct coupled (ac+dc coupled) to
the shunt so that the internal DMM maintains DC continuity in the test circuit. Performing AC current meas-
urements demands additional care. The burden voltage (loading) varies with frequency and input induct-
ance, often causing unexpected behavior in the test circuit.
Sources of Error in DC Current Measurements
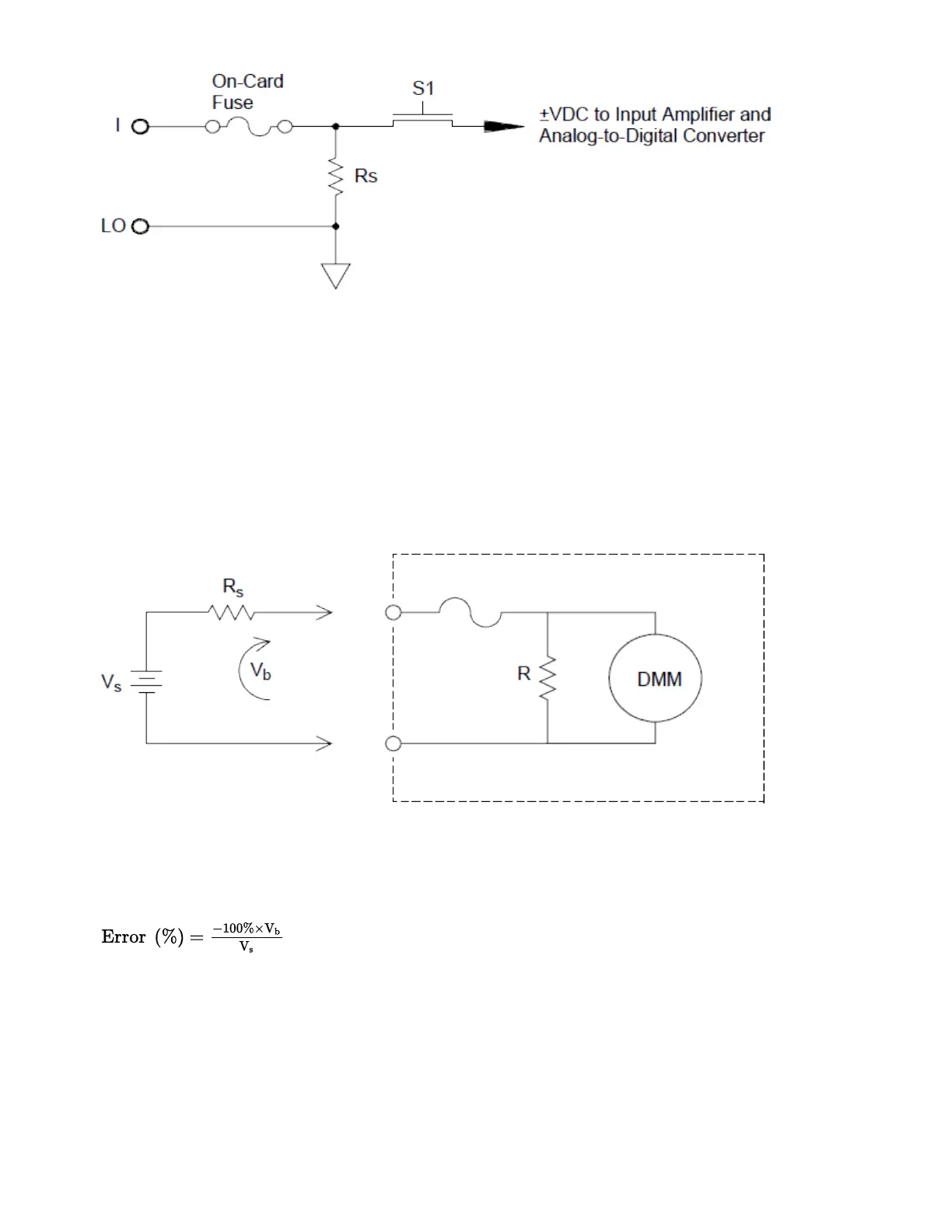
When you connect the internal DMM in series with a test circuit to measure current, a measurement error
is introduced. The error is caused by the DMM’s series burden voltage. A voltage is developed across the
wiring resistance and current shunt resistance of the internal DMM as shown below:
Where:
V
s
= Source voltage
R
s
= Source resistance
V
b
= Current shunt resistance
Sources of Error in AC Current Measurements
Burden voltage errors, which apply to DC current, also apply to AC current measurements. However, the
burden voltage for AC current is larger due to the internal DMM’s series inductance and the measurement
connections. The burden voltage increases as the input frequency increases. Some circuits may oscillate
when performing current measurements due to the internal DMM’s series inductance and the meas-
urement connections.
Keysight DAQ970A User's Guide 203
4Measurement Tutorials
 Loading...
Loading...