5-22 Image Optimization
5.7 PW/CW Doppler Mode Optimization
PW (Pulsed Wave Doppler) mode or CW (Continuous Wave Doppler) mode is used to
provide blood flow velocity and direction utilizing a real-time spectral display. The
horizontal axis represents time, while the vertical axis represents Doppler frequency shift.
PW mode provides a function to examine flow at one specific site for its velocity, direction
and features; while CW mode proves to be much more sensitive to high velocity flow
display. Thus, a combination of both modes will contribute to a much more accurate
analysis.
5.7.1 PW / CW Mode Exam Protocol
1. Select a high-quality image during B mode or B+ Color (Power) scanning, and adjust
to place the area of interest in the center of the image.
2. Press <PW>/<CW> to enter the sampling state,
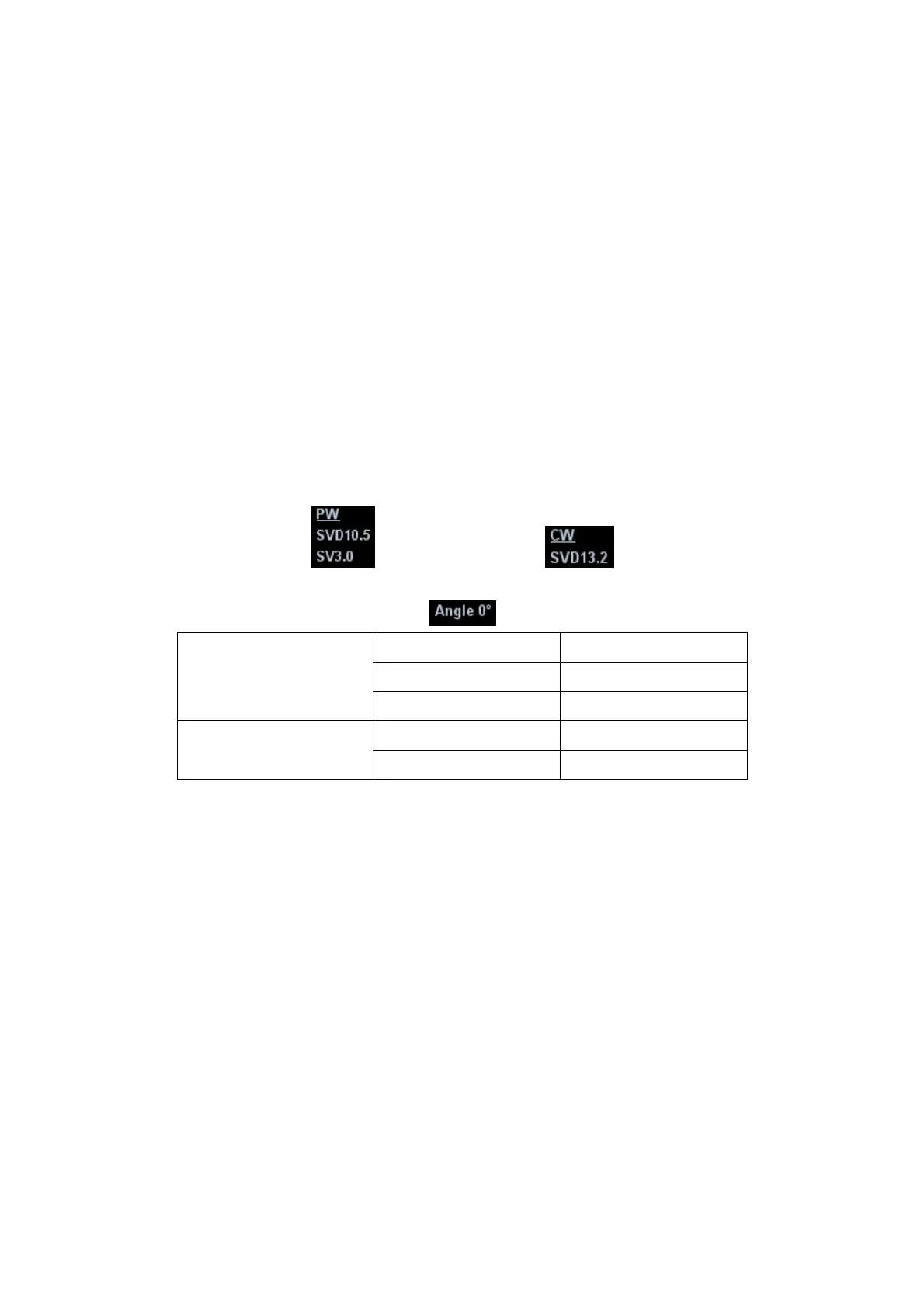
The sampling parameters will be displayed in the image parameter area on the
left part of the screen as follows:
The sampling correction angle value will be displayed above the image, as
described in the following table:
PW Sampling Line
Adjustment
SV Size SV 3.0
Angle
Angle 0°
SVD SVD 10.5cm
CW Sampling Line
Adjustment
Angle
Angle 0°
CW Focus Depth SVD 13.2cm
3. Set the SVD by rotating the trackball; adjust the angle and SV size according to the
actual situation.
4. Press <PW>/<CW> again or <Update> to enter PW/CW Mode and perform the
examination. You can also adjust the SV size, angle and depth in the real-time
scanning.
5. Adjust the image parameters during PW/CW mode scanning to obtain optimized
images.
6. Perform other operations (e.g. measurement and calculation) if necessary.
If you choose "Enter 1D Mode Directly" in "[Setup]→[Image Preset]→[Other]", then
the sampling line will be displayed at all times in B mode images, and pressing <PW>/
<CW> will directly enter PW/ CW mode.
5.7.2 PW/CW Mode Image Parameters
In PW/ CW mode scanning, the image parameter area in the upper left corner of the
screen displays the real-time parameter values as follows:
 Loading...
Loading...