PROTOCOL-SPECIFIC INFORMATION
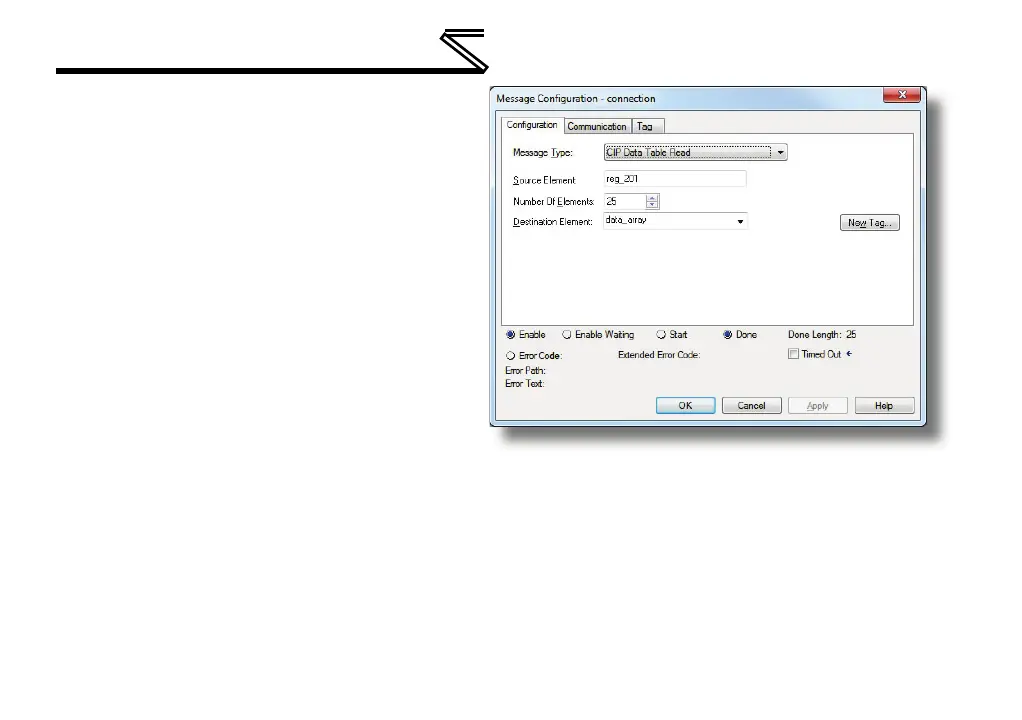
iii) Enter the Number Of Elements to
read. In this example, we will read
25 registers.
iv) For the Destination Element,
select “data_array.
d) “Communication” tab settings (refer to
Figure 60):
i) Enter the Path to the interface
card. A typical path is formatted
as
“Local_ENB,2,target_IP_address”,
where:
• Local_ENB is the name of the
1756-ENBx module in the
local chassis (we named ours
“EIP” in section 9.2.10),
• 2 is the Ethernet port of the
1756-ENBx module in the local chassis, and
• target_IP_address is the IP address of the target node.
In our example, this path would be entered as “EIP,2,192.168.16.163”.
Figure 59: MSG Instruction Configuration

 Loading...
Loading...











