The safety laser scanner’s internal configuration memory is integrated in the system
plu
g. The system plug and all connecting cables can remain at the installation site
when the safety laser scanner is replaced. The system plug is detached from the
defective safety laser scanner and connected to the new safety laser scanner. The
new safety laser scanner reads the configuration from the configuration memory when
switching on.
4.2.6 Field types
During operation, the safety laser scanner uses its laser beams continuously to check
whe
ther people or objects are present in one or more areas. The areas to be checked
are called fields. A distinction is made between the following field types, depending on
how the safety laser scanner is used:
•
Protective field
•
Reference contour field
•
Contour detection field
•
Warning field
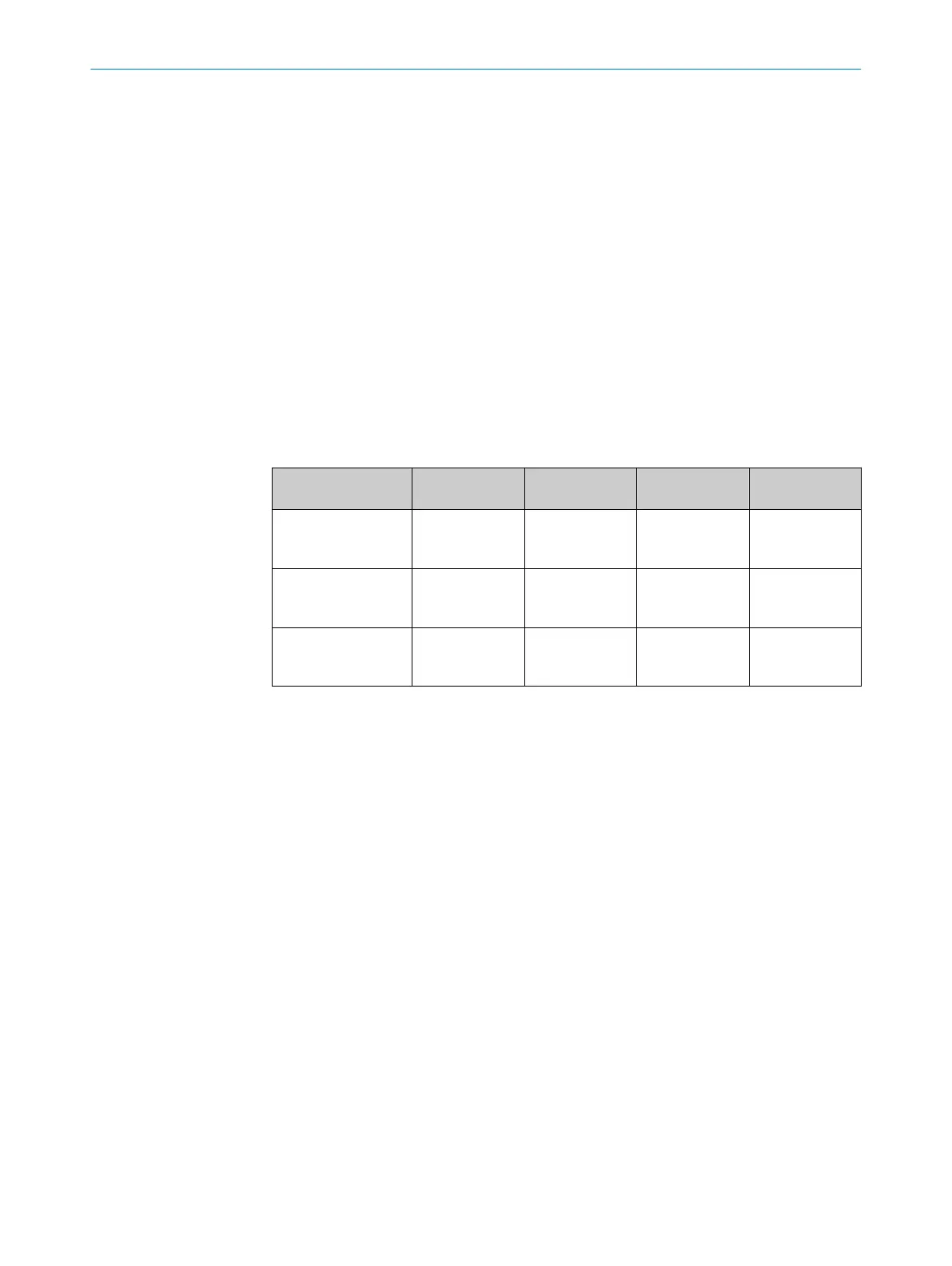
Table 4: Field types and their function
Protective field Reference con‐
t
our field
Contour detec‐
tion field
Warning field
Safe switch off
(according to ISO
13849-1)
Yes (PL d) Yes (PL d) Yes (PL d) No
Max. scanning range
of the safety laser
scanner
5.5 m 5.5 m 5.5 m 40 m
Purpose Detection and
pr
otection of
people
Tamper protec‐
tion
e.g. door moni‐
toring
Functional use
(no safety-rele‐
vant use)
Protective field
T
he protective field protects the hazardous area of a machine or vehicle. As soon as the
electro-sensitive protective device detects an object in the protective field, it switches
the associated safety outputs to the OFF state. This signal can be passed to controllers
resulting in the dangerous state coming to an end, e.g. to stop the machine or the
vehicle.
4 P
RODUCT DESCRIPTION
18
O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | microScan3 Core I/O 8025870/2020-09-04 | SICK
Subject to change without notice
 Loading...
Loading...











